RAID 5 vs RAID 6: which one is better? Before answering this question, you should have a basic understanding of the 2 RAIDs and compare RAID 5 vs RAID 6 performance, application, and pros & cons, etc. Today, MiniTool will focus on RAID 5 vs RAID 6 to help you make a correct decision.
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) is a data storage virtualization technology, which can combine multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. These units can help you make data redundancy and performance improvement realistic.
There are several commonly used RAID levels such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10. Hence, many users are confused about them and don’t know how to choose a suitable one. For instance, they compare RAID 5 and RIAD 10, RAID 5 and RAID 6 and others to find a proper array to their storage.
The focus in this post is RAID 5 vs RAID 6. In order to conclude the difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6, you should have a comprehensive understanding of the 2 RAID levels. Now, we introduce them briefly.
An Introduction to RAID 5
What is RAID 5? RAID 5 consists of block-level striping with distributed parity. The parity information on RAID 5 is distributed among the drives, which is different from RAID 4. In this case, if one drive fails to work, subsequent reads will be calculated from the distributed parity. So, no data will lose.
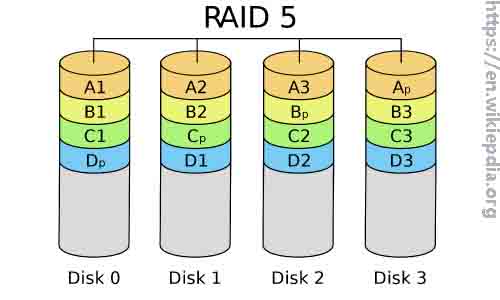
What the large RAID 5 implementation similar to all sing-parity concepts is that it is vulnerable to system failures. Besides, rebuilding an array demands from all disks, which can cause a second drive failure or the entire array loss.
Pros
The RAID 5 boasts some advantages that are summarized as follows.
- It has a high read speed.
- It offers data redundancy.
- This configuration is stable and reliable.
- It can rebuild a failed drive in a short time.
- It can make use of the available space efficiently.
- With RIAD 5, drives are able to be hot-swapped preventing downtime.
Cons
However, it also has some disadvantages. They are listed in the below.
- It cannot handle two simultaneous hard disk drive fail
- Due to parity, the writing speed is relatively slow compared with other configurations.
- The data restoration on RAID 5 can take you a long time.
- It is a little complicated to execute.
What is RAID 5? Read here, you may find the answer.
An Introduction to RAID 6
What is RAID 6? RAID 6 is made of block-level striping with double distributed parity. The double parity makes RAID 6 fault-tolerant. In addition, this feature makes larger RAID groups especially for high-availability systems possible.
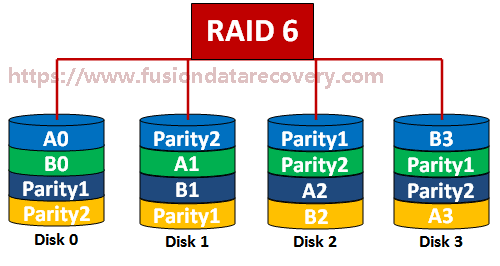
You are required to get at least 4 disks to make the RAID 6. For a RAID 5, the performance will be affected when a single hard drive failure occurs unless the fault hard drive is taken place of. The case is different on RAID 6. As you use drives from multiple sources and manufacturers with a can be handled. In a word, you can minimize problems by using RAID 6.
Pros
What pros does the RAID 6 have? You can check them in the below.
- It has a high redundancy and fault tolerance.
- It allows you carry out operations at a reasonable fast speed.
- It has an excellent data accessibility.
- It is rather safe.
- It can handle two disk failures.
Cons
What about the cons of RAID 6? It has the following drawbacks.
- The write speed is slow because of double parity.
- It is complex to implement.
- The restoring process is long.
- You will suffer from a data loss when three or more disk failures happen.
The Difference Between RAID 5 and RAID 6
The above information shows you what RAID 5 and RAID 6 are. And you may have a basic understanding of the 2 RAID levels. Now, let’s explore the difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6.
Well, the differences will be explained in the aspects of fault tolerance, performance (including write and read performance), capacity utilization, application, and hardware or software RAID.
Similar post: RAID 0 VS RAID 1: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is vital for the sake of data security. If one RAID is fault-tolerant, you don’t have to worry about data loss when the hard drive failure occurs. If it isn’t, you’d better make a backup for your Windows in case of system failure. The RAID 5 can support one-drive failure, which indicates that the RAID 5 can still run when one hard drive is failing.
However, if there are two or more disk fail to work, you will experience data loss. The RAID 6 can support up to 2 hard drive failure. Therefore, RAID 6 has better fault tolerance than RAID 5.
RAID 6 vs RAID 5: which one wins? In terms of fault tolerance, RAID 6 wins.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Performance
The performance of a hard drive is important and there is no exception for RAIDs too. How about the performance of RAID 5 and RAID 6? When talking about the performance of hard disk, it is mainly divided into 2 aspects (write performance and read performance).
Actually, the read performance of a RAID 5 is very close to that of RAID 6. But the write performance of RAID 6 is a little slower compared with RAID 5 because of the additional parity information that needs to be calculated.
To be specific, if you implement with the same number and types of disks, the RAID 6 probably slower than a RAID 5 array. If you want to know the exact performance of RAID 5 or RAID 6, you can test it under the professional benchmark testing tool – MiniTool Partition Wizard.
This program can help you manage the disk efficiently such as convert MBR to GPT, copy disk, move/resize partition, recover missing data, etc. Don’t hesitate to download it!
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here is the tutorial for benchmarking drives.
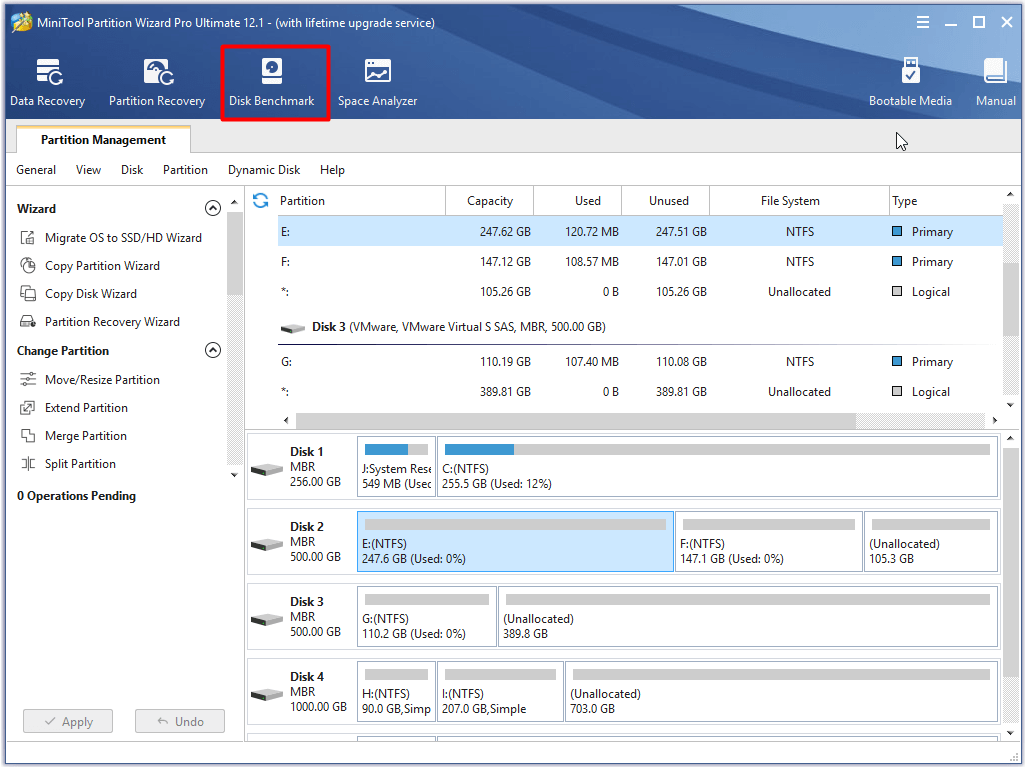
Step 1: Launch the software to enter its main interface and then click Disk Benchmark to go on.
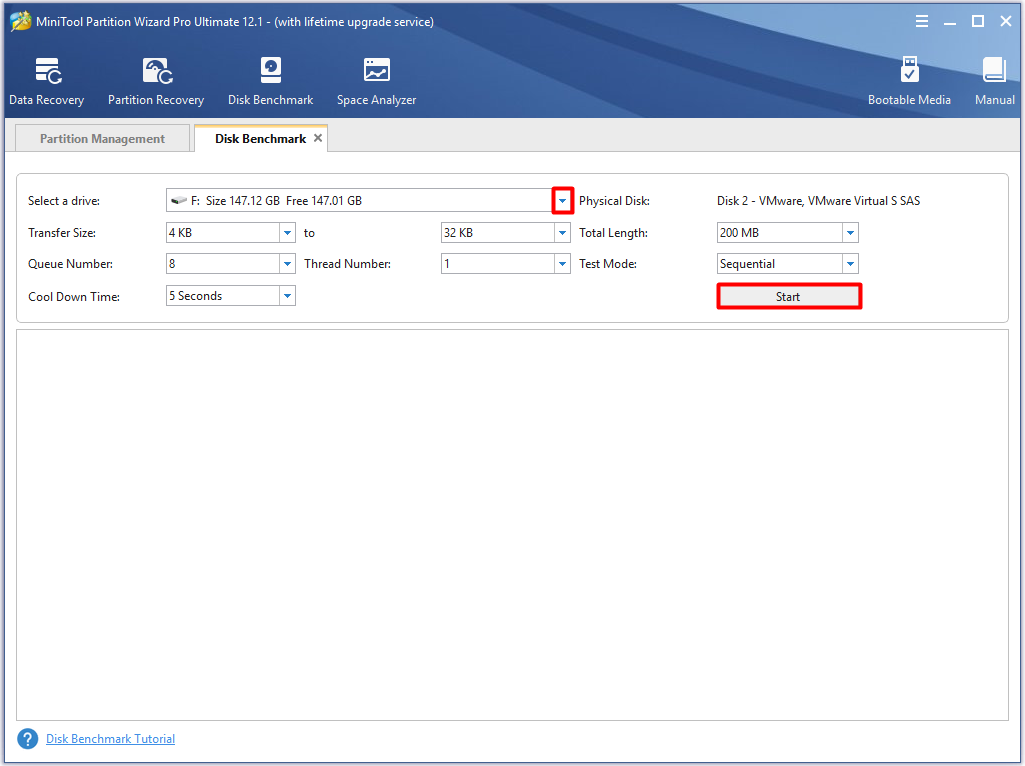
Step 2: Click the symbol marked in the following picture to choose the target drive, and then click Start to begin the process.
Step 3: After a while, you will get the result.
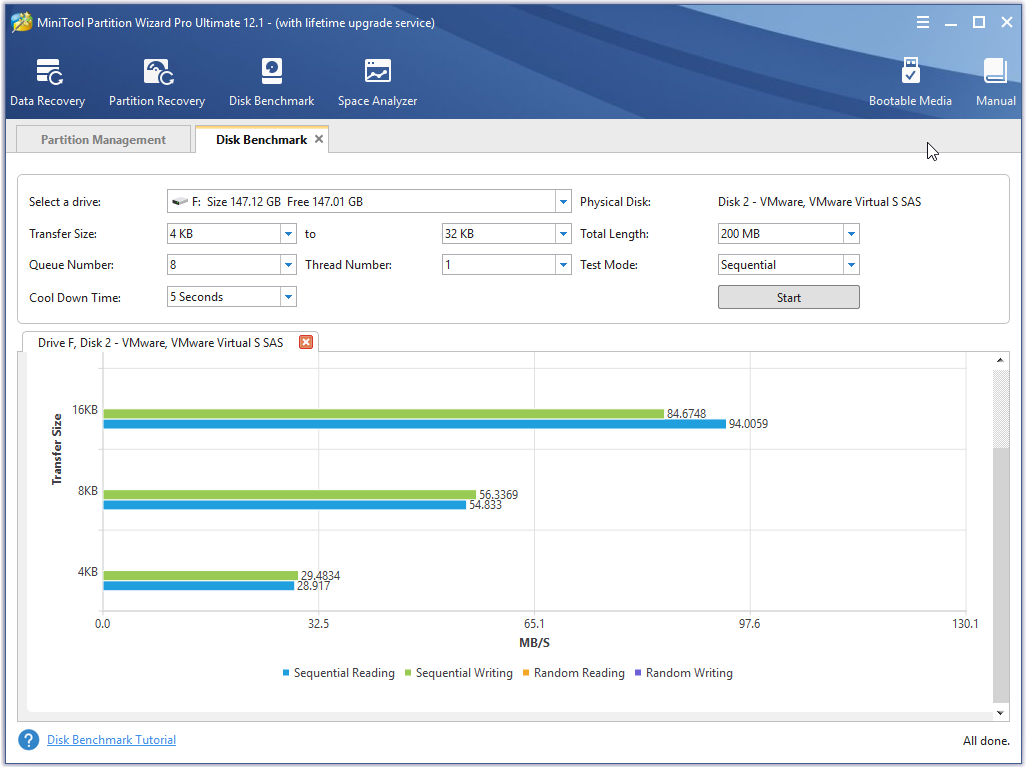
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Capacity Utilization
If one drive has better capacity utilization, it can help you store more data. Therefore, this is also an important factor when choosing a drive. Which one is a better capacity utilization? RAID 5 or RAID 6?
According to investigation, the capacity utilization of RAID 5 ranges from 67% to 94%, while the RAID 6 ranges from 50% to 88%. It is obvious that RAID 5 has a better capacity. RAID 5 vs 6: which one is better? On capacity use rate, RAID 5 wins.
To get more space, you can expand RAID5 partition. Read this post for details: Look Here! The Best Way to Partition RAID 5 without Losing Data
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Application
The difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 also manifests on application. According to their characteristics, they have different applications in life. For example, RAID 5 is mainly applied on data warehousing, web serving, as well as archiving,
As for RAID 6, it is primarily used to data archive, back up to disk, offer high availability solutions, and servers with large capacity requirements. You can see that RAID 6 has a wider application. So, RAID 5 or RAID 6? You can make the decision based on your demand.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Software or Hardware RAID
The software/hardware RAID configuration is one aspect of RAID 5 vs RAID 6. Generally speaking, a software RAID doesn’t require a RAID hardware but a hardware RAID does. When comes to RAID 6 vs RAID 5, you can configure either software or hardware RAID for RAID 5 array. But for RAID 6 array creation, you are required to get a hardware RAID.
Conclusion
RAID 5 vs RAID 6, which one is better? You may have answers in your mind now. You can make your own decision based on the understanding of RAID 5 & RAID 6 and the factors talked about in this post.
If you have any new ideas on RAID 5 vs RAID 6, please leave your words in the below comment area. When encountering any issues when using MiniTool software, just directly send us an email via [email protected].

User Comments :