What Is a Thumb Drive?
A thumb drive, or USB flash drive, is a portable storage device that connects to a computer’s USB port for saving and transferring files. It uses flash memory, which is durable and compact, allowing for significant data storage.
Thumb drives are convenient for moving large files, serving as backup devices, or running software directly from the drive. Here are the main characteristics:
- Portability: The thumb drive is small and lightweight. Also, it is easy to carry in a pocket or on a keychain.
- Integrated USB Interface: Thumb drive connects directly to a device’s USB-A or USB-C port without a cable, using an integrated USB interface.
- Flash Memory: Thumb drives use non-volatile flash memory, meaning the data remains stored even when the power is off. Also, it can be both rewritten and erased multiple times.
- Durability: Without mechanical components, thumb drives are more durable than traditional hard drives and are less likely to be damaged by movement.
- Compatibility: They are compatible with most devices, including PCs, Macs, and some smartphones.
- Power: They do not need an external power source and draw power directly from the device they are plugged into.
Common Thumb Drive Sizes
The thumb drives come in a wide range of sizes, from less than 1GB to over 1TB. The common thumb drive sizes include 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64GB, 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, and 1TB or more. Here’s a table of USB thumb drive sizes whose value comes from Kingston:
| Thumb Drive Sizes | Photos(12MP) | Songs (3MB) | Videos (1080P minutes) |
| 8GB | 6,696 | 2,604 | 42 |
| 16GB | 13,393 | 5,208 | 84 |
| 32GB | 26,786 | 10,417 | 168 |
| 64GB | 53,571 | 20,833 | 336 |
| 128GB | 107,143 | 41,667 | 672 |
| 256GB | 214,286 | 83,333 | 1,344 |
| 512GB | 428,571 | 166,667 | 2688 |
| 1TB | 857,143 | 333,333 | 5,376 |
Use of Different Flash Drive Sizes
Here’s the use and prices of these different flash drive sizes:
4GB – 8GB (Obsolete / Utility-only): Not Recommended
- Use for: BIOS/UEFI updates, tiny boot tools, text-only projects
- Cost: under $5
- Limitations: Can’t hold modern OS images (too small for full ISOs)
16GB – 32GB (Basic Everyday Use): They have limited space for media or backups. Also, their speed varies.
- Use for: Documents, photos, music, basic Linux distros (e.g., Ubuntu), Windows Media Creation Tool, lightweight encrypted personal storage (e.g., ID docs)
- Cost: $5–$10 (USB 3.0 models)
64GB – 128GB (Sweet Spot for Most Users): It is encryption-friendly and has enough room for full containers with space to spare.
- Use for:
- Portable OS (Linux Mint, Tails, Windows To Go)
- Encrypted volumes (BitLocker, VeraCrypt)
- Backup important folders (Docs, Photos)
- Cost: $10–$25 (USB 3.1)
256GB – 512GB (Power Users): It can hold a full encrypted volume + recovery partition.
- Use for:
- Bootable OS + workspace (portable dev or forensic environments)
- Large file transfers (video, RAW images, CAD)
- Full device backup
- Cost: $30–$70 (good brands with high-speed USB 3.2)
1TB – 2TB (Enterprise / Creative / Archival): It is best for secure, encrypted backups (BitLocker, VeraCrypt full-volume).
- Use for:
- Carry full operating systems (Windows, Linux distros, virtual machines)
- Data science datasets, legal archives, forensic images
- 4K/8K video editing on the go
- Cost: $70–$250+
Is It Better to Choose a Bigger Thumb Drive
Is bigger always better? Not necessarily. Larger capacity flash drives and storage solutions tend to cost more, so it’s best to avoid overspending on unused space. For promotional items or transferring a few files, smaller drives are cost-effective.
In short, choose your flash drive size based on your storage needs. 8GB to 32GB is ideal for simple files, 32GB to 64GB for photos, music, or videos, and 128GB or more for larger media libraries.
What Factors to Consider When You Choose a Thumb Drive
What should you consider when you buy a thumb drive? You need to prioritize USB thumb drive sizes to store your files, speed for faster transfers, compatibility with your devices, the thumb drive’s durability, security features, and the warranty.
Storage Needs
When you pick up a thumb drive, you need to consider the types of files that you’ll be saving and estimate how much total data you plan to store. Normally, documents take up less space than high-resolution photos, which are smaller than video files.
So, if you just need to store or transfer documents, you can choose a thumb drive with a small capacity. On the contrary, if you want to store large files like high-resolution photos, 4K videos, etc., a large-capacity thumb drive is necessary. For example:
- For document storing, a 16GB drive is enough.
- For large video files, you can choose a 128GB or larger thumb drive.
- For bootable operating systems, a 16GB or 32GB drive is often sufficient.
False Capacity
If you’ve used a thumb drive before, you may have noticed that its practical capacity is smaller than its labeled capacity.
This is because some space is reserved for the drive’s formatting and other internal functions. So, you need to search for the practical capacity of a thumb drive when you choose it.
What’s more, some sellers use technical manipulation to make a thumb drive report a higher capacity than it physically has. If you buy a fake thumb drive like this, you may encounter data loss or corruption when you attempt to write data beyond the actual storage.
To avoid it, you can identify these drives by comparing their listed capacity to their price, as legitimate high-capacity drives are not inexpensive.
Speed
If you pay more attention to the flash drive’s speed, you can follow these tips when you choose a thumb drive:
- Look for USB 3.0 or newer for faster data transfer rates, especially if you’ll be moving large files.
- Check both read and write speeds, as a higher speed results in better overall performance.
Compatibility
When you choose a thumb drive, you also need to consider the compatibility of the connector type. Normally, you may encounter two connector types:
- USB-A is common on older devices
- USB-C is standard on modern laptops, tablets, and phones
If you need to connect to both USB-A and USB-C ports, you’d better choose a dual-port thumb drive.
Durability
If you often use the thumb drive or with rough handling, you’d better choose a flash drive with protective features like metal casings, rubberized exteriors, or shockproof and water-resistant designs.
Security
If you plan to store some sensitive data on the thumb drive, you’d better consider a drive with built-in hardware encryption or password protection.
Price
The price of a thumb drive varies based on capacity, speed, and brand. Here’s some things you should notice:
- Avoid too-cheap drives
- Pay more in these aspects: hardware encryption, high-speed interfaces, rugged design
- Compare $/GB but also factor in speed and warranty
Warranty
In addition to considering the above factors, you also need to check the warranty of the thumb drive. It can range from one year to a lifetime warranty, depending on the manufacturer and model.
If you want to get more protection for your data, you’d better choose a thumb drive with a long-time warranty.
How to Reformat Thumb Drives
For some reasons, like erase all data, fix file system errors or corruption, ensure compatibility between different operating systems, or prepare them for a new purpose, you may need to reformat thumb drives.
So, how to complete that? To do that, I highly recommend MiniTool Partition Wizard. It is a powerful partition disk manager that offers the Format Partition feature to help you reformat your thumb drive with ease.
Furthermore, this software surpasses Diskpart and Disk Management by allowing you to easily format a drive larger than 32GB to the FAT32 file system. Here’s how to use this feature:
Step 1. Download and install MiniTool Partition Wizard on your computer. Then, launch it to enter the main interface.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2. Choose your thumb drive’s partition from the disk map and select Format Partition from the left pane.
Step 3. In the prompt Format Partition window, set Partition Label, File System, and Cluster Size. Then, click OK to go back to the main interface.
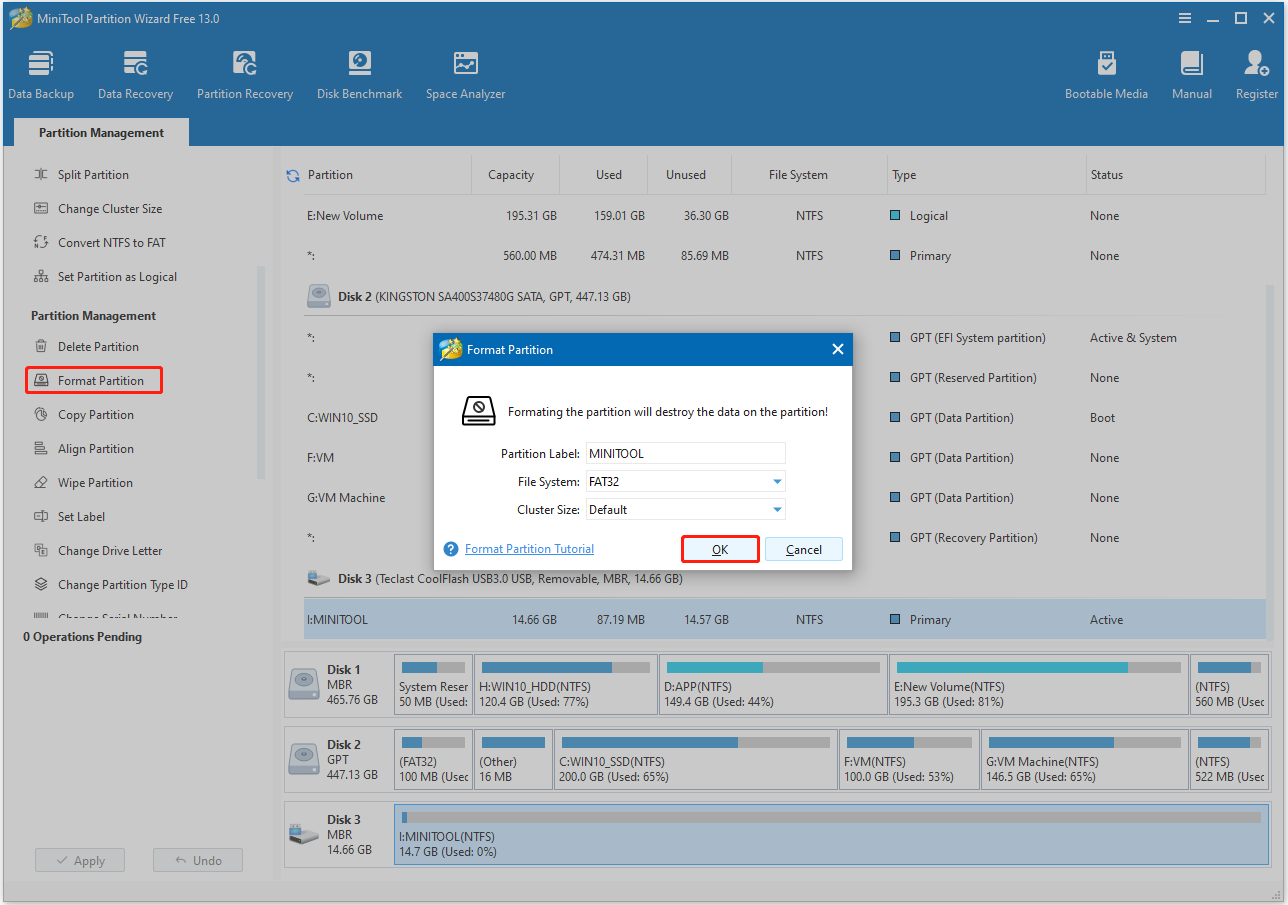
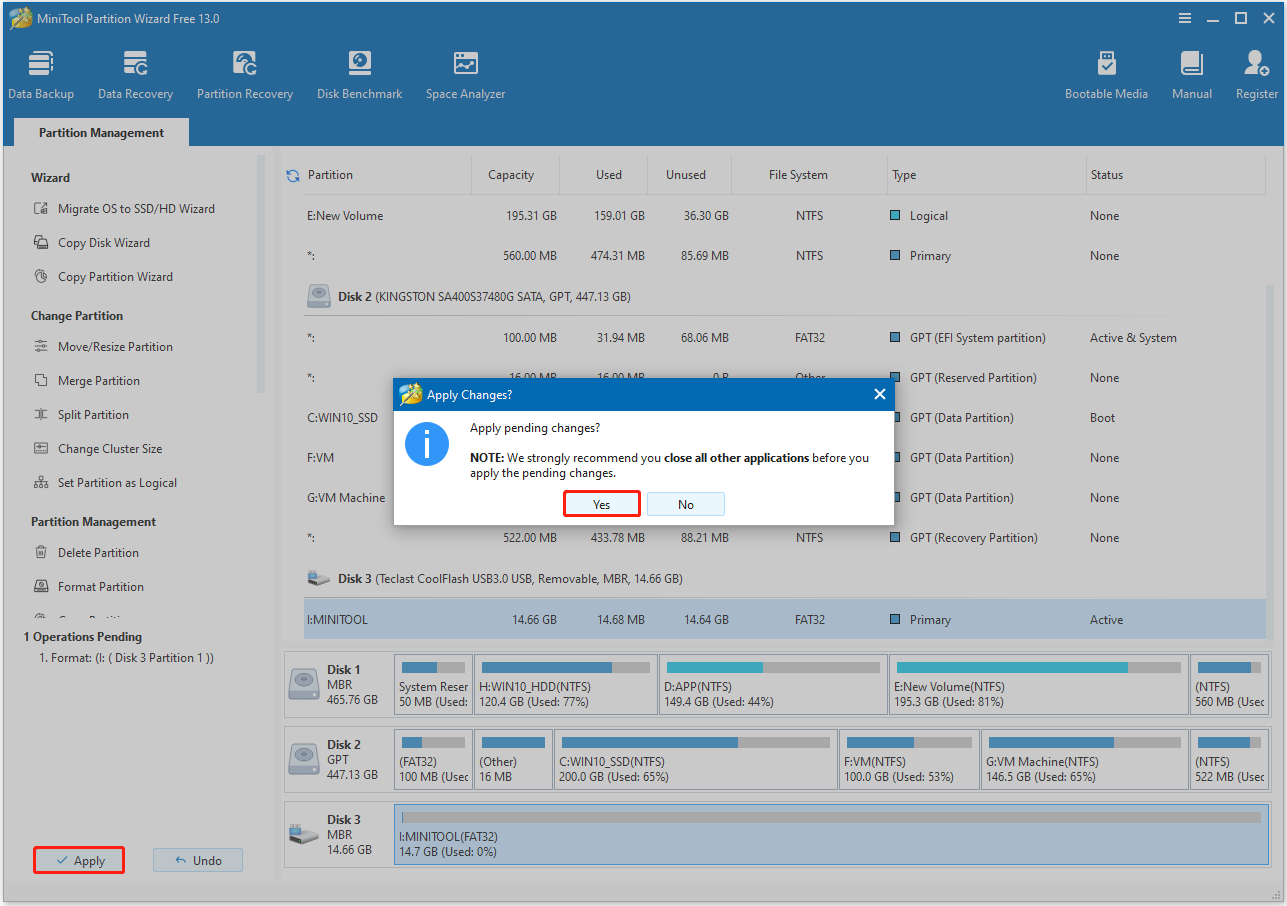
Step 4. Click Apply and Yes sequentially to execute the pending operation.
How to Recover Data from a Thumb Drive
If you want to recover data from a thumb drive, MiniTool Partition Wizard is a good choice. It offers the Data Recovery feature to help you recover data from various storage devices, including thumb drives, HDDs, SSDs, SD cards, etc.
Here’s how to do that:
Step 1. Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro Platinum on your computer.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
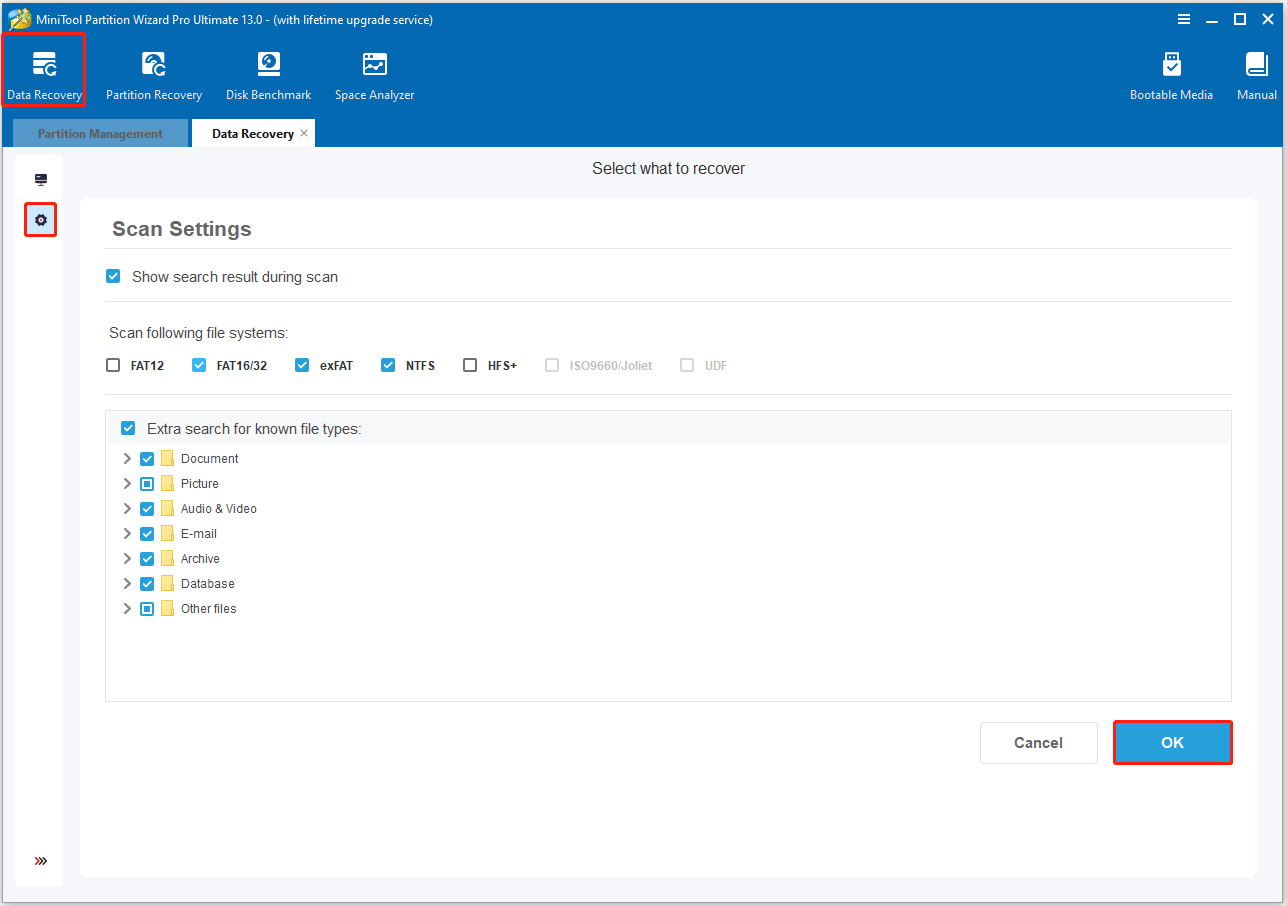
Step 2. Choose Data Recovery from the top toolbar, and click the gear icon in the left corner to enter the Scan Settings page. Then, check the file system and file types you want to scan here and click OK to move on.
Step 3. Move your cursor to the thumb drive, and click Scan. Then, this software will start to scan.
Step 4. During the scanning process, you can click the Pause or Stop button to end the scanning when you find the files you want to recover.
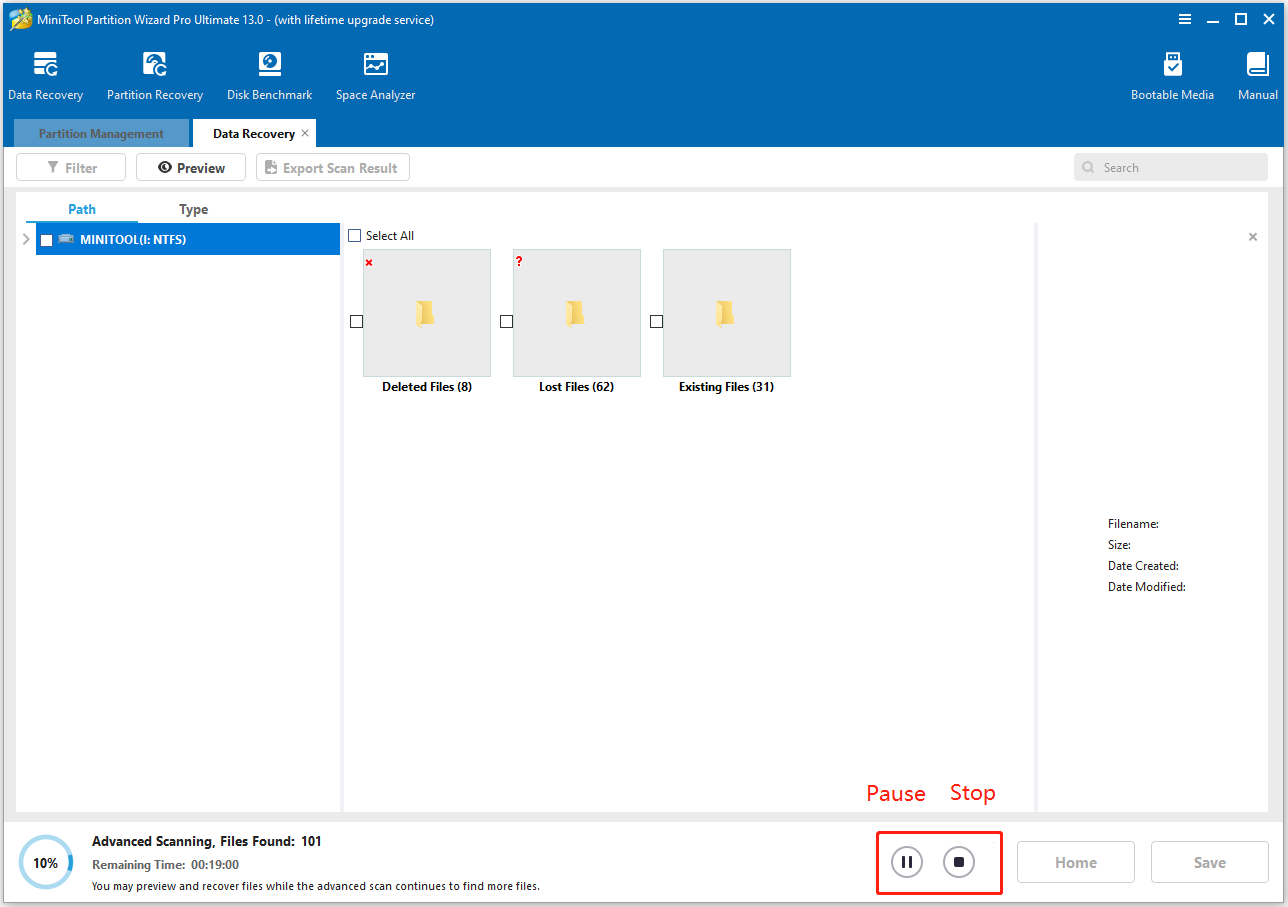
Step 5. Once done, check the files that you want to recover and click Save. Then, in the pop-up window, choose a safe location and click OK to confirm.
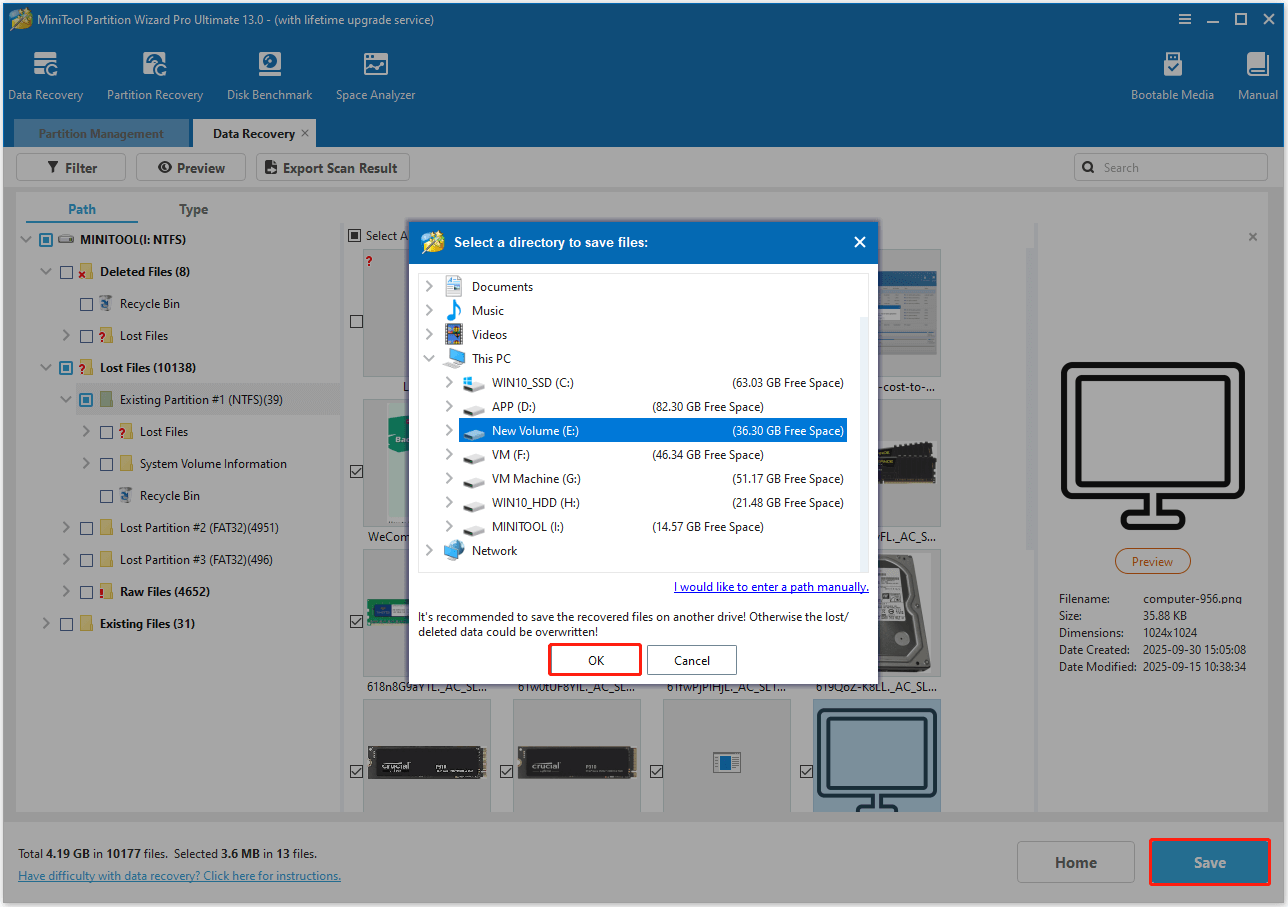
You have recovered the lost files from a thumb drive successfully.
Tips for Protecting a Thumb Drive
Thumb drives can last 10,000 to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on usage. Proper care is vital to extend their lifespan and avoid expensive file recovery. Here are some useful tips for protecting a thumb drive and avoiding data recovery:
- Avoid plugging into public computers: Avoid connecting your USB drive to public computers, as they might have malware that can infect your drive.
- Write-Protection Switch: Some USB drives have a physical write-protection switch. If your drive has one, slide it to the “Lock” position to prevent malware from writing to or modifying your drive.
- Label the Drive: Consider laser-etching or labeling the drive with your contact information; this makes it easier for someone to return it if found.
- Keep Backups: A lost or damaged drive shouldn’t result in lost data. Always maintain at least one encrypted backup stored in a separate location.
- Store Securely and Avoid Physical Damage: Designate a specific, secure place for your USB drive at home or work to prevent misplacing it. Keep the drive in its case or a protective cover when not in use to protect it from physical damage.
- Software Encryption: Use a software-based encryption tool like BitLocker (on Windows) or Disk Utility (on Mac) to secure your thumb drive data.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure your computer and antivirus software are up to date to provide the best protection against new threats.
- Run Antivirus Scans: Always scan the drive with updated antivirus software before opening files to prevent malware infection.
In Conclusion
Thumb drives are available in various storage sizes. You should now understand what a thumb drive is and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Additionally, this guide includes detailed instructions on how to reformat a thumb drive and recover data from it.
If you encounter any issues or have suggestions while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please feel free to contact us at [email protected]. We will respond to your email as soon as possible.

User Comments :