What is the difference between memory and storage? This post of Partition Magic offers a full comparison of computer memory vs storage, including definitions, differences, and similarities. Also, you can learn how to check and increase them here.
For tech pros, it may be easy to understand the difference between memory and storage. However, for those PC novices, this can be challenging. For example, here is a user report from the Reddit forum:
Hi all, I’m building my first PC and trying to understand the basics of all the parts... But I don’t understand the difference between RAM and storage. What exactly does RAM do? Also, why would you ever need to add more RAM? Is a 2 TB stick of RAM not enough for a PC?https://www.reddit.com/r/buildapc/comments/1h1xpdy/difference_between_ram_and_storage/
Are you confused about the differences between RAM and storage? If so, continue reading, and then you can get a complete guide on that.
Further Reading: Is a 2 TB stick of RAM not enough for a PC?
Strictly speaking, there is no such thing as a single 2TB memory module on the market. What is often referred to as “2TB memory” in high-performance servers or workstations is typically a package made up of multiple high-capacity memory modules.
For personal computers, due to the limited number of motherboard slots, it is physically impossible to achieve 2TB. Many beginners mistakenly confuse 2TB of storage (such as a hard drive) with memory.
In reality, personal computers generally require only 16GB to 32GB of memory for smooth operation. Pursuing TB-level memory is not only expensive but may also lead to compatibility issues.
Memory vs Storage: A Full Comparison
This section provides a full comparison a full comparison of RAM and storage, including the definition, similarities, and differences.
Definition
In computing, memory and storage are two fundamental components that work together but serve different purposes.
What Is Computer Memory?
Computer memory, mainly RAM, is a short-term workspace for data and instructions that the CPU actively uses. It is volatile, meaning all data is lost once the computer is powered off.
Memory is crucial for multitasking and running applications smoothly, as it allows quick access to data in real-time.
Key features of memory (RAM):
- Volatile (data is erased when power is off).
- Fast read/write speed.
- Used for active processes and running programs.
- Typically measured in gigabytes (GB).
What Is Computer Storage?
Computer storage refers to the devices and systems that hold data permanently. Examples include hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB drives, and cloud storage.
Unlike memory, storage keeps files, applications, and operating systems safe even when the computer is turned off.
Key features of storage:
- Non-volatile (data remains without power).
- Slower than RAM but offers much larger capacity.
- Used to save operating systems, applications, and personal files.
- Typically measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB).
Similarities
Although memory and storage serve different purposes in a computer system, they share several common traits that make them closely related. Here are the similarities between them:
- Both are essential for a computer to function properly.
- Both hold data in digital form (binary).
- Both can impact system performance (low memory or slow storage affects speed).
- Both are measured in units like GB or TB.
Differences
What is the difference between memory and storage? While memory and storage share some similarities, their roles in a computer are fundamentally different.
Understanding these differences between them helps clarify why both are necessary and how they complement each other in a computer system.
| Feature | Memory (RAM) | Storage |
| Volatility | Data is lost when the power is off | Data persists even when the power is off |
| Speed | Much faster than storage | Slower compared to RAM |
| Latency | Very low | Higher |
| Purpose | Temporarily holds data for active processes, such as apps running | Permanently stores files and programs, including all files, OS, applications, user data, logs, etc. |
| Examples | RAM, Cache | HDD, SSD, NVMe, USB drives |
| Capacity | Common capacities of RAM modules are 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, and 64GB per module. *Modern consumer-grade motherboards usually support 128 GB to 256 GB of RAM, depending on the chipset and CPU. 1TB modules are usually only supported on server-grade motherboards. | Usually larger (e.g., 256GB – 100TB) *100TB is too expensive for average users |
| Price | Higher | Cheaper |
| Accessibility | Data is accessed randomly and very quickly | Access can be sequential or random, slower |
| Lifespan | Shorter write cycles, but rarely a concern for RAM | Storage devices wear out over time (especially SSDs) |
| Used By | CPU is used directly during computation | System and users for storing and retrieving data |
| Installation Location | Installed on the motherboard | Installed in dedicated drive bays, M.2 slots (for SSDs), or external enclosures |
| Interface | Installed in the motherboard’s RAM slots | Connects via SATA, M.2, PCIe, or USB |
| Form Factor | DIMM (desktops), SO-DIMM (laptops) | HDD: 3.5″/2.5″, SSD: 2.5″, M.2, NVMe, U.2 |
After reading this section, you will know that what is the difference between memory and storage. Go on and you can learn how to check memory and storage on your PC.
How to Check Your Computer’s Memory and Storage
Do you want to know how much memory and storage you have on your PC? This section offers a step-by-step guide on how to check them.
How to Check a Computer’s Memory?
If you want to check the memory (RAM) on your computer, follow these steps:
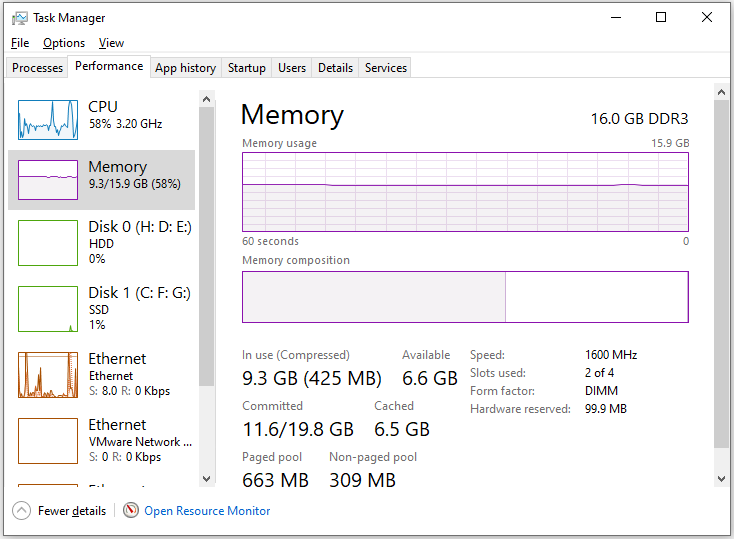
- Press Ctrl+ Shift + Esc at once to open the Task Manager window.
- Go to the Performance tab.
- Select Memory from the left pane.
- Then, in the right panel, you can see the total memory size, slots used, etc.
How to Check a Computer’s Storage?
To check the storage of your PC, you can do as follows:
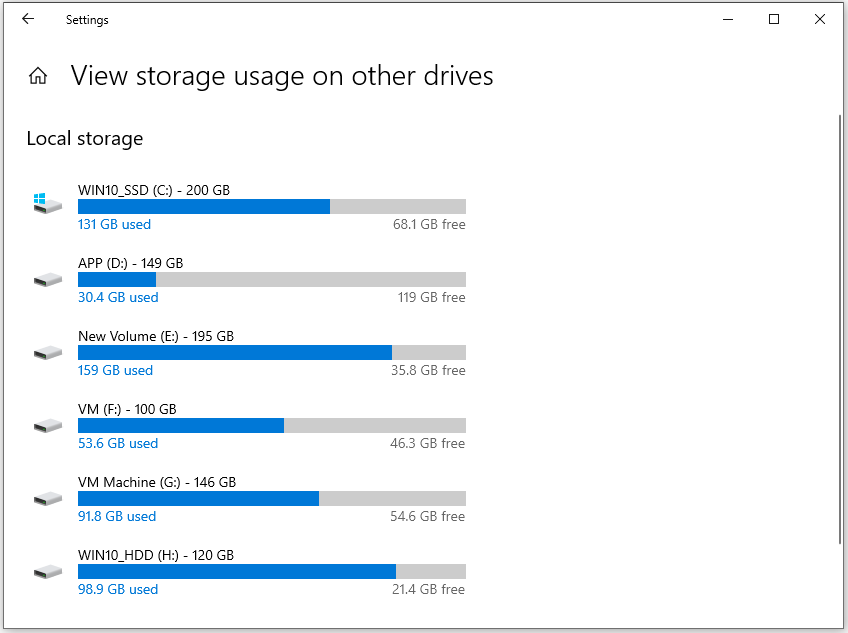
- Press Win + I to open the Settings window.
- Select System > Storage.
- Click View storage usage on other drives in the right panel.
- You can view all your local storage here, clearly displaying used and free space on each drive.
How Much Memory and Storage Do You Really Need?
The amount of memory and storage you need depends on your usage. Different uses of computers have different needs for memory and storage.
Memory (RAM)
- 4-8GB: Sufficient for basic tasks, such as web browsing, email, and document creation.
- 16GB: Ideal for moderate multitasking, light gaming, and entry-level photo or video editing.
- 32GB and above: Best for heavy multitasking, professional content creation (including video editing and 3D rendering), and high-end gaming.
Storage (SSD/Hard Drive)
- Light Users (Documents, Basic Photos/Music): 250-500GB is generally adequate.
- Moderate Users (High-Resolution Photos, Movies, Basic Games): While 250-500GB may suffice, 1TB is a safer choice.
- Heavy Users (Gaming, HD Movies, Content Creation): A minimum of 1TB is recommended.
How to Increase the Memory on PC?
To increase the memory on PC, you just need to physically install more RAM (like adding another RAM module or upgrading to larger RAM modules) or increase the virtual memory.
Way 1. Physically Installing More RAM
The most efficient way to increase your computer’s memory is to add more RAM or upgrade RAM sticks to bigger ones.
To do that, you need to buy a compatible RAM module first, turn off your PC, open the case, and install the RAM module into the available slots on the motherboard.
Here are the detailed steps:
Move 1. Prepare Compatible RAM
If your budget is tight and you only have one installed RAM module, you can keep the original RAM module and add another module to set up dual-channel operation and increase the memory. Here are some tips to consider when you prepare the RAM module:
- Use two modules with identical specifications for dual-channel operation.
- Ideally, buy two modules of the same generation, frequency, and brand.
Move 2. Gather Other Supplies
In addition to preparing a new compatible RAM module, you still need to prepare a Philips-head screwdriver and a static-discharge (ESD) wrist strap or a way to ground yourself.
Move 3. Install the New RAM
After preparing all the needed supplies, you can do the following steps to install the new RAM:
- Turn off your computer completely.
- Unplug the power cable.
- Hold the Power button for a few seconds to discharge the residual power.
- Open the computer case or laptop cover.
- Put on an ESD wrist strap or touch a grounded metal surface to prevent static electricity from damaging the components.
- Find the long RAM slots on the motherboard. To replace RAM, push the clips on the sides to release the old modules and lift them out.
- Align the notch on the new RAM module with the slot, then push down until the clips snap into place.
- Close the case, plug in the power cable, and turn on your PC to detect the new RAM.
Way 2. Increasing Virtual Memory (Paging File)
If you have a tight budget, you may not want to buy another RAM module. In this situation, you can choose to increase the paging file to increase the memory. Here’s the guide:
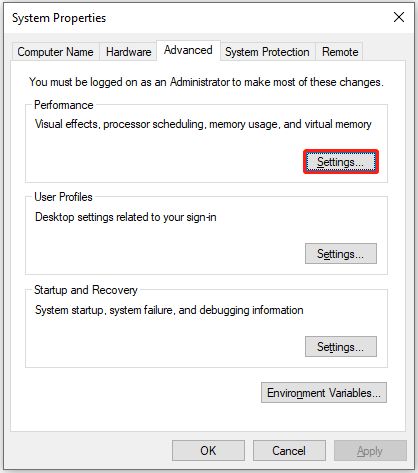
Step 1. Press Win + I to open the Settings window, choose System > About, and click Advanced system settings on the right side.
Step 2. In the pop-up System Properties window, click Settings under the Performance section.
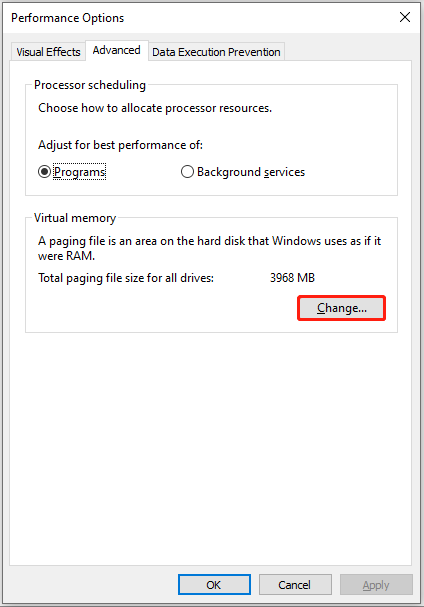
Step 3. In the Performance Options window, go to the Advanced tab, and then click the Change button under the Virtual memory section.
Step 4. In the Virtual Memory window, uncheck the box for Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.
Step 5. Select the drive where you want to change the paging file size, typically your C: drive. Select the Custom size radio button and enter your desired values for the Initial Size (MB) and Maximum Size (MB).
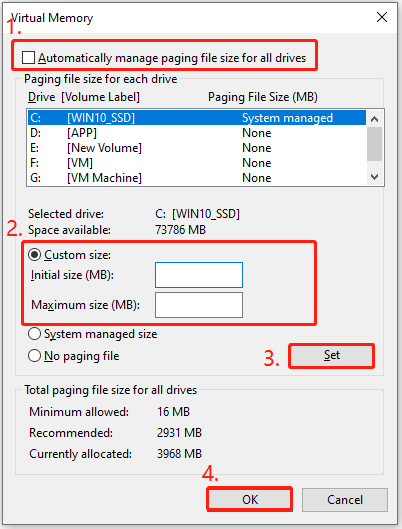
Step 6. Click the Set button, then click OK to close the Virtual Memory window. You will be prompted to restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
How to Increase the Storage on PC?
To increase the storage on a PC, you have three choices: removing unwanted files, extending the partition, and upgrading the storage to a bigger one. Want to know the detailed steps, continue reading.
Method 1. Freeing Up Space on Your Current Drive
The easiest way to increase the storage on the PC is just to remove unwanted/unnecessary files to free up more space. To do that, MiniTool Partition Wizard is a good choice.
It offers the Space Analyzer feature to help you scan and layout disk usage and help you make a clearer mind to decide which files to remove. Here’s how to use it:
Step 1. Download and install MiniTool Partition Wizard on your computer.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
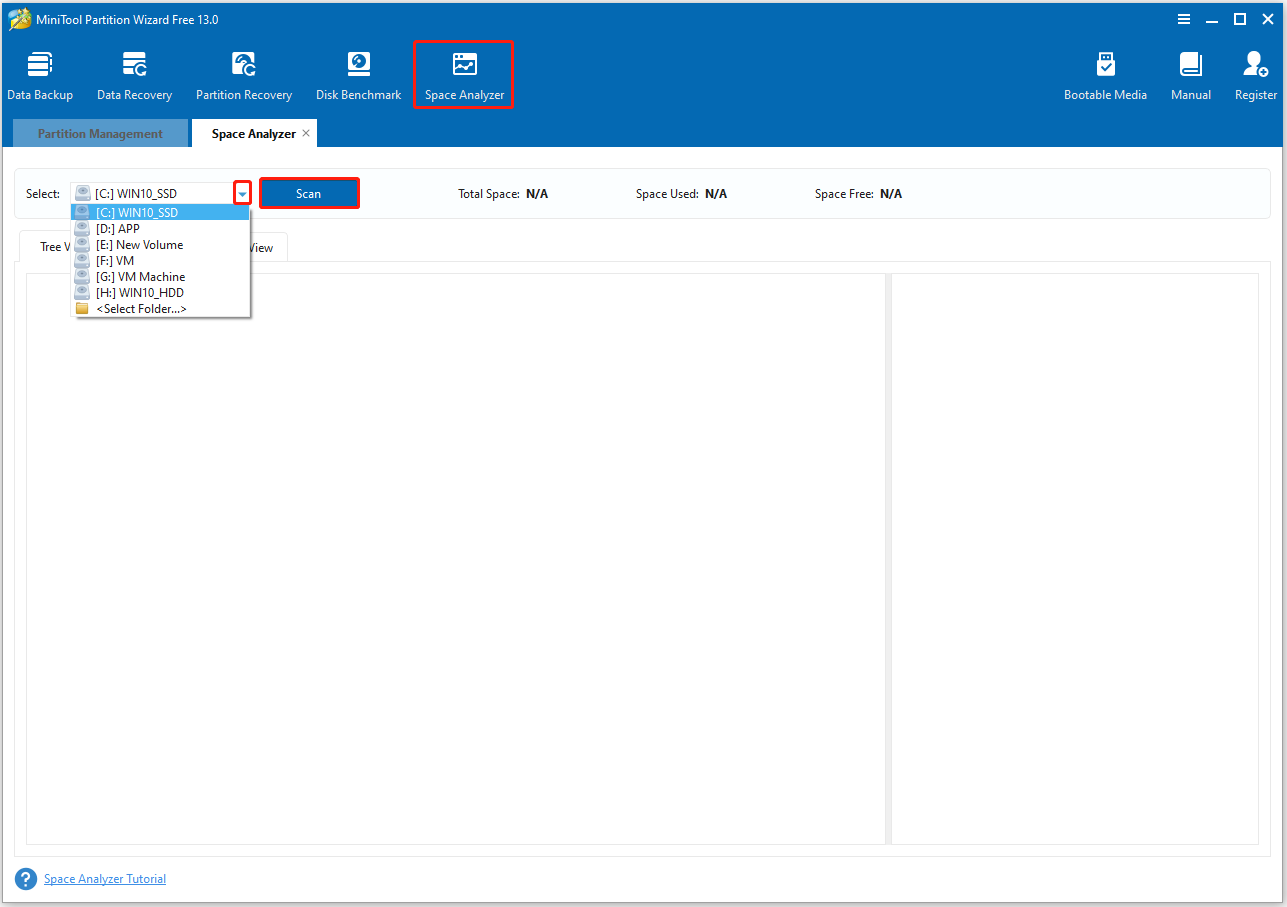
Step 2. Launch this software to enter its main interface and click Space Analyzer from the top toolbar.
Step 3. Click the Down arrow to select the drive that you want to check, and click Scan to start scanning the selected drive.
Step 4. Once the scanning process is complete, you can see all the files listed in the Tree View tab. Right-click the file/folder that you don’t want to keep and select Delete (Permanently).
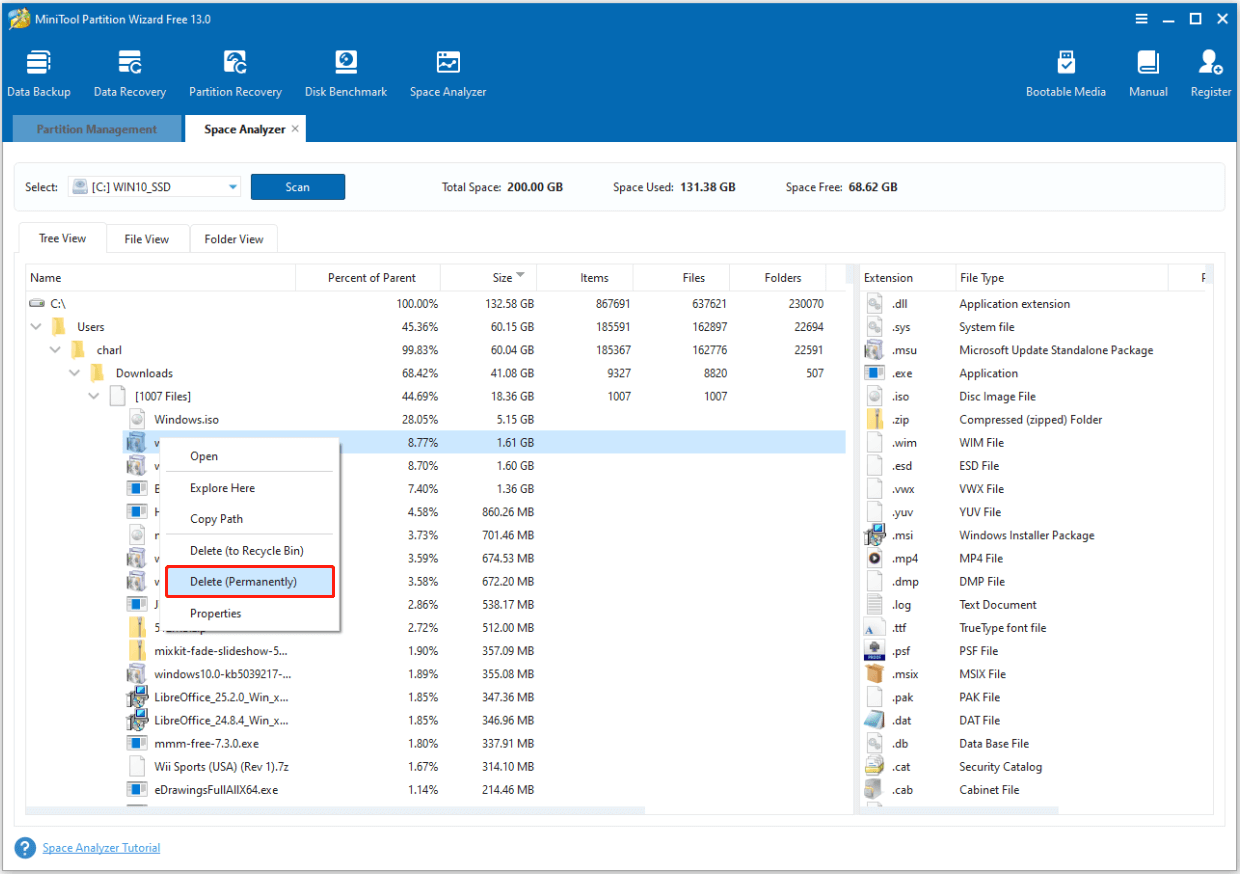
Step 5. Repeat the same steps to remove all the unwanted files. Once done, you can get more free space on the selected drive.
Method 2. Take Space from Other Partitions to Expand the Partition
In addition to removing unwanted files to increase the storage on the drive, you can also expand the drive size by taking free space from other drives. To do that, I recommend MiniTool Partition Wizard’s Extend Partition feature. Here’s the way:
Step 1. Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to enter its main interface.
Step 2. Choose the partition that you want to add more free space to from the disk map.
Step 3. Select the Expand Partition feature from the left panel.
Step 4. In the Extend Partition window, click the down arrow to select which partition to take free space from, and then drag the small blue block to decide how much free space you want to take. After that, click OK to go back to the main interface.
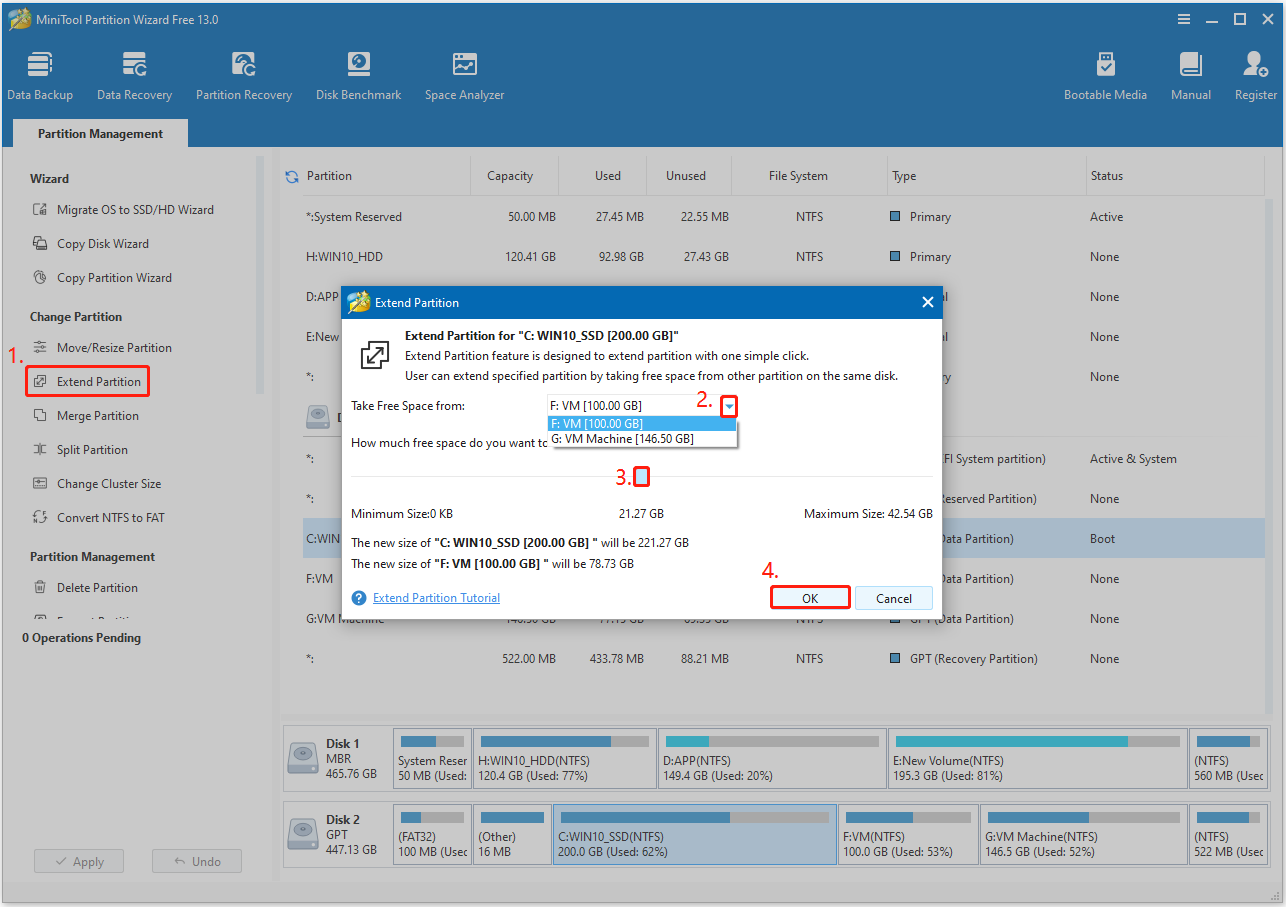
Step 5. Click the Apply button at the bottom left corner. Then, click Yes in the prompt window to execute the pending operation.
Step 6. Once done, click OK to confirm. Now, the partition that you selected may have more free space.
Method 3. Upgrade to a Larger Disk
If the above two methods can’t help you get enough free space you need, you can also choose to upgrade your internal storage to a larger disk.
If you don’t want to lose your data on the original disk or reinstall Windows, you can use MiniTool Partition Wizard’s Copy Disk feature. It can help you upgrade your storage device without reinstalling Windows.
Here’s how to use MiniTool Partition Wizard’s Copy Disk feature:
Step 1. Connect the new storage device to your computer.
Step 2. Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro Platinum or higher edition, click the Copy Disk Wizard feature from the left panel, and then click Next in the pop-up window to continue.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
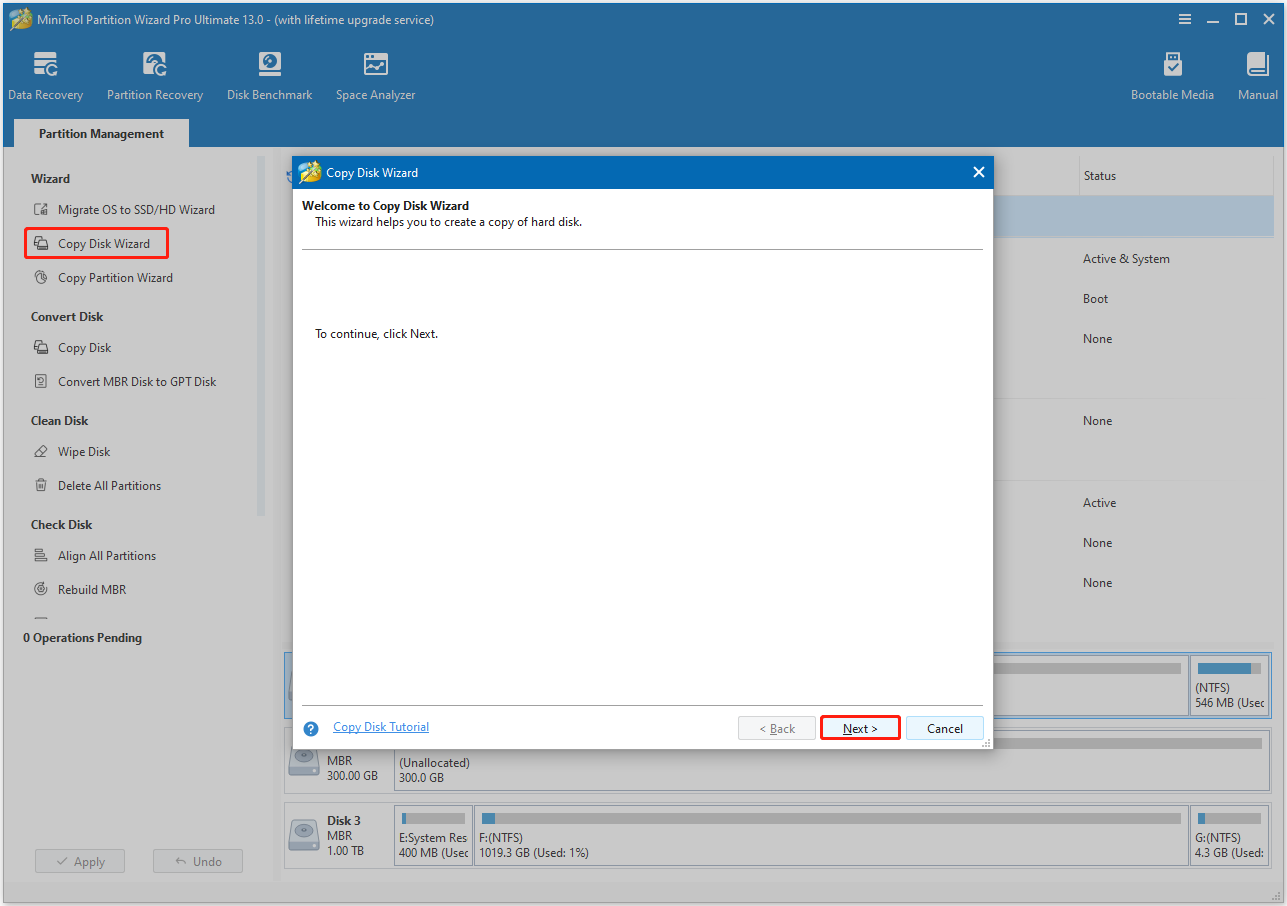
Step 3. Choose the original disk and click Next. Then, select the new disk and click Next.
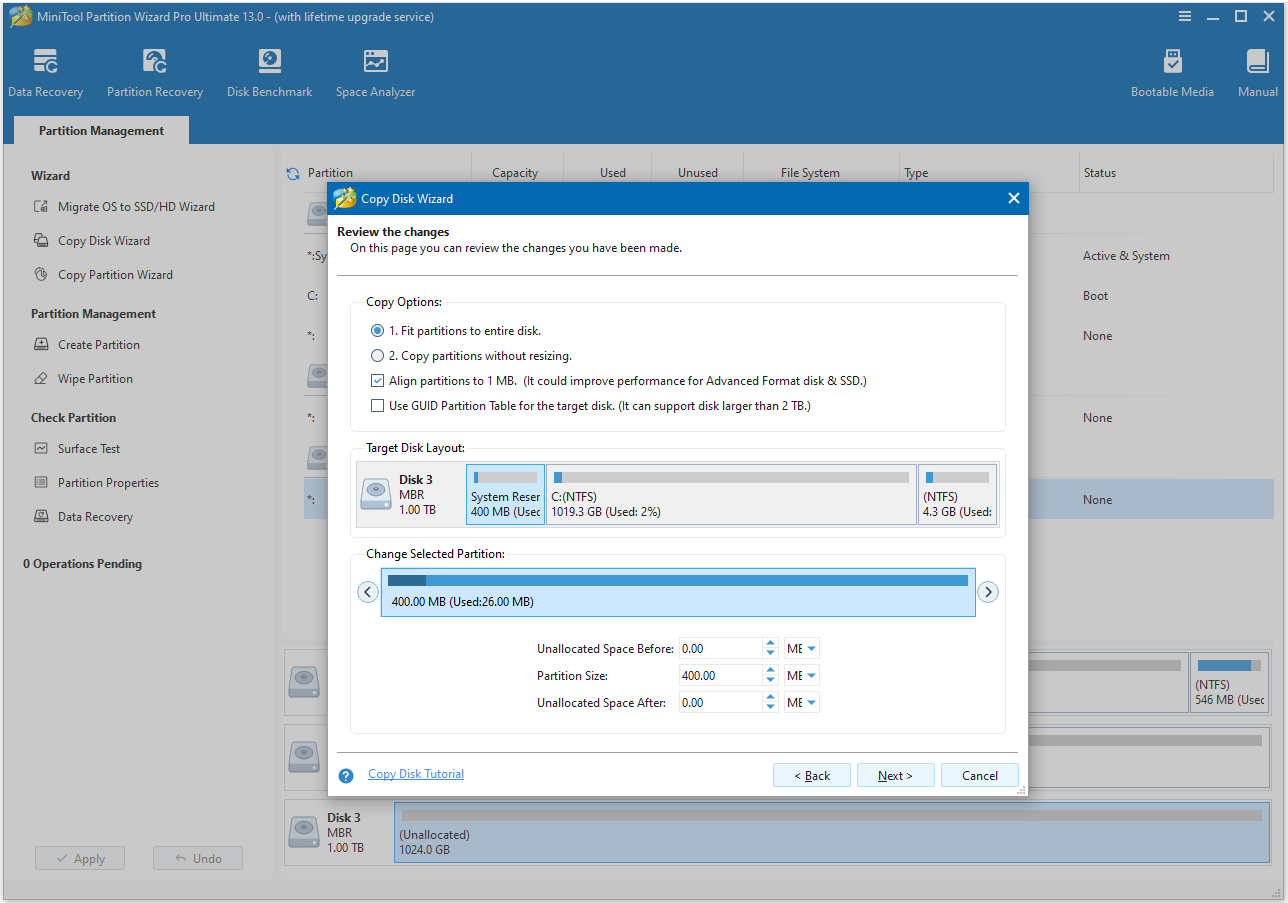
Step 4. You can review the target disk layout in the Review the changes window. Here, you need to set Copy Options and adjust Target Disk Layout according to your needs. After that, click Next to move on.
- Fit partitions to entire disk. If you choose this option, the software will resize the original partitions to fit the target disk. Each partition will be larger on the target disk if it is bigger. Or vice versa.
- Copy partitions without resizing. This option copies all partitions from the original disk to the target disk without resizing them. It will leave the target disk with unallocated space as a result if it is larger than the original.
- Align partitions to 1MB. This option is selected by default. It can improve performance for Advanced Format disk & SSD.
- Use GUID Partition Table for the target disk. If the target disk is larger than 2TB, you’d better select this option.
Step 5. Read the Please Note in the next screen and click Finish.
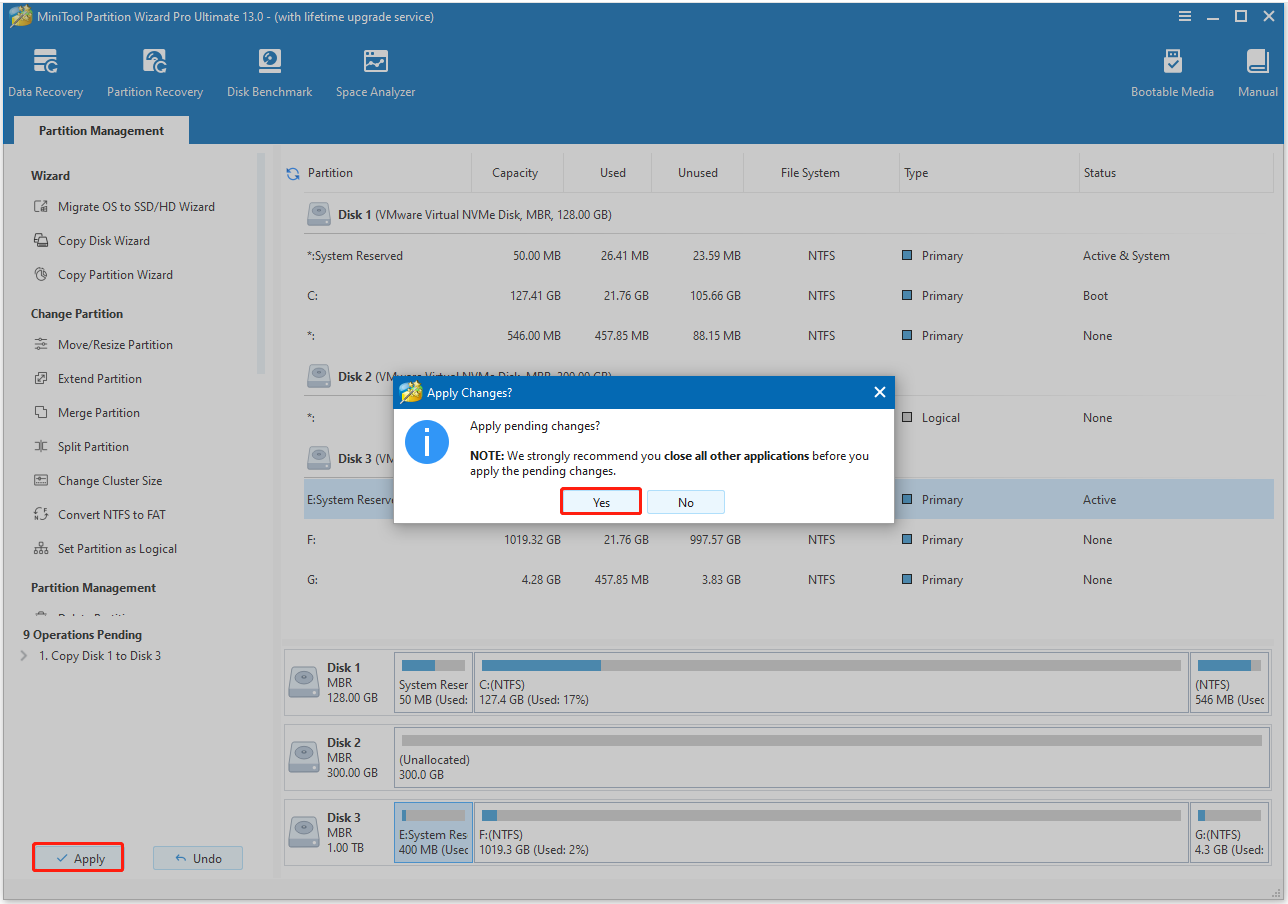
Step 6. In the main interface, click Apply at the bottom left corner. Then, click Yes in the prompt window to continue.
Step 7. Once finished, a notice window pops up. Click OK to confirm.
Now, you can replace the original disk with the new and bigger one to increase the storage on your PC.
In Conclusion
Memory and storage are essential parts of a computer and can store files on your PC. This post provides a detailed comparison of computer memory vs storage. Besides, it includes a comprehensive guide to help you upgrade RAM and storage.
What’s more, if you encounter issues or have any suggestions while you are using MiniTool Partition Wizard on your PC, you can send an email to us via [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.
Memory vs Storage FAQ
This combination makes the device powerful and versatile, suitable for gaming, creative work, and everyday tasks.

User Comments :