When your Windows PC runs slowly, you might experience long application launch times, a spinning mouse cursor, or system freezes while performing tasks. This can impact work efficiency, entertainment, and even your mood.
Why is my computer running so slow? In this guide, we’ll delve into the reasons, from insufficient system resources, software issues, and hardware limitations, to low-end components that struggle to keep up with modern software.
More importantly, we’ll provide corresponding solutions to help you improve your computer’s performance.
Causes 1. Insufficient System Resources
When your computer doesn’t have enough system resources to handle all the tasks you open, it needs to constantly manage the workload by switching between tasks or using slower storage devices as temporary memory. This will result in noticeable latency and performance bottlenecks.
Below is the detailed information about causes and solutions.
#1. Too Many Programs and Browser Tabs Running at Once
Each open application, background process, and even individual browser tabs consumes a portion of your system resources. When running these tasks and browser tabs at once, your system resources may be insufficient, which can lead to performance issues.
Many applications are set to run automatically when your computer starts. This increases startup time and allows numerous programs to run in the background, consuming memory and CPU resources even when you don’t use them.
To release resources, you can try:
- Close unnecessary browser tabs. Close browser tabs by clicking the “x” icon on each tab.
- Close unused applications. Completely exit programs you are not actively using.
- Monitor usage. Use Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) to identify and close programs using a high amount of CPU or Memory.
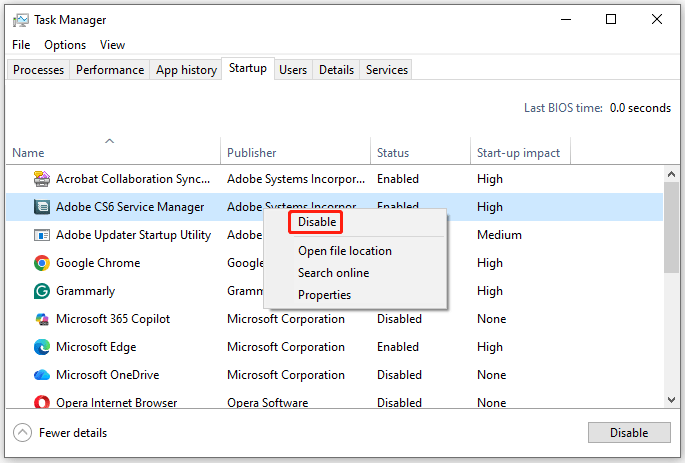
- Close startup programs: Open Task Manager. Go to the Startup tab. Each app has a “Start-up impact” rating (Low, Medium, High) indicating how much it slows down boot time. Right-click apps you don’t need and select Disable.
#2. Low Storage Space
A nearly full hard drive, especially the main system drive, can significantly slow down your computer. It is generally recommended to keep at least 15-30% of your disk space free.
In this case, freeing up disk space can fix low storage space. MiniTool Partition Wizard provides the Space Analyzer and Extend Partition feature to help you do that.
#1. Free up disk space
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a disk space analyzer that can find what’s taking up your hard drive space and delete these useless files.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
- Download, install, and launch this free partition manager.
- On its main interface, click the Space Analyzer feature on the top toolbar.
- From the drop-down menu, select the system drive, and then click Scan.
- Wait for the process to complete. After that, this tool displays scan results in Tree View, File View, and Folder View.
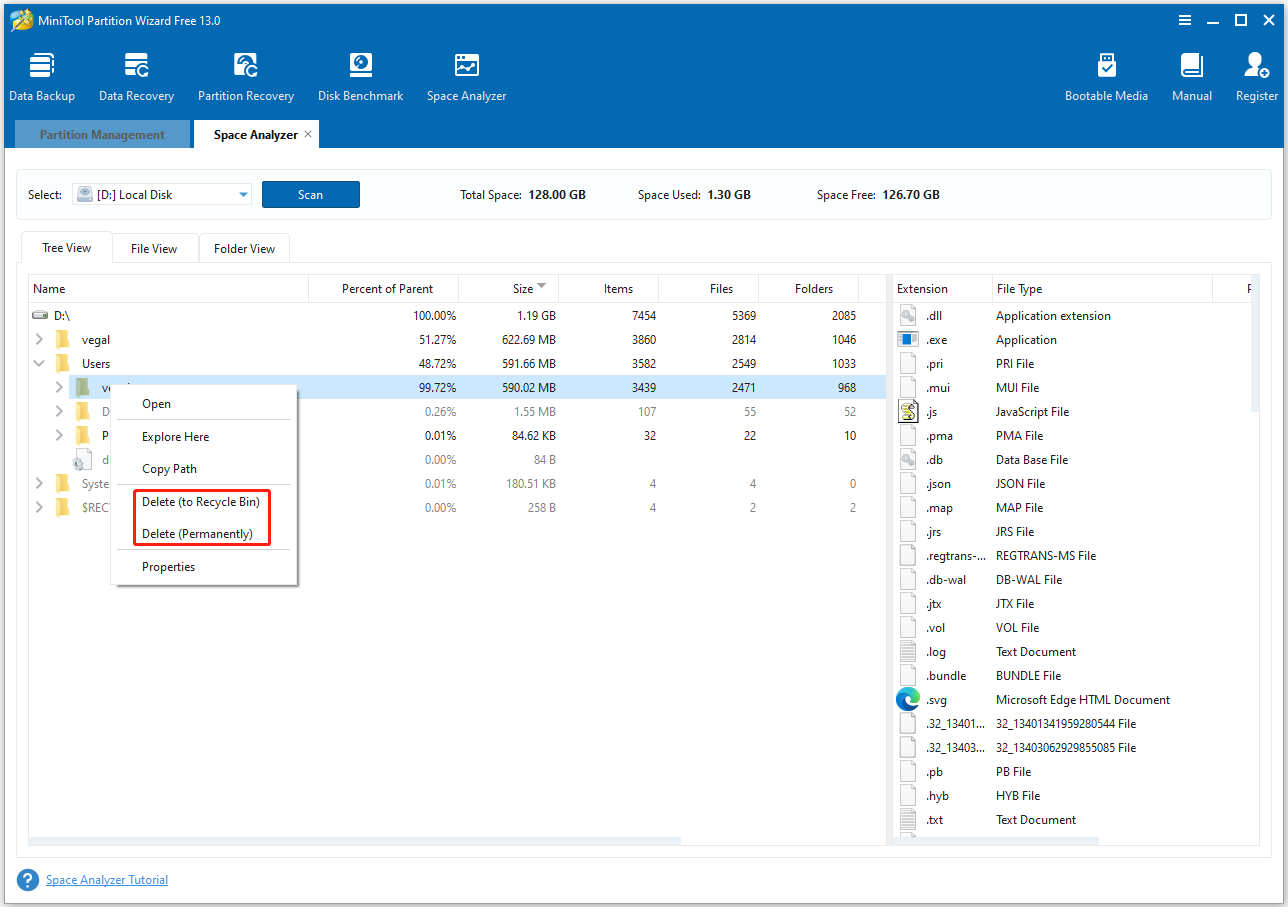
- Find unused files and select Delete (to Recycle Bin) or Delete (Permanently).
#2. Extend the disk space
MiniTool Partition Wizard can enlarge a partition by taking free space from an existing partition or unallocated space on the same disk. In this way, your C drive can also get more space.
Now, follow the steps to extend the C drive using MiniTool Partition Wizard:
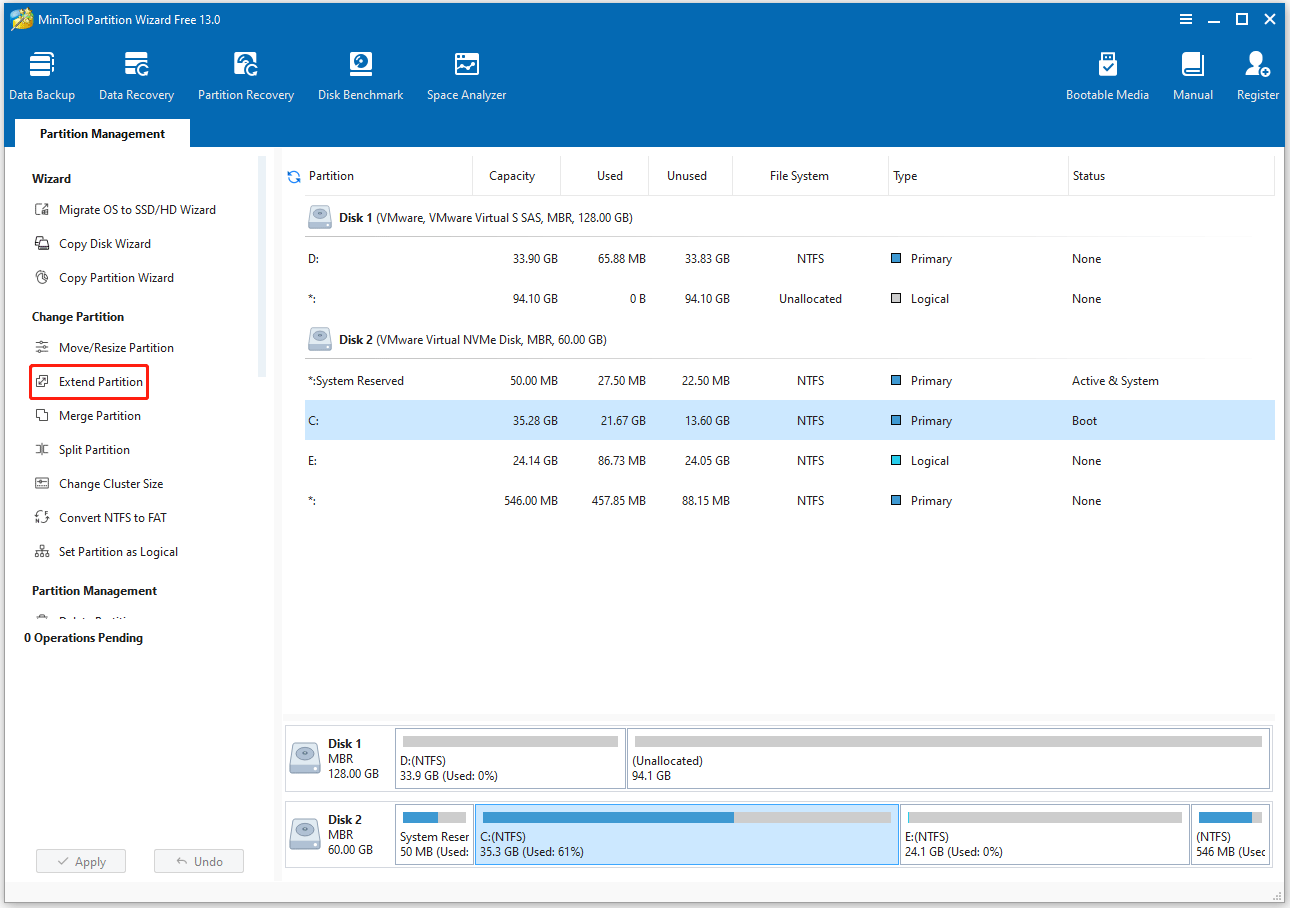
Step 1. On the main interface of MiniTool Partition Wizard, highlight the C drive and select Extend Partition from the left action panel.
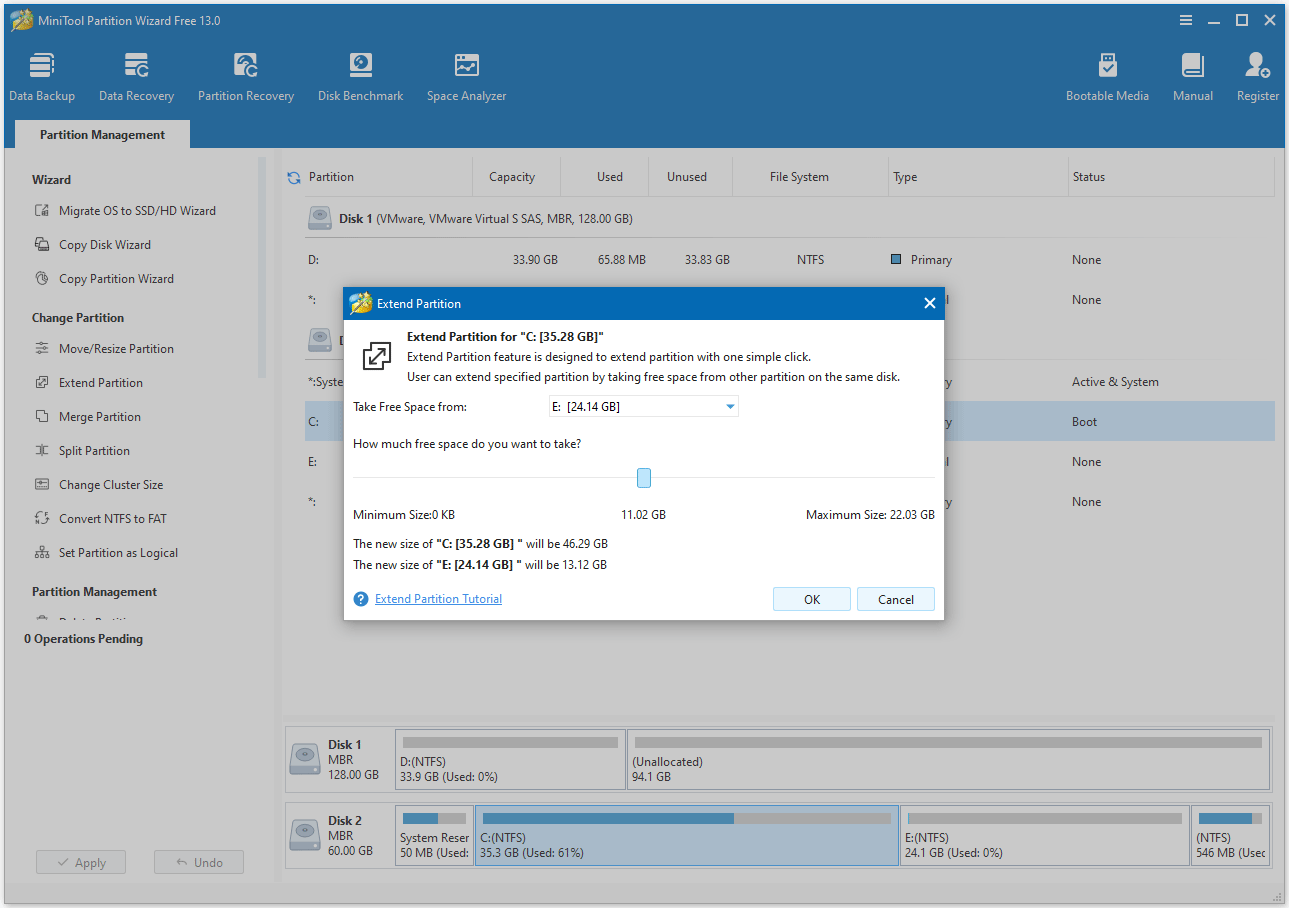
Step 2. In the pop-up window, open the Take Free Space from drop-down list and select a partition or unallocated space to take space. Then, drag the blue block to determine the amount of space to occupy. After that, click OK.
Step 3. After returning to the main interface, you can preview the extended drive. Then, click the Apply button to execute the pending operation.
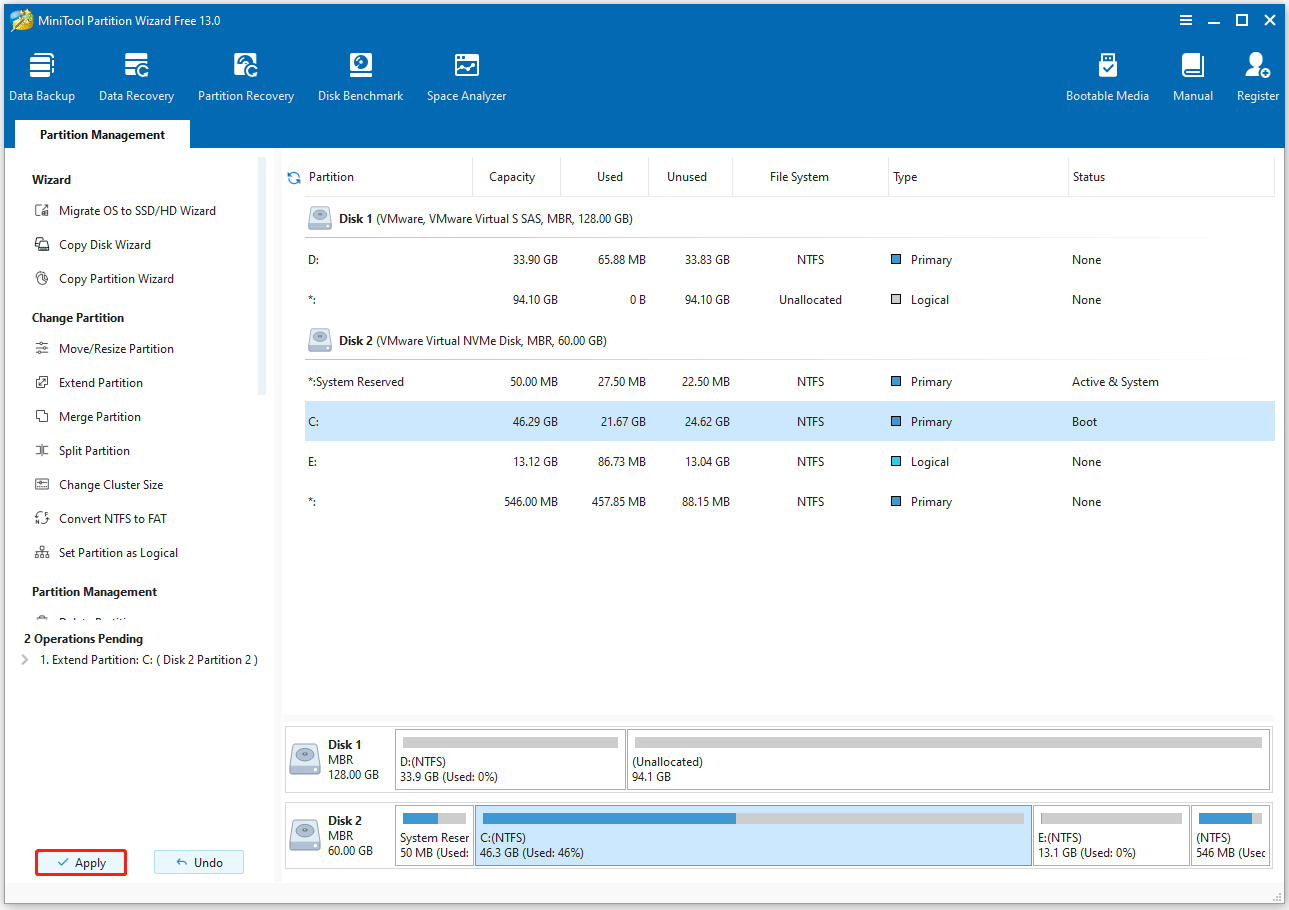
Step 4. Select Restart Now to allow the computer to restart. When your computer successfully restarts, you will find that the C drive has been extended.
#3. Insufficient RAM (Memory)
If your computer has insufficient physical memory, it will be difficult to perform multitasking efficiently, which may result in the computer running slowly or even crashing.
To check RAM usage, open Task Manager and see the percentage of Memory under the Memory tab. Here, you can see the RAM information, including the memory total and used size.
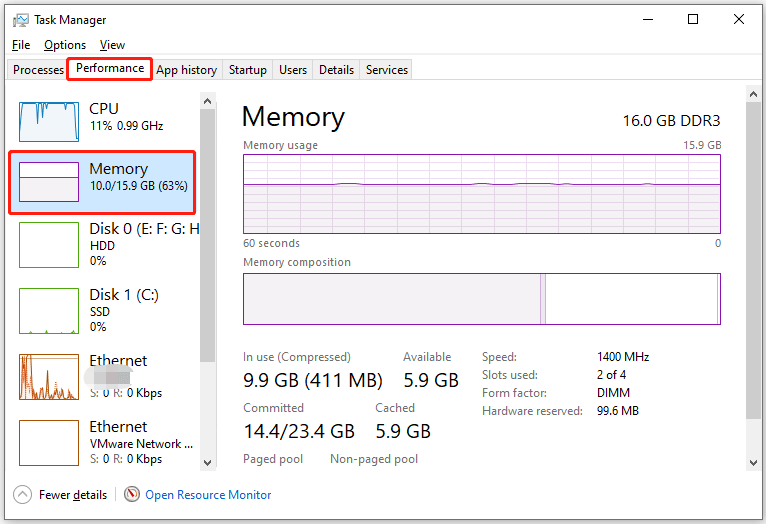
If it’s consistently over 80% with normal use, consider upgrading your RAM. This provides the system with the space it needs to run all your programs efficiently.
Before that, you should know if your laptop supports a memory upgrade. Check the manufacturer’s specifications, or use software tools like Crucial System Scanner or CPU-Z to see if RAM is upgradeable and find the maximum supported capacity.
Additionally, you should optimize some system settings for better performance.
Causes 2. Software Issues
Various software problems are also a common cause of slow computer performance. The main software problems include:
#1. Outdated OS, Drivers, and Software
Outdated operating systems (OS), drivers, and applications can cause compatibility issues and performance problems. So, you should update your OS, drivers, and software. Here is the guide.
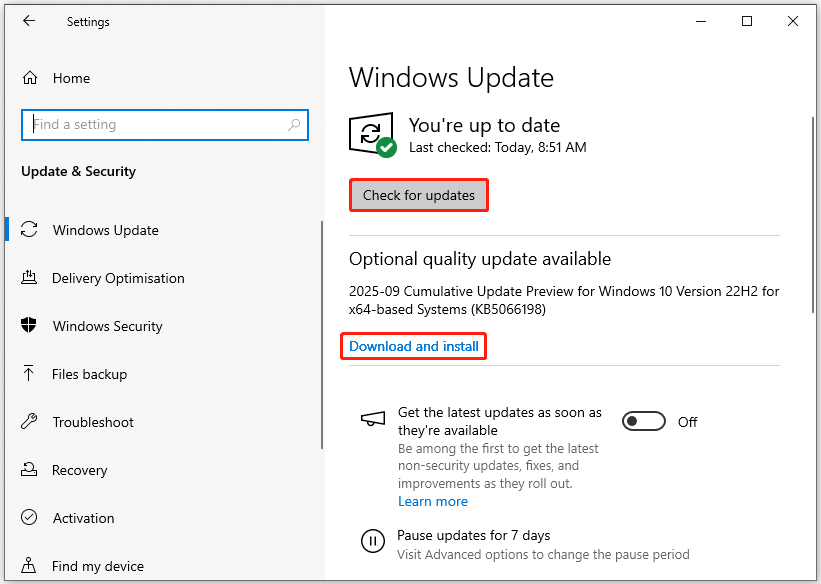
Update OS
- Press Windows key + I to open Settings, and then click Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates. If updates are available, click Download & install.
- After installation, restart your PC to apply the updates fully.
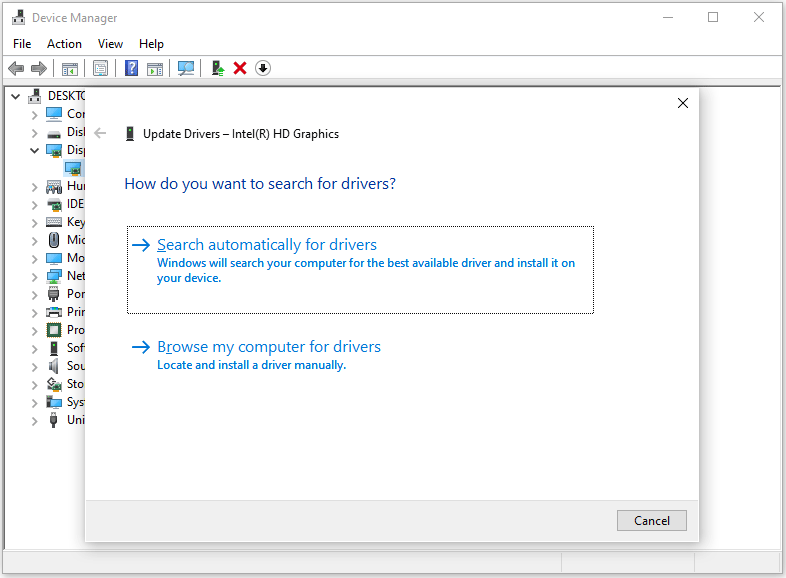
Update drivers
- Press Windows key + X, and then select Device Manager.
- Expand the category for the device, right-click the driver, and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for drivers and follow the on-screen instructions.
Update applications
Most apps on Windows can be updated via the Microsoft Store or their own built-in update option. Here are the steps to update apps via the Microsoft Store:
- Open the Microsoft Store.
- Go to the Library option in the bottom-left corner of the sidebar.
- Next to Updates & downloads, click the Get updates button.
#2. Malware or Virus Infection
Malicious software often runs hidden in the background, consuming CPU, memory, and network resources. This can slow down your computer and compromise security.
To scan for malware and viruses, run a full system scan using Windows’ built-in antivirus (Windows Security) or third-party antivirus software (Norton or McAfee).
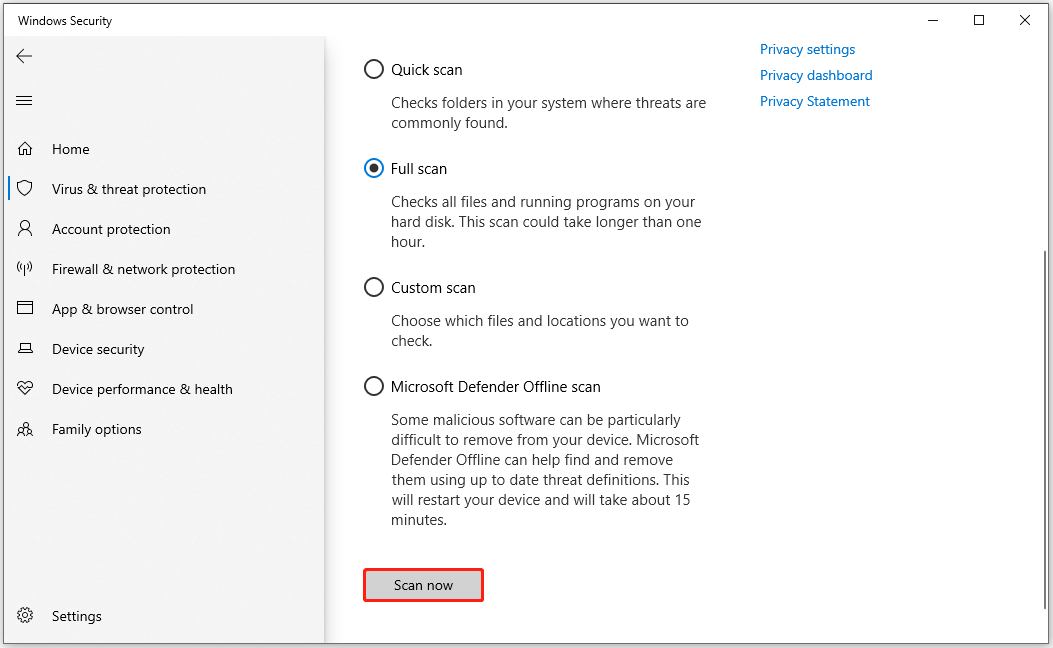
Here are the steps using Windows Security:
- Open Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection.
- Click Scan options and select Full scan. It scans all files and programs.
- Click Scan now and follow prompts to remove detected threats.
#3. Accumulated Temporary Files and Caches
Windows and other programs constantly create temporary files during normal operation, such as when opening files, browsing the web, or installing updates.
If there isn’t enough available space, these operations will slow down or fail, affecting the overall performance and stability of the system.
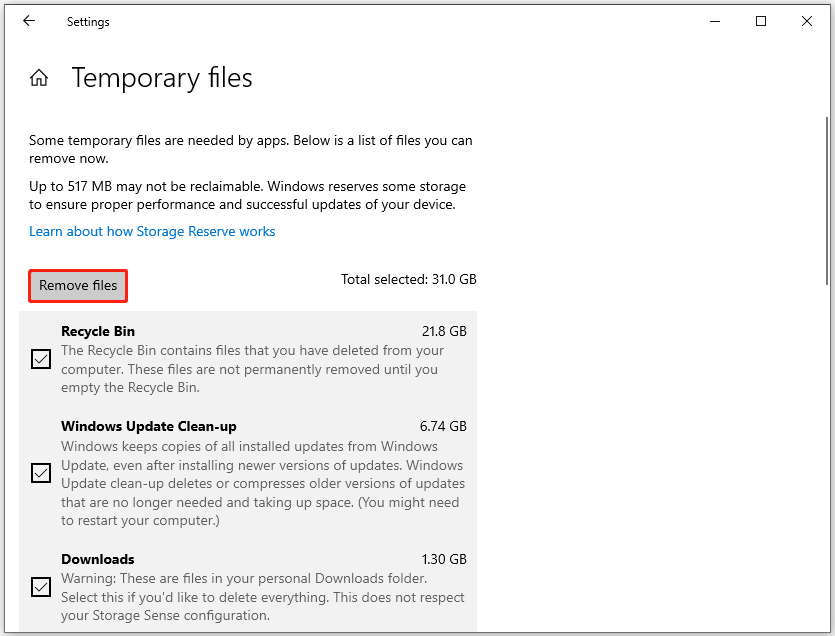
To clear temporary files in Windows Settings, the steps are as follows:
- Go to Settings > System > Storage.
- In the right panel of Storage and click the Temporary files category.
- Check boxes to select files to remove, like the Recycle Bin and Downloads.
- Click Remove files.
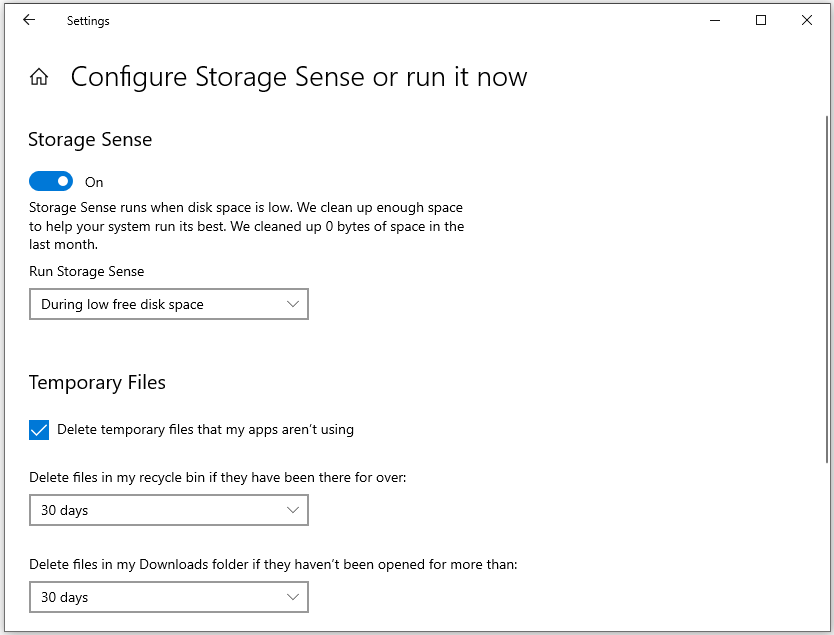
To delete temporary system and app files regularly, Storage Sense can help you. To enable Storage Sense, follow these steps:
- Back to the Storage settings.
- Toggle Storage Sense to On.
- To configure the settings, click Configure Storage Sense or run it now in Windows 10 (or Storage Sense in Windows 11). You can determine how often it runs and deletes files in the Recycle Bin and the Downloads folder.
Causes 3. Hardware Issues
While software issues are more common, hardware problems often become the bottleneck for older computers or those used for resource-intensive tasks such as video editing or 3D modeling.
Hardware issues usually require repair, replacement, or upgrade to resolve.
#1. Overheating
Overheating can also cause a computer to run slowly. Modern computers have a built-in safety mechanism called thermal throttling, which automatically reduces the processor’s speed and performance to prevent permanent damage from overheating.
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) generate heat when working. The more demanding the task (such as playing games or video editing), the more heat is generated.
The computer’s fans and heatsinks are responsible for dissipating this heat. If the cooling system is inadequate (due to dust, clogged vents, or a malfunctioning fan), hot air can get trapped inside the computer, causing internal temperatures to rise.
When the temperature reaches a critical threshold (typically around 90°C), the thermal sensor triggers a safety mechanism.
Then, the system will intentionally reduce the clock frequency and voltage of the CPU and GPU to decrease heat generation. This immediately leads to performance degradation, stuttering, screen tearing, and longer loading times.
In this case, you need to ensure proper airflow, use compressed air to remove dust from the vents, and verify the fans are functioning correctly.
#2. Slow or Failing Hard Drive
The computer running slow issue can be caused by the following 2 factors.
- Slow HDD: HDDs (hard disk drives) have significantly slower read and write speeds than modern solid-state drives (SSDs). If your computer uses an older HDD, it will slow down the overall system response.
- Failing Hard Drive: The operating system constantly relies on the hard drive for data access. If the hard drive fails, the entire computer must wait, resulting in a significant performance drop.
#1. Upgrade the Hard Drive to SSD
SSDs have no moving mechanical parts, so their data access speeds far exceed those of HDDs. Upgrading from an HDD to a fast SSD can significantly improve system response speed and startup time.
Fortunately, MiniTool Partition Wizard offers an OS migration feature to help you migrate the system and other data to the new SSD. It can also clone HDD to SSD.
How to migrate the OS with this software? Here is the guide. Before that, connect the SSD to your computer with an NVMe/SATA to USB adapter. Then download and install this software on your computer.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1. Start the migration.
- Open MiniTool Partition Wizard.
- Select the Migrate OS to SSD/HD Wizard feature from the left action panel.
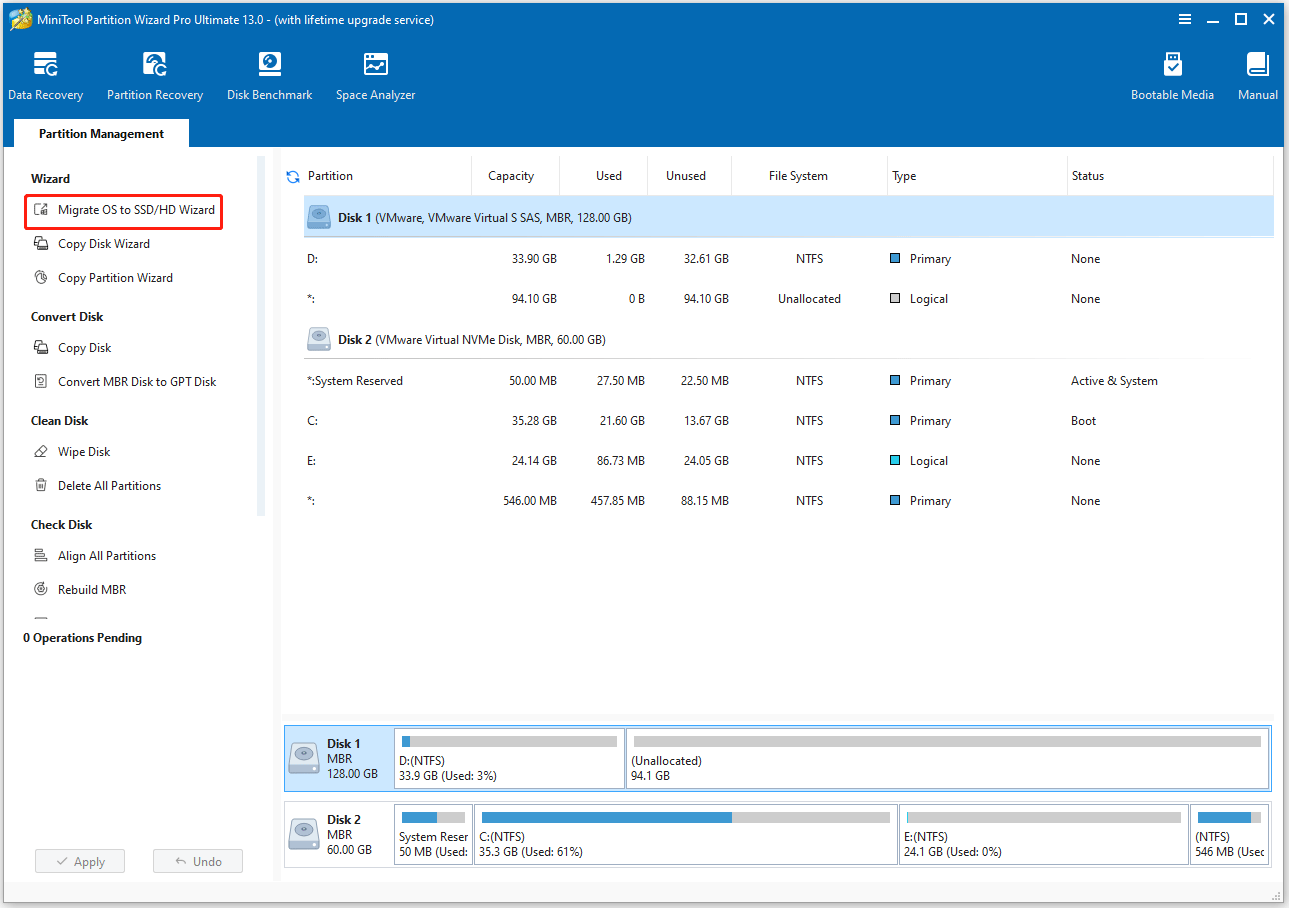
Step 2. Choose the migration method.
Choose a migration method, and then click Next.
- To transfer all the data to the new SSD, choose option A.
- To migrate the operating system only, choose option B.
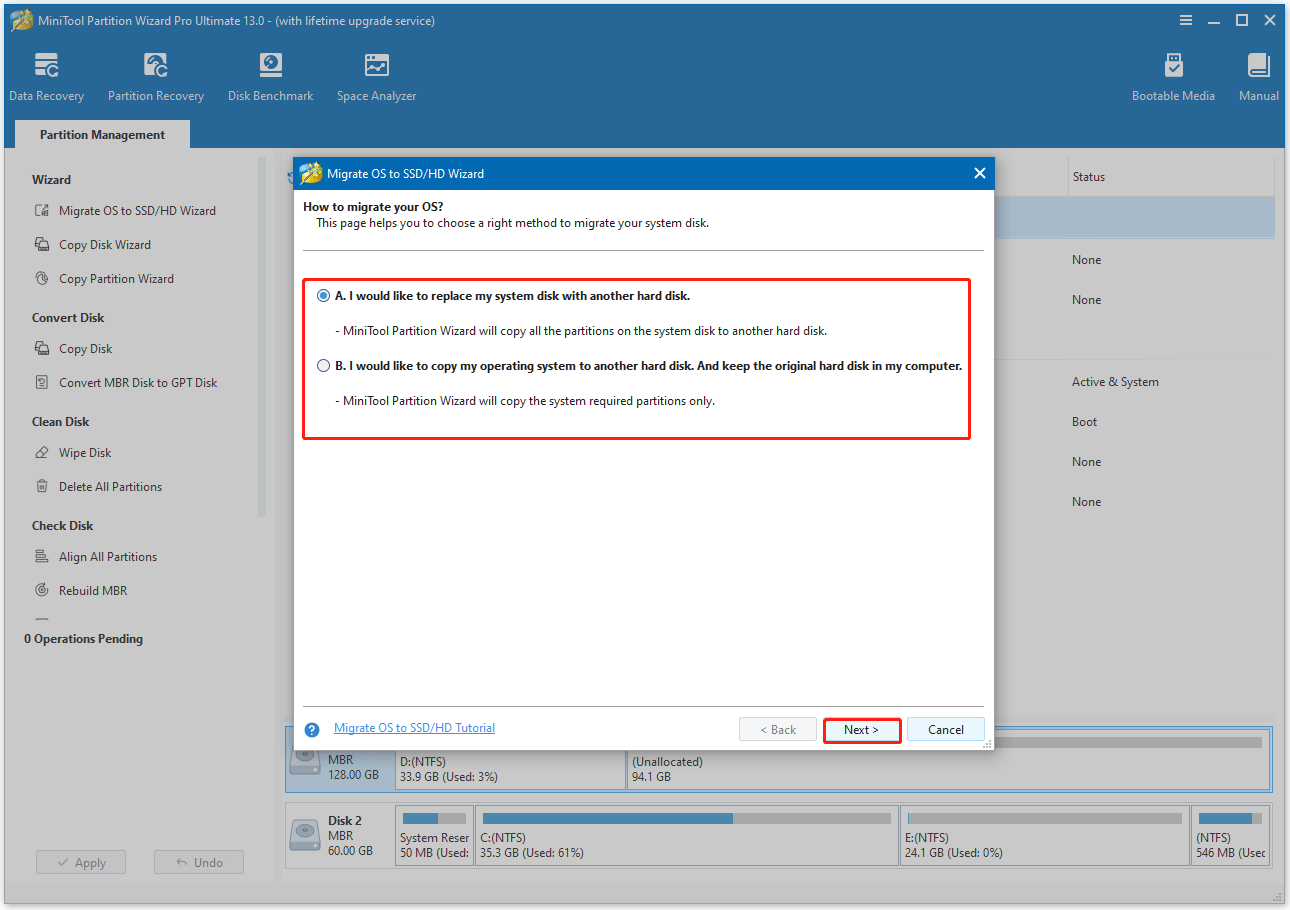
Step 3. Select the target disk and adjust copy options.
- Select the new SSD as the target disk. You will be warned that all data on the target disk will be erased.
- Review the copy options and disk layout. Keeping the default option is recommended. Then, click Next.
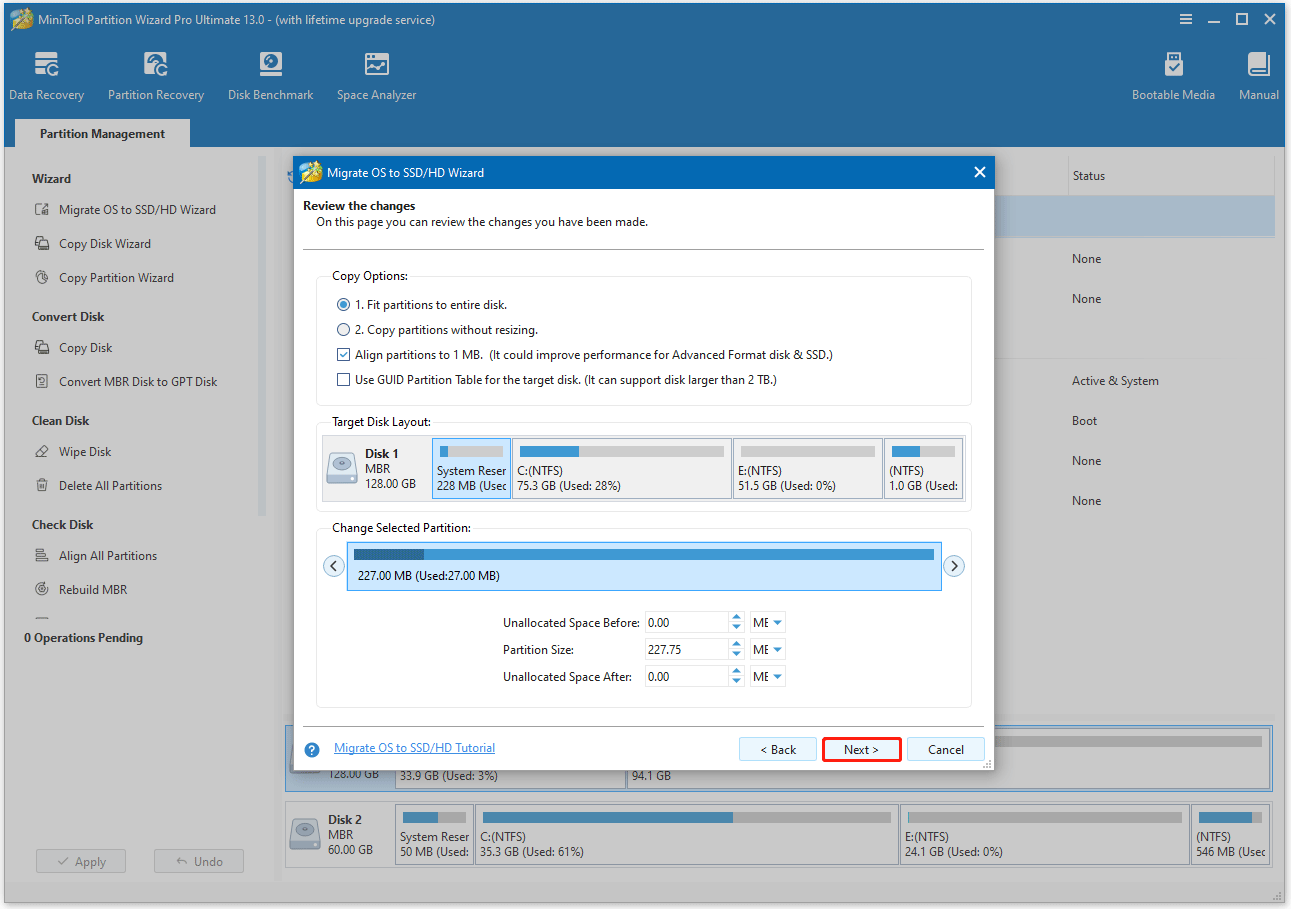
Step 4. Apply the migrating changes.
- Read the NOTE information and click Finish.
- Preview the changes and click Apply to start the cloning process.
- Click Yes to confirm and allow the operation to proceed. The process may take some time to complete, especially for large disks.
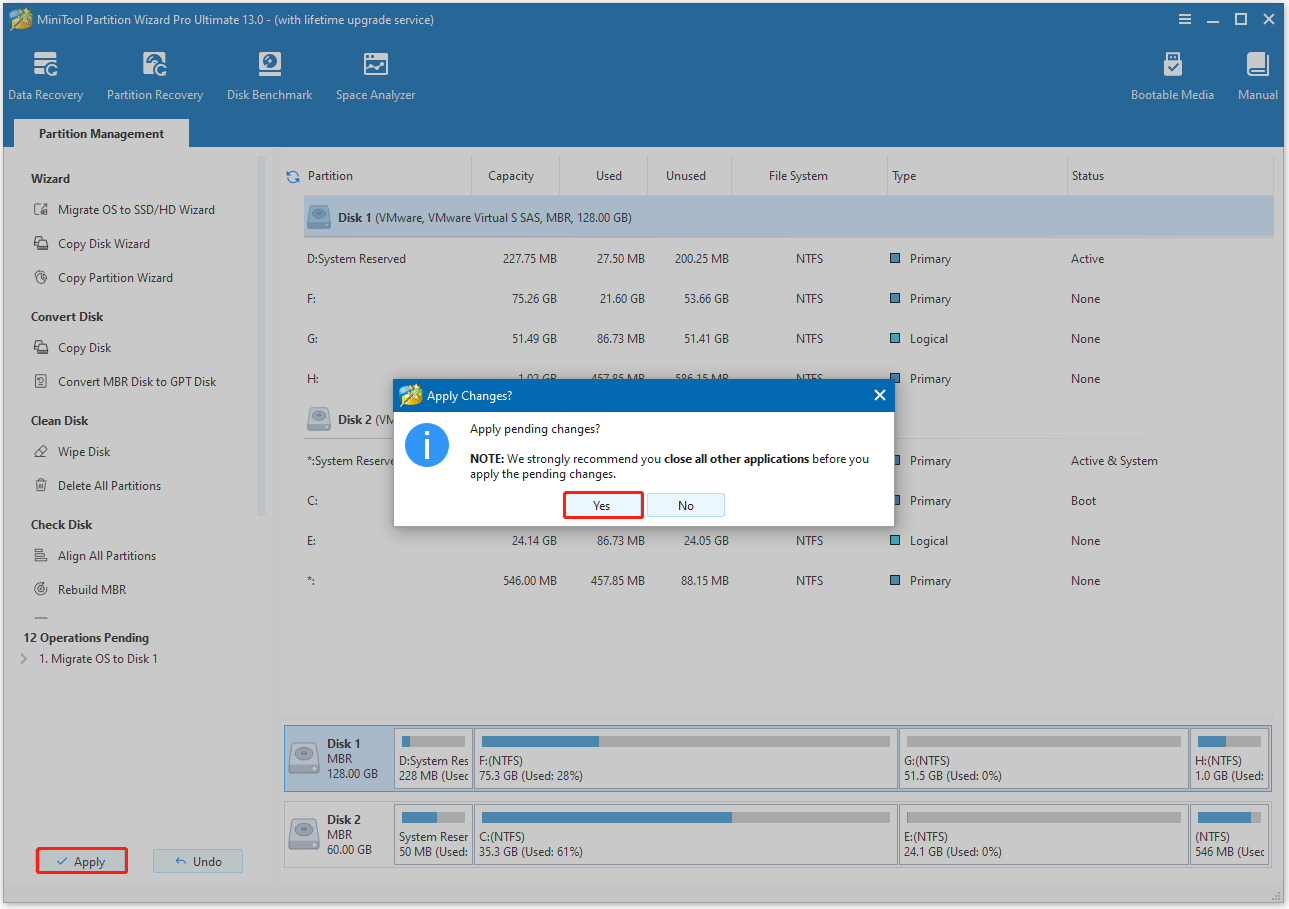
Once done, go to BIOS and set the new SSD as the first boot order.
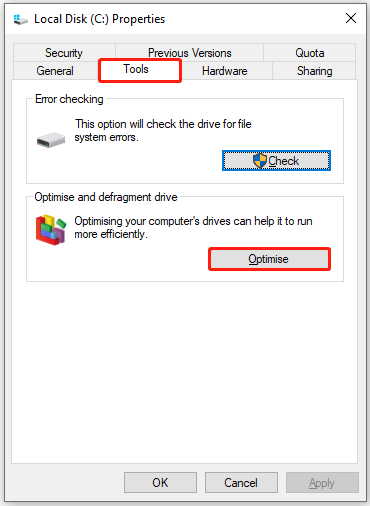
#2. Optimize Hard Drive
In Windows, the Defragment and Optimize Drives tool performs disk defragmentation for HDDs and TRIM for SSDs, which can improve the performance of both HDDs and SSDs. The steps are as follows:
- In File Explorer, right-click the hard drive and select Properties.
- Go to the Tools tab, click Optimize.
#3. Check the Hard Drive
When the drive fails with bad sectors, your computer repeatedly attempts to read the data, which causes delays and freezing for minutes.
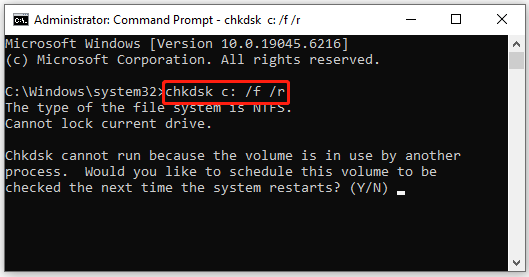
You can use the CHKDSK command for bad sector scanning. Here is the guide:
Step 1. Open Command Prompt as administrator again.
Step 2. In the Command Prompt window, type chkdsk x: /f /r and press Enter. Replace “x” with the letter of your drive.
- /f fixes errors found on the disk.
- /r locates bad sectors on the disk, recovers readable information from them, and marks them as bad.
Step 3. If the drive is in use (the C: drive is usually in this state), you will be asked if you want to schedule the check for the next time you restart your computer. Type Y and press Enter.
#3. Misaligned Partitions on SSD
Partition misalignment on an SSD can slow down a computer, especially when performing write-intensive tasks, and can also shorten the lifespan of the hard drive.
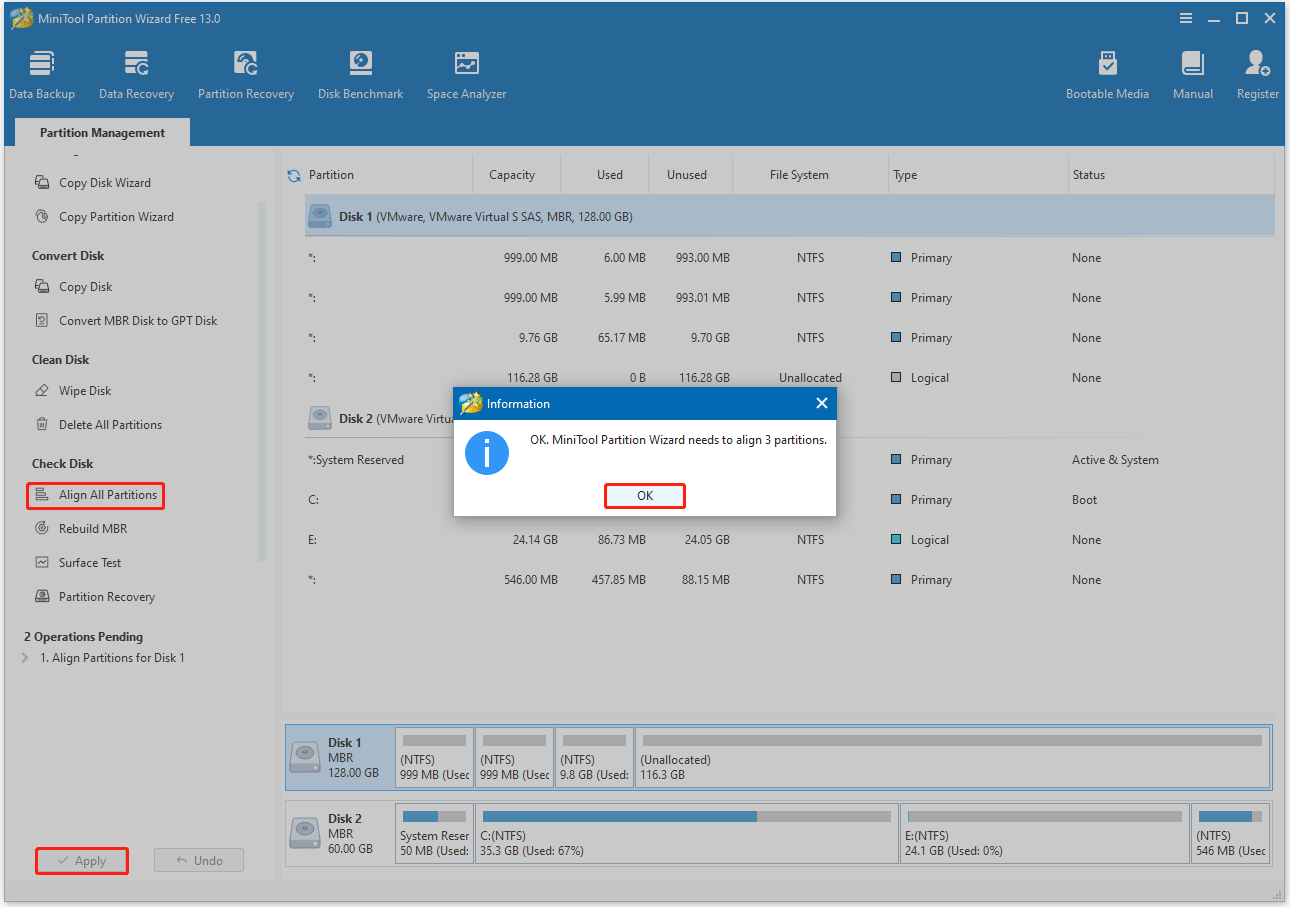
You can utilize MiniTool Partition Wizard to align all partitions on the SSD. The steps are as follows:
- Run MiniTool Partition Wizard to get the main interface.
- Select the misaligned SSD and choose Align All Partitions from the left action panel.
- If any partitions are misaligned, a message will appear showing the number of partitions to align. Click OK to proceed.
- Click Apply to start the alignment process.
#4. Old Hardware Not Meeting Modern Software Demands
If your computer is several years old, and these old components (CPU, GPU) may simply not be capable of running modern, more demanding software efficiently.
The CPU handles most of the computation for the operating system and applications. An outdated or underperforming CPU may struggle to keep up with the speed of modern software.
The GPU handles graphics-related tasks such as video playback, gaming, and 3D rendering. An underperforming GPU will cause graphics-intensive applications to run slowly.
In this case, it’s time to upgrade the CPU and GPU.
If you’ve tried all these fixes and your computer is still slow, it may be time to consider a new machine.
My Computer Is Running Slow FAQ
1. Restart your computer to clear memory and reset all running programs.
2. Uninstall unnecessary applications that are consuming excessive memory.
3. Scan your computer for malware, as it can consume a large amount of available memory.
4. Adjust virtual memory settings.
5. Install more memory.
6. Use reliable memory cleaning software.
1. Run Disk Cleanup: Delete temporary files and Recycle Bin items to free up disk space.
2. Regularly scan for malware: Malware (viruses, worms, and Trojans) run hidden processes in the background that consume CPU/RAM resources, causing slowdowns and lag. Antivirus programs can scan and kill viruses.
3. Check for updates: Install Windows Updates, driver updates, and application updates to have the latest performance and security fixes.
4. Monitor hardware health: Use CrystalDiskInfo to check hard drive health and component temperatures.
Bottom Line
Why is my computer running slow? This post analyzes the possible reasons. By understanding the cause, whether it’s a resource-intensive process, insufficient memory, or aging hardware, you can more effectively target your repairs for optimal results.
Furthermore, regular maintenance is key to preventing future computer slowdowns.
If you have any problems or suggestions when using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can contact us by sending an email to [email protected]. We’ll get back to you as soon as possible.


User Comments :