Computer Storage Devices Definition/Functions/Advantages
What are storage devices on a computer? Usually, storage devices of computers refer to the hardware used to store digital data pre-input or generated later within a computer. They can retain information temporarily (short-term) or permanently (long-term). A storage device can also be called a storage media or storage medium.
With the storage devices for computers, you can write data into them, carry data by them, and read data through them. A storage device is one of the basic and necessary components/elements of a computer (desktop, laptop, notebook or tablet). Except for hardware firmware, it contains almost all data and applications on a computer.
Related article: Different Types of Hard Drives: Which One Should You Choose
Hierarchy of Storage
Practically, nearly all computers make use of a storage hierarchy to arrange computer storage. Storage hierarchy puts fast, small yet expensive computer storage devices close to the CPU (Central Processing Unit), while slow, large yet cheap ones far away.
The fast storage media adopting the volatile technologies, which lose data when power is off, are referred to as “memory”. While the slow storage options relying on the non-volatile (persistent) technology, which retains data when there is no electricity, are referred to as “storage”.
In contemporary use, “memory” is usually read and write random-access memory (RAM) of semiconductor storage like dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM). Based on the speed, “memory” is divided into processor registers (fastest yet smallest), processor cache, and main memory (slowest yet largest) with registers and cache memory locate inside of the CPU.
While “storage” consists of storage devices and their media aren’t directly accessed by the CPU, such as hard drives and optical disc drives.
In history, “memory” is also known as “core memory”, “main memory”, “internal memory” or “real storage”. While non-volatile computer storage devices are also called “secondary storage”, “external memory” or “auxiliary/peripheral storage”.
The lower a storage is in the hierarchy, the lesser its bandwidth and the greater its access latency is from the CPU. This divides storage into primary, secondary, tertiary and off-line storage.
Primary Storage
Primary storage, also called a prime memory, main memory or internal memory, is often referred to as memory. It is the only directly accessible storage to the CPU, such as RAM and ROM (Read-only Memory). The CPU continuously reads instructions saved in the primary storage and executes them as required. All data actively operated on are also saved there in a uniform manner.
Secondary Storage
Secondary storage, also called an external memory or auxiliary storage, differs from the primary storage for its indirectly accessible by the CPU. Computers often rely on input/output (I/O) channels to access the secondary storage and transfer the desired data to the primary storage.
Examples of secondary storage devices of computer are hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).
Tertiary Storage
Tertiary storage, also called tertiary memory, is a level below the secondary storage. Typically, it involves a robotic mechanism that mounts and dismounts removable storage media into computer storage devices under the system requirements. Such kind of data is usually copied to the secondary storage before being used.
The tertiary storage is mainly used for archiving rarely accessed data and it is much slower than the secondary storage. The tertiary storage is primarily used for extraordinarily large data storage like tape libraries or optical jukeboxes, accessed without human intervention. Thus, tertiary storage is also known as nearline storage. Magnetic tape, magnetic card and CD/DVD, for example, are all tertiary storage.
Kind reminder:
- Online storage is immediately available for I/O.
- Nearline storage is not immediately available yet can be made online quickly without human operation.
- Offline storage is not immediately available and needs human operation to be online.
Off-line Storage
Offline storage is a kind of computer digital data storage on a media that isn’t controlled by the CPU. The media is usually recorded as a secondary or tertiary storage device and be physically removed or disconnected from its attached computer. To access it again, you must insert or connect it to your computer.
Offline storage devices are usually used to data transfer and long-term data storage, and are also called disconnected or removable computer storage devices. Some examples are floppy disk, magnetic tape, CD and DVD.
Type of Computer Storage Devices
After learning the hierarchy of storage, it is reasonable to say that there are 4 types of computer storage devices: primary, secondary, tertiary and offline storage devices. As for the common secondary storage devices, they can be further divided into internal and external storage devices of computer according to their location, inside or outside of computers or servers. And, external storage devices are also called portable computer storage devices.
Based on the material of the pc storage devices, there are semiconductor storage devices, magnetic storage devices and optical storage devices:
Semiconductor Storage Devices
Semiconductor memory makes use of semiconductor-based integrated circuit (IC) chipsets to save data and both volatile and non-volatile forms of semiconductor memory exist. In modern times, primary storage nearly all consists of dynamic volatile semiconductor RAM, especially DRAM.
At the beginning of the 21st century, a kind of non-volatile floating-gate semiconductor memory known as flash memory became popular as offline storage. It is also used as secondary storage with an example of SSD.
Magnetic Storage Devices
Magnetic storage media makes use of different patterns of magnetization on a magnetically coated surface to contain data. It is non-volatile. The data stored within are read via one or more read/write heads that may include one or more recording transducers.
The magnetic head only reaches a part of the media surface. Thus, the head or medium or both must move relative to another to reading data. Below is a list of storage devices of computer of magnetic type:
- Floppy diskette
- HDD
- Magnetic tape
- Magnetic strip
- Super disk
- Zip diskette
- Carousel memory
Optical Storage Devices
Typically, optical computer storage devices refer to optical discs. They save data in deformities on the surface of a circular disc. To access the data on an optical disc drive, computers illuminate its surface with a laser diode and observe the reflection.
Optical disc storage is non-volatile. The deformities can be permanent (read-only media), formed once (write once media), or reversible (recordable or read/write media).
- Read-only media: CD, CD-ROM, DVD, BD-ROM
- Write-once media: CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R, BD-R
- Recordable media: CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, DVD-RAM, BD-RE
- Ultra-density optical (UDO)
- Blu-ray: BD-R, BD-RE, BD-R XL, BD-RE XL
Other Storage Devices
- Flash memory: USB flash drive, thumb drive, jump drive, memory card, memory stick, NVMe, SD card, SSD, etc.
- Paper data storage: paper tape, punched card and OMR (Optical Mark Recording)
- Online/cloud storage: cloud drives (Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, etc.), NAS & network media
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disk)
How to Make Use of Computer Storage Devices?
Though computer related storage devices are mainly for storing digital information, different types are used in different situations and they are in different shapes & sizes depending on the needs and functionalities.
Usually, the primary memory storage is used to store the data directly used by the CPU; The secondary internal storage is used for saving digital data frequently used in your daily life; the tertiary storages are served as mass storage devices of computer; while the secondary external storage, off-line storage, some flash memory storage and online/cloud storage are used for carrying data for transferring.
Prepare a Computer Storage Device for Usage
If you get a new data storage device, an external hard drive, for instance, the first thing you should do is to format it properly for future use. Here, you need a professional and reliable software like MiniTool Partition Wizard. Download and install it on your computer, install your drive into your machine and launch the program.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step1. In the main screen of Partition Wizard, find the target disk, right-click on it and select Initialize GPT Disk (or Initialize MBR Disk). It depends on the original type of your hard drive.
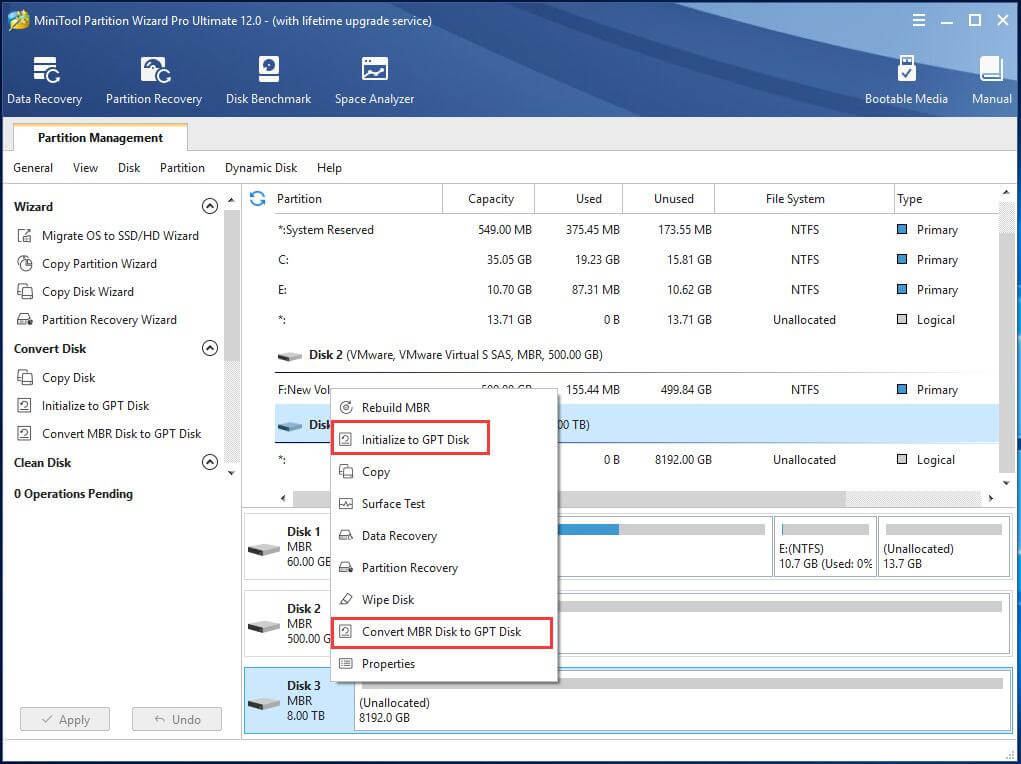
Step 2. Preview the change and confirm it by clicking Apply on the bottom left.
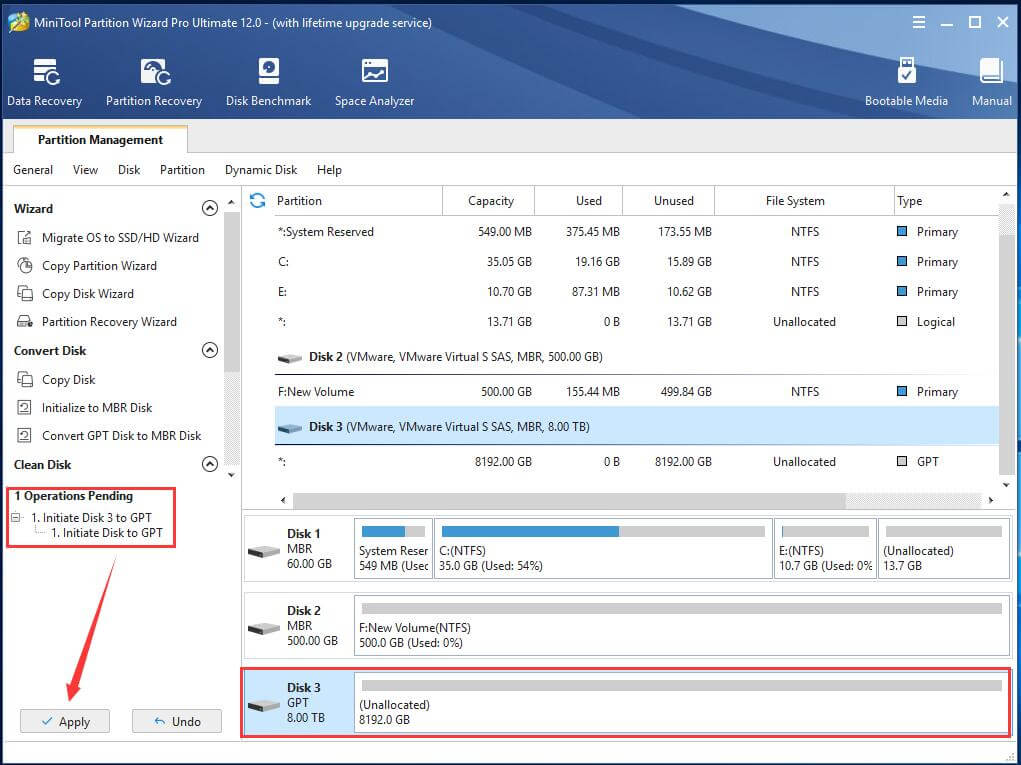
Step 3. When the initializing process finishes, right-click on the unallocated space of the hard disk again and choose Create.
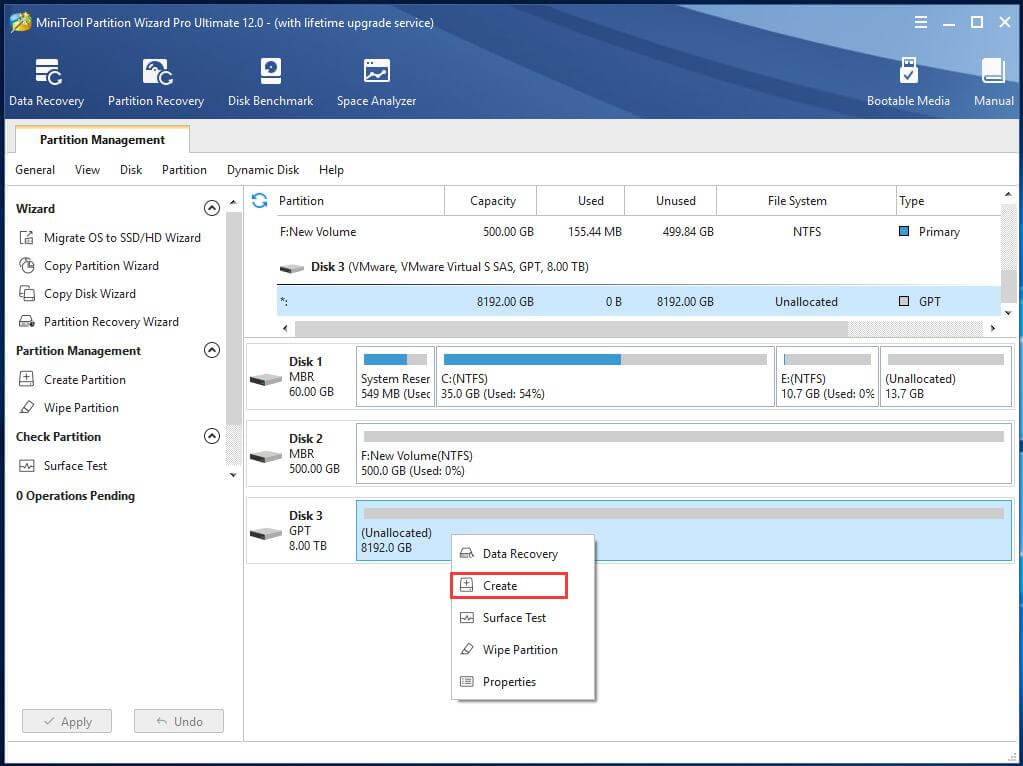
Step 4. In the pop-up window, specify the details of the new partition: partition label, primary or logical partition, drive letter, file system, cluster size as well as partition capacity.
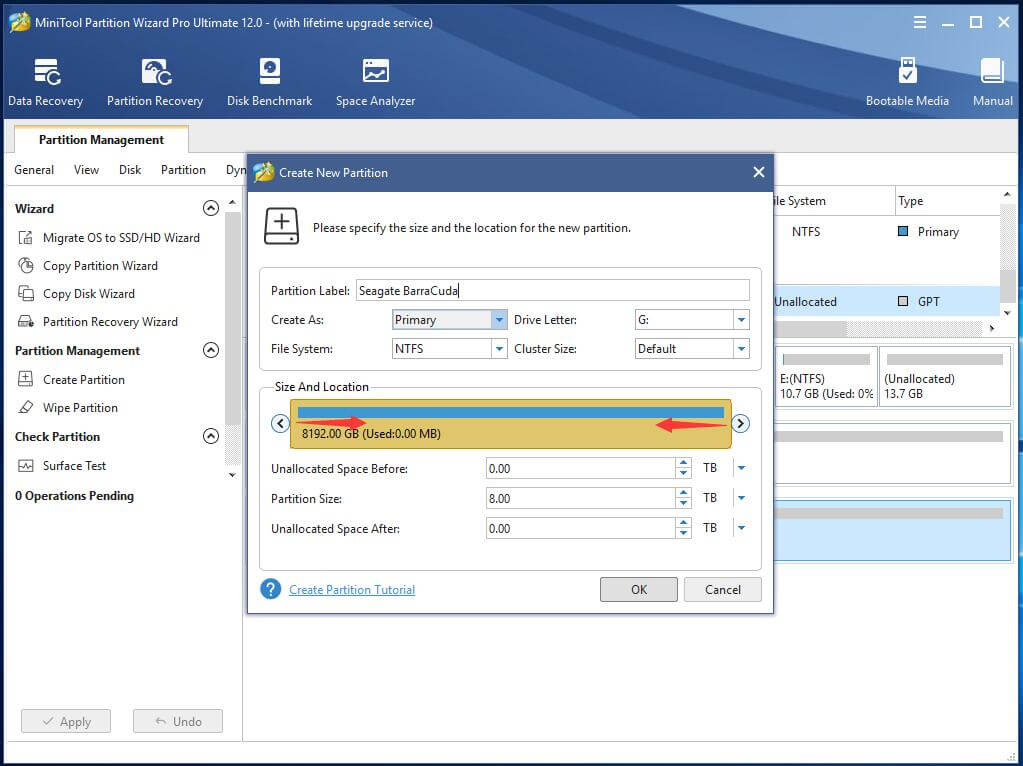
Step 5. Once again, check for the change the creation will make. If there is no problem, just click Apply on the lower left to carry out the partition creating task.
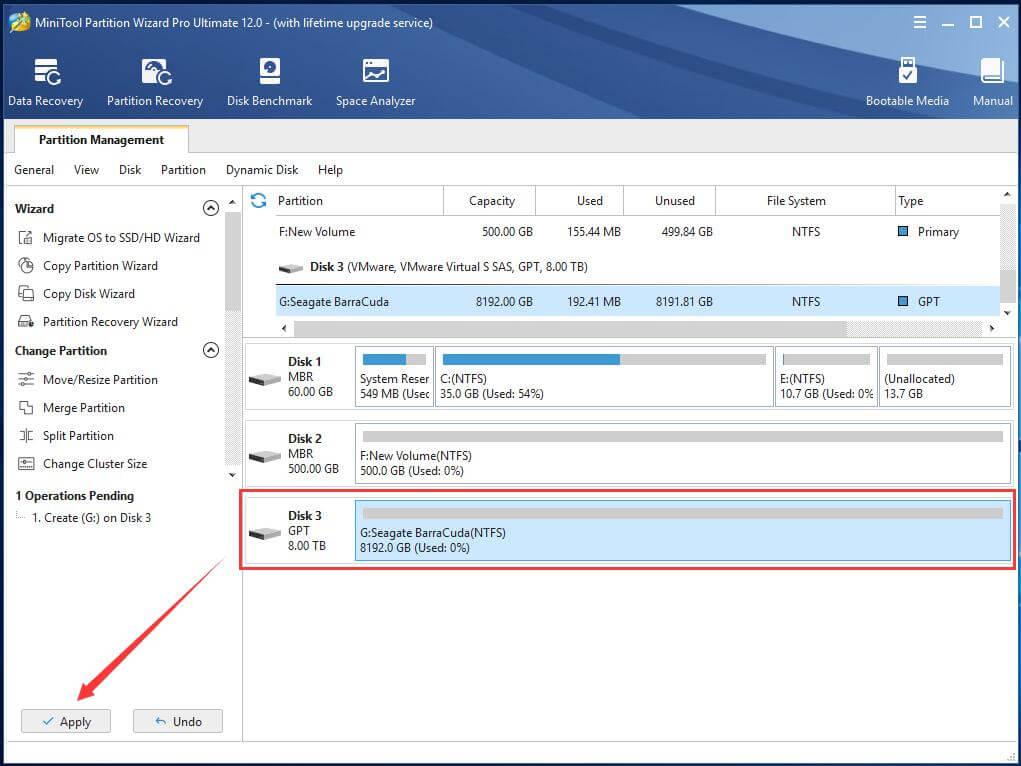
Until now, you are able to make full use of the formatted computer storage device either for storage function or for tool function.
Backup Your System Disk with the Formatted External Hard Drive
Once you get your external hard drive ready following the above guide, you can continue to back up your operating system disk with it under the help of MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Step 1. Right-click the OS disk and choose Copy.
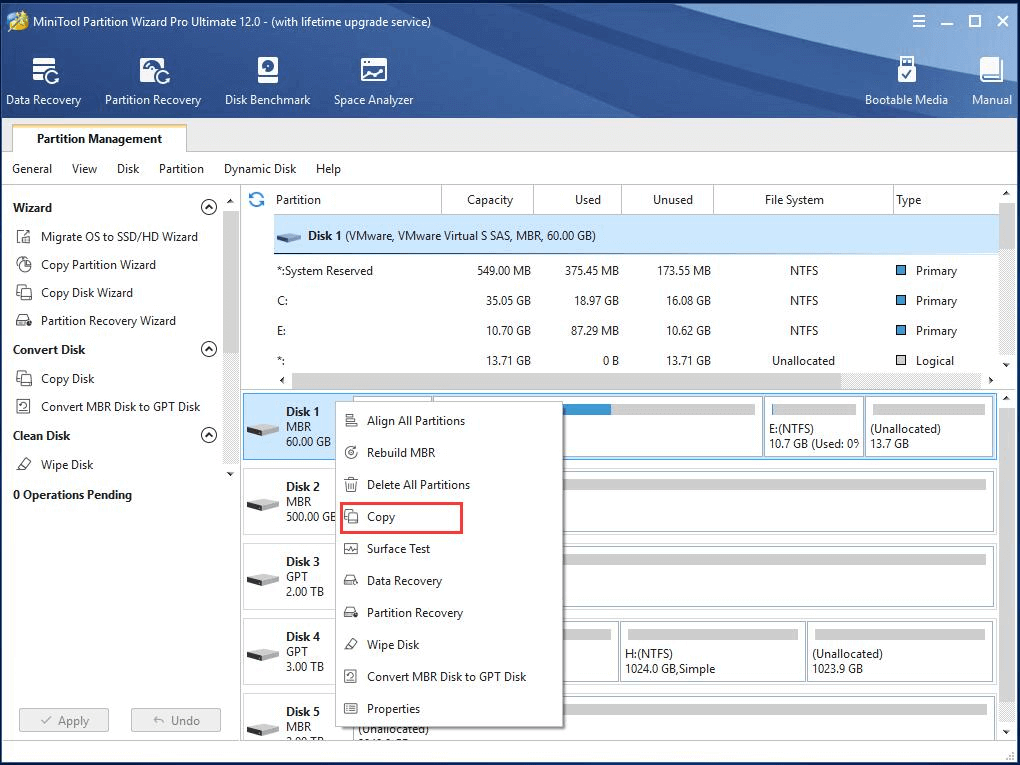
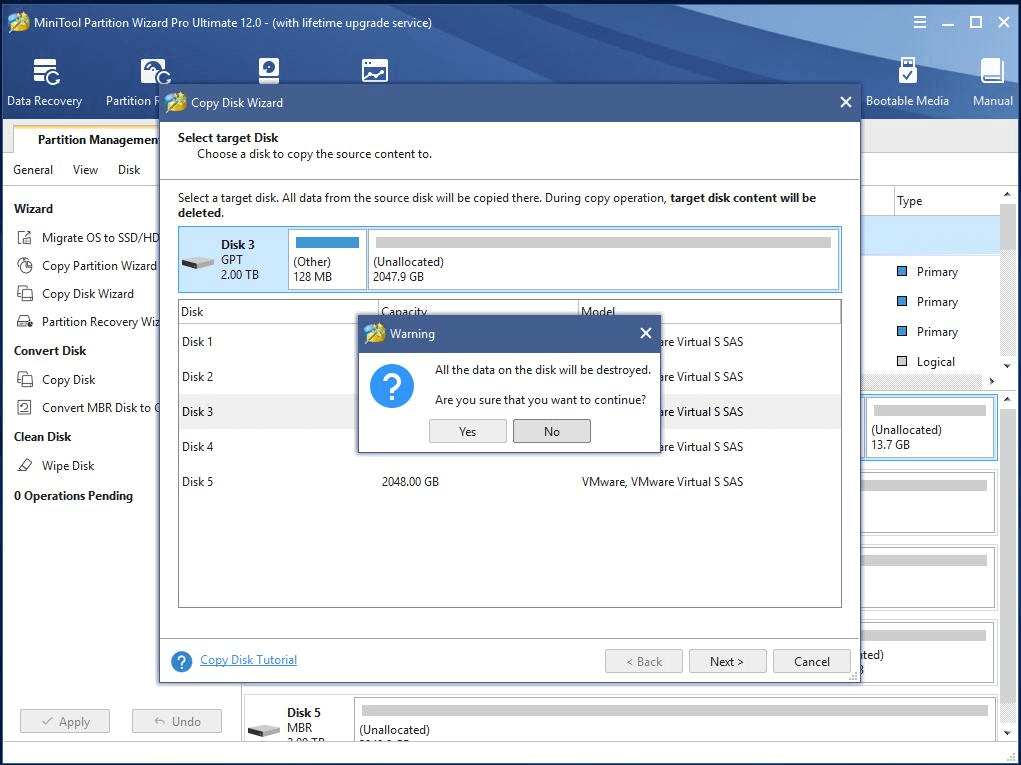
Step 2. In the pop-up window, select the external hard disk as the destination of the system backup image.
Note: All data on the target disk will be wiped out or overwritten if there is any.
Step 3. You need to select a copy option to go on. If the destination disk is an SSD, you are recommended to check “Align partition to 1 MB” to improve the performance of your SSD.
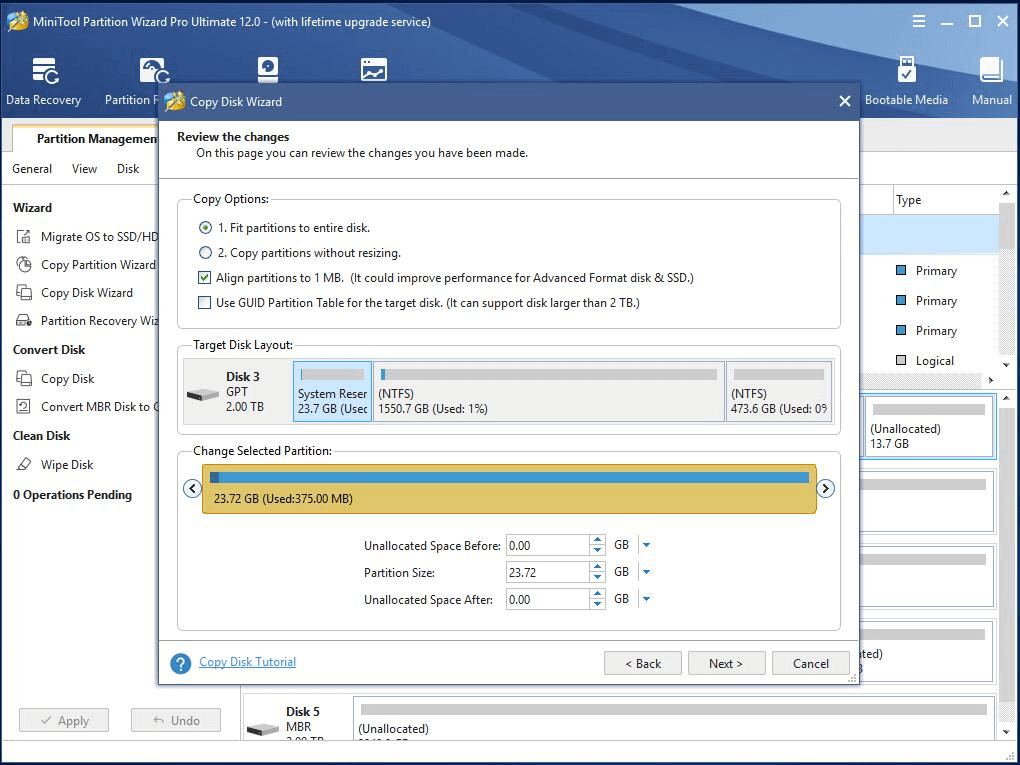
Step 4. Similarly, have a look at the pending operations that are going to be carried out. If everything is what you wish, just click Apply to start the process.
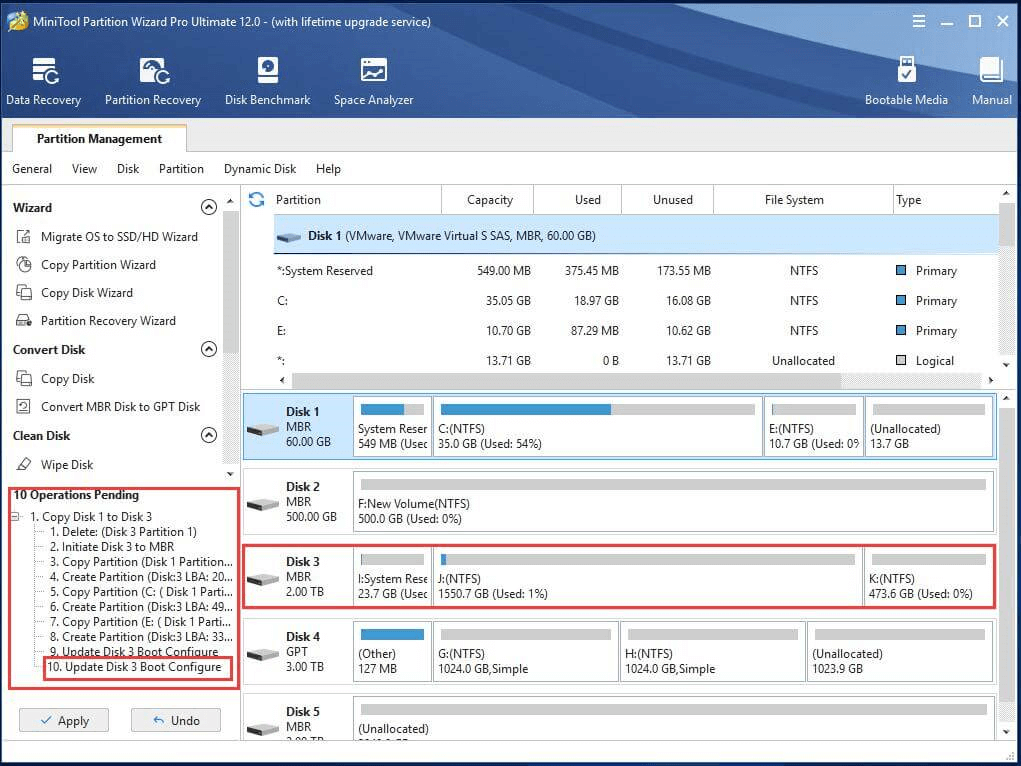
Wait until the backup progress finishes. Then, you may reboot your computer into BIOS, change its first boot device from the current disk to the new drive, and try to boot up your machine to see whether you can make it or not. It should be successful if you just do as the above guidance.
Besides, you can also use the external hard drive as a bootable device by creating it as a bootable media still with Partition Wizard.
That is all about computer storage devices and their advantages. If you still want to know something about it, either leave a message in below comment part or directly contact our support team at [email protected].


User Comments :