In today’s digital age, SIM cards and SD cards both play a vital role in mobile devices. Despite their similar appearance, their functions are quite different.
The following sections explain the definitions of SIM cards and SD cards and their primary uses.
The Introduction of SIM Card and SD Card
What Is a SIM Card?
A SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card is a small, removable chip that stores the information your phone needs to connect to the mobile network.
A SIM card enables you to make calls, send text messages, and surf the internet. It acts as your phone’s network ID, storing your phone number, plan information, and authentication data.
What Is an SD Card
An SD (Secure Digital) card is a small, portable card used to store and transfer files such as photos, videos, and music.
It is widely used in devices such as digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, and game consoles to expand storage capacity.
SIM Card vs SD Card
The following section compares SD cards and SIM cards based on types, sizes, uses, and compatibility. Please read on.
SD Card vs SIM Card: Type
1. SD Card Types
- SD Card: The SD card is the most basic type of memory card, with a maximum storage capacity of 2GB and using the FAT12 or FAT16 file system. Measuring 32mm × 24mm × 2.1mm, it is larger than newer card types.
- SDHC Card: SDHC memory cards use the FAT32 file system, have capacities ranging from 2GB to 32GB, and are faster than standard SD cards.
- SDXC Card: Capacities range from 32GB to 2TB and typically use the exFAT file system. Compared to SDHC cards, they offer both larger storage capacities and faster transfer speeds.
- SDUC Card: SDUC cards can store over 2TB of data, up to 128TB. They are primarily used in professional equipment, such as cameras that shoot 8K video.
2. SIM Card Types
Based on their technical form, SIM cards can be categorized as traditional SIM cards, embedded chip SIM cards, and eSIM cards.
- Traditional SIM card (UICC): This is a small, removable plastic card that stores user identity, network authentication, and subscription data.
- Embedded SIM chip (MFF2 UICC): Also known as a chip SIM card or embedded SIM card, this is a soldered UICC card based on the MFF2 standard.
- eSIM (eUICC): The eSIM is a newer programmable SIM technology. Unlike fixed-function SIM cards, eSIMs support remote provisioning.
SD Card vs SIM Card: Size
1. SD Card Sizes
- Standard SD cards: These cards measure 32 x 24 mm and are widely used in digital cameras, SLR cameras, printers, and some laptops.
- miniSD cards: These cards measure 21.5 x 20 mm and were used in some early mobile phones, but have now been largely replaced by microSD cards.
- microSD cards: These cards measure 15 x 11 mm and are currently the smallest and most commonly used SD card type. They are widely used in devices such as smartphones, action cameras, drones, car cameras, and smartwatches.
2. SIM Card Sizes
- Standard SIM card: This is the oldest and largest type of SIM card, measuring 25 x 15 mm.
- Micro SIM card: A micro SIM is a smaller version of the standard SIM card, measuring 15 x 12 mm. It was widely used in earlier generations of smartphones and tablets.
- Nano SIM card: The nano SIM is currently the smallest physical SIM card, measuring just 12.3 x 8.8 mm.
SD Card vs SIM Card: Function and Purpose
Another major difference between SIM cards and SD cards is their function and purpose.
Below, I will use a table to show you the difference between SIM card and SD card,
| SIM Card | SD Card | |
| Main Uses | User identification mobile network connection | Extending storage space saving and transmitting digital data |
| Core Features | Make/receive calls Send/receive text messages Use mobile data | Store photos, videos, music, documents, and apps Transfer files between devices |
| Can it be disassembled | Available in removable (physical SIM) and non-removable (eSIM) formats | Generally removable, slot-type design |
| Usage scenarios | Mobile phones tablets smart watches | Digital cameras, mobile phones, tablets Drones, car recorders Music players, etc. |
SD Card vs SIM Card: Compatibility
SIM cards are designed for mobile communications and are typically tied to a specific carrier. They may be locked to certain carriers or regions.
If you want to use the same SIM card in another country or with a different carrier, you may need to unlock it first or replace it with a new SIM card supported by the target network.
In contrast, SD cards are more versatile. They can be used freely across multiple devices that support SD card slots.
How to Use SIM Card and SD Card?
Understanding how to use SIM and SD cards correctly can help you manage your device and data more efficiently.
Here’s how to use them with your phone and Windows.
Use a SIM Card in a Phone
To use a SIM card in your phone, simply use a SIM eject tool to remove the tray, insert the SIM card, and then reinsert it into the phone.
Most phones will automatically recognize the new card and begin service. If necessary, contact your carrier for activation.
To insert a SIM card
- Locate the SIM card tray: It’s a small, removable tray, usually located on the side of the phone.
- Find the tray release hole: There’s a small hole on the side of the tray.
- Insert tool: Use the included SIM eject tool or a bent paperclip to gently insert the hole to eject the tray.
- Remove the SIM card tray: Push it in until it pops out.
- Insert the SIM card: Align the SIM card with the notch on the tray, ensuring it fits securely.
- Push the tray back in: Gently push the SIM card tray back into the phone until it’s fully seated.
After inserting the SIM card
- Restart your phone: This will help the system recognize and activate the new SIM card.
- Verify your network connection: Your phone should now be able to make calls and connect to the mobile data network.
Use an SD Card in Windows
To use an SD card on a Windows computer, simply insert the card into a card reader or connect it via a USB adapter.
Then, find and open the card in This PC to conveniently browse and manage your files.
Here are the steps to use an SD card:
1. Insert the SD card:
- If your computer has an SD card slot, simply push the SD card into the slot.
- If you have a microSD card, insert the microSD card into the adapter, then plug the adapter into a USB port on your computer.
- If there’s no built-in slot, you’ll need to use an external USB card reader or adapter to connect the SD card to your computer.
2. Open File Explorer:
Right-click the Start icon and select File Explorer.
3. Locate the SD card:
- Click This PC.
- In the right pane, look for the SD card. It may be labeled as a removable disk.
4. Browse and transfer files:
- Browse files: Double-click the SD card icon to view your files.
- Copy files to the SD card: Open another window, select files, and drag them to the SD card window.
- Copy files from the SD card: Select files in the SD card window and drag them to the desired location on your computer.
If you’re unable to open your SD card or transfer files to it, formatting the card may help repair it or ensure compatibility with your computer.
In Windows, you can format the SD card using File Explorer, Disk Management, or the Diskpart command.
Here are the detailed steps:
#1. Via Disk Management
- Right-click the Windows Start menu and select Disk Management.
- Right-click the SD card’s partition to select Format.
- Set Volume label, File system, and Allocation unit, and then click OK > OK.
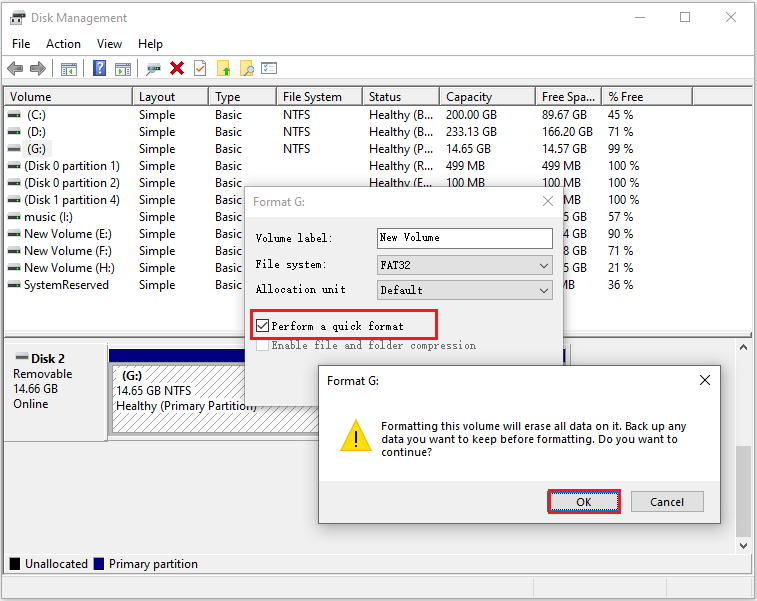
However, when you use Disk Management or other Windows tools to format an SD card larger than 32GB, you will find that the FAT32 format option is not available.
In this case, you can try MiniTool Partition Wizard, which can break the limit.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
#2. Via MiniTool Partition Wizard
- Open MiniTool Partition Wizard.
- Right-click the target partition and select Format from the context menu.
- In the new pop-up window, set the Partition Label, File System, and Cluster Size.
- Then click OK to continue.
- Click Apply > Yes to execute the pending operation.
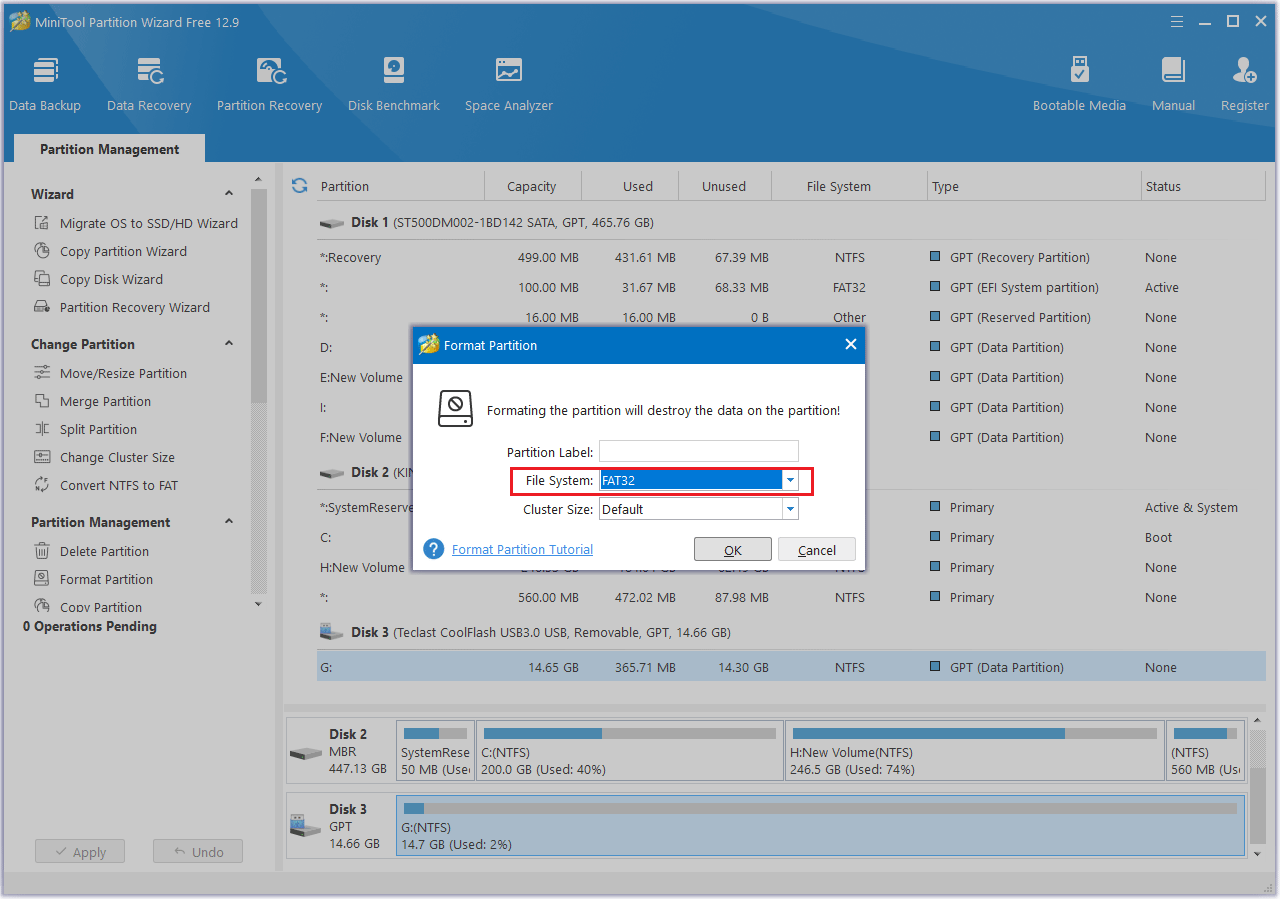
As you can see, MiniTool Partition Wizard is a handy tool for formatting SD cards.
In fact, it also has powerful Data Recovery features for recovering files lost due to deletion, formatting, virus attacks, and more.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Launch the software and scan the SD card.
- Open MiniTool Partition Wizard. The main interface shows: Logical Drives, Devices, and Recover From Specific Location.
- Find the SD card, move your cursor to the section, and click Scan.
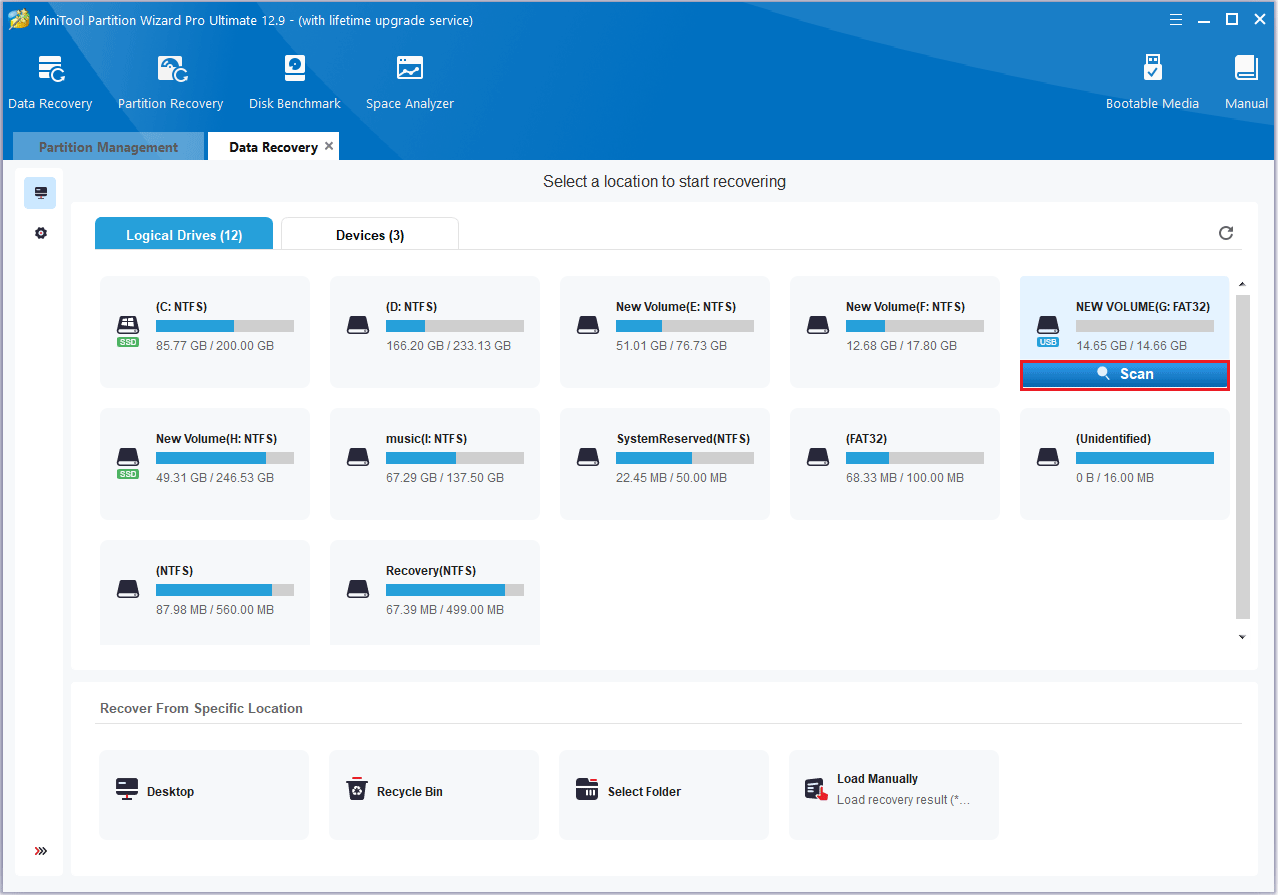
Step 2: Locate the target files using Type, Filter, or Search.
You can find files under the Path tab.
- Type: It allows you to find files based on file types. The specific file format will also be displayed below.
- Filter: You can set filtering criteria to narrow down the scope.
- Search: This feature supports searching for file names to locate files.
Step 3: Save files to a new location.
- After finding the files, you can preview them.
- Now, you can tick the lost files and click the Save button.
- Choose a new destination and then click OK.
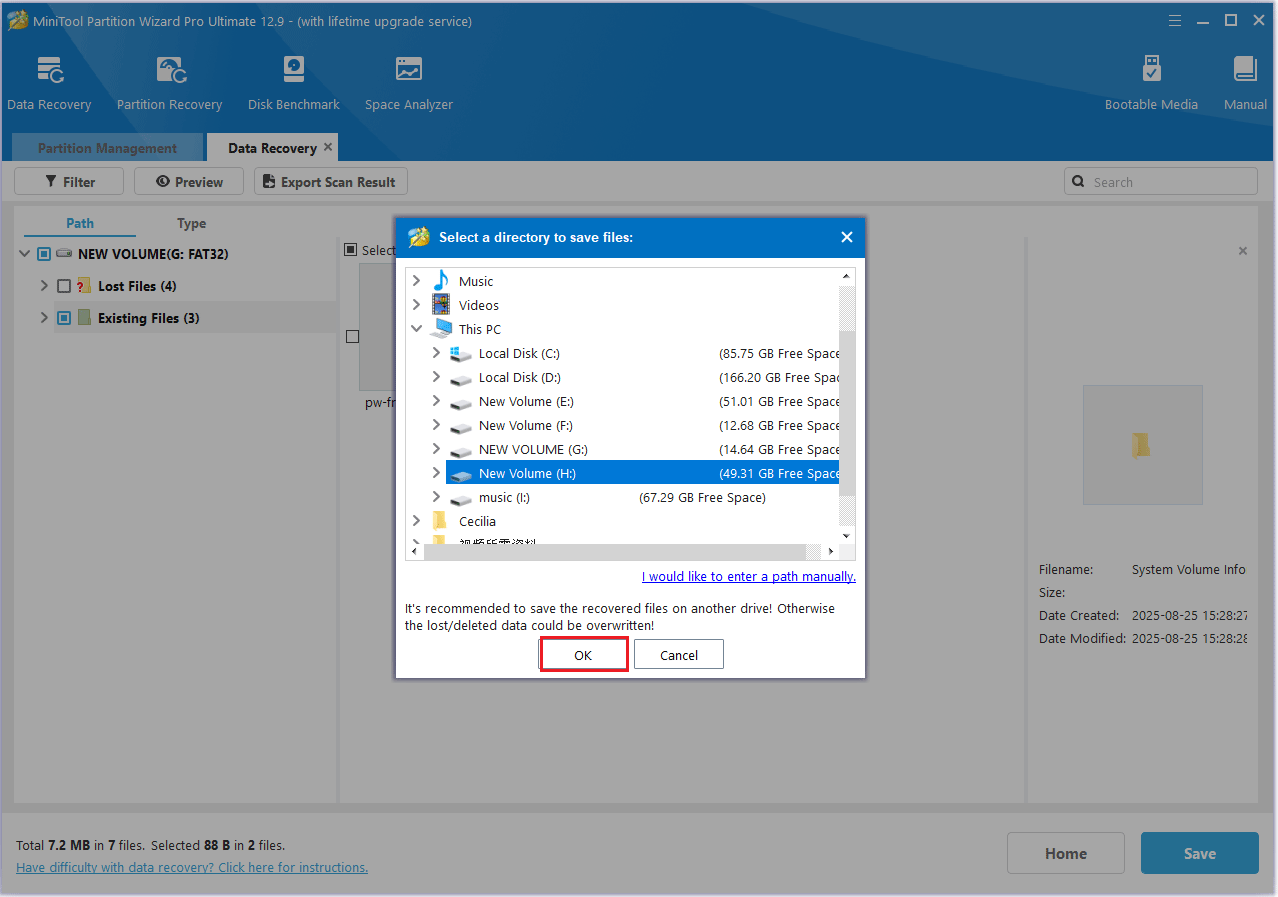
Now you’ve learned how to format an SD card and recover lost data using MiniTool Partition Wizard.
If you think that’s all there is to it, there’s a lot more to learn. It has many more powerful features worth exploring.
- Extend Partition: When your SD card is running low on space, you can use this feature to increase the capacity of a partition.
- Wipe Disk: This feature completely erases all data on the SD card.
- Delete Partition: When you no longer need a partition, you can delete it to free up space.
- Surface Test: This feature detects whether the disk has bad sectors. Bad blocks appear in red, while healthy blocks appear in green.
Bottom Line
This article systematically defines SIM cards and SD cards, and provides a detailed comparison of the two in terms of size, type, purpose, and compatibility.
Additionally, you can use MiniTool Partition Wizard to format and recover data from an SD card.
If you have any questions or suggestions while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can contact us via [email protected] to get a quick reply.

![Quick Format VS Full Format [How to Choose For Data Security]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/06/quick-format-vs-full-format-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :