If you want to run two operating systems on one PC, you can use the dual-boot or the virtual machine method. But some people may want to know the difference between dual boot and virtual machine so that they can decide which one to use. This post from MiniTool Partition Wizard talks about dual boot vs virtual machine.
Dual Boot vs Virtual Machine: Introduction
Before talking about VM vs dual boot, I should introduce them first.
What Is Dual Booting?
As we all know, the operating system is installed on the C drive of the PC. In general, one PC has only one OS. However, through the dual-boot method, you can install two operating systems on the PC.
1. How does dual boot work?
When dual systems are installed, the two systems are installed in different partitions, and the system installed later will not overwrite the previous system. Each individual system has its own partition format, which will not cause conflicts.
For example, if you dual boot Windows 10 and Ubuntu, you should first install an OS (Windows 10 in most cases), make/leave space for another OS (it could be unallocated space or an empty partition), and then install the second OS. In this case, the Windows partitions use NTFS while the Ubuntu partitions use EXT4.
After the dual systems are installed, there is a multi-boot selection menu when booting, and you can choose which operating system to enter. Please note that you can’t run the two systems at the same time. In addition, if you want to switch to another system, you should restart the PC and select OS again.
2. Are there popular dual boot partition schemes?
In general, when you install an OS, it will require at least 2 partitions. One partition is the active system partition, which is very small (around 500MB) and stores data used for loading the OS. Another partition is the boot partition, which stores all data used for running the OS. This partition is large and some people may also use it to store personal apps and files.
In Windows, the active system partition is usually called System Reserved or EFI partition. The boot partition is the C drive. In Linux, the active system partition is usually mounted under the /boot directory and the boot partition is usually mounted under the root directory (/).
If there is only one hard drive on the PC and you want to make a dual boot, you should make at least 3 partitions on the hard drive. The first partition is used as the shared system partition for the 2 operating systems, the second partition is used to store the 1st system, and the third partition is used to store the 2nd system.
However, if your PC has 2 disks, you can adopt a different dual-boot scheme. You should install an OS on a disk and then install the second OS on another disk. In addition, you can also create a system partition for each of the operating systems. In this case, if you want to switch to another OS, you should change the BIOS.
The two schemes have their advantages. For example, the first scheme makes the OS switch easy, while the second scheme provides stability. In the first scheme, if some errors happen to the system partition, the 2 systems will fail to boot. But the second scheme can avoid this case.
3. Is dual booting safe?
When you do dual booting, it means that you will install a second OS on the hard drive. this process will write data on the hard drive and the system partition. If your operation is improper, the existing system may become unbootable.
In addition, both of the two systems are the real OS. It means that what you do in them will affect the whole PC. Therefore, if you get virus in one system, the whole PC may be infected with the virus.
What Is a Virtual Machine?
A virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization/emulation of a computer system. Most people will use VM software to create and manage multiple VMs on their local PCs.
How do virtual machines work? When you create VMs, you should install the VM software first. And then, you can use the VM software to create VMs. The VM you created will be stored as files. You don’t need to create a new partition for the VM.
You install operating systems on the VMs and run these systems via the VM software. In general, the VM software allows you to run multiple systems at the same time. And the OS switch is very easy.
How to create a virtual machine? To create a virtual machine, you should use VM software. Please choose the best VM software and then you can refer to its tutorial to create VMs.
Dual Boot vs Virtual Machine: Conclusion
Should you choose dual boot or virtual machine? In this part, I will compare dual boot and virtual machine and make a conclusion. You can choose between them according to your condition.
PC Performance
In dual booting, the system is running on the real PC, and only one system is running at a time, so the speed of the system is fast. However, if you use the virtual machine, your PC will run the host OS, the VM software, and the guest OS at the same time. Therefore, the PC performance is affected greatly.
When you choose between dual boot and virtual machine, you should consider the following questions:
- Do you have a powerful computer? If your PC doesn’t have an excellent CPU, enough RAM space, or a fast SSD, I don’t recommend you choose the virtual machine. Otherwise, the low running speed will make you mad.
- Do you want to run resource-intensive programs on the second OS? If so, I recommend you use dual boot because virtual machines can’t smoothly run resource-intensive tasks like gaming, 3D animation, video editing, etc., even with a powerful computer.
Security
In terms of VM vs dual boot security, virtual machine is better. The reasons are as follows:
- If you operate improperly, your computer may don’t boot after making the dual boot. However, the virtual machine is just a program and the VM setup won’t make the PC unbootable.
- As mentioned before, in dual boot, if you get virus in one system, the whole PC may be infected with the virus. But VM will avoid this case because it is sandboxed. The virtualized operating system runs in a completely isolated environment and therefore what you do within the virtualized operating system won’t affect the native operating system.
Interactivity
In terms of dual boot vs virtual machine interactivity, virtual machine is better. The good interactivity of virtual machine is reflected in the following two ways:
- By using the virtual machine, you can run multiple operating systems (the host system and guest systems) at the same time. But if you use dual boot, you can only run one system. VM is very useful when you need to do a job using two or more systems.
- VM allows you to share files easily between the host and guest systems via drag and drop, even if the host system is Windows while the guest system is Linux. If you use dual boot, when the first system is Windows and the second system is Linux, the file sharing method will be complicated.
Then, how to choose between the dual boot and the virtual machine? To be honest, compared to virtual machine, dual boot has no advantages, except for the performance. Many people will use virtual machine if they just want to try a new OS, run a specific program that isn’t available on their native operating systems, or have low space on PC.
Make Space for Dual Boot or Virtual Machine
If you adopt the dual boot method, making enough unallocated space is necessary. If you adopt the virtual machine method, I recommend you go further to create a separate partition on the unallocated space.
To complete this job, I recommend you use MiniTool Partition Wizard’s free feature Move/Resize. This feature is very useful when each of partitions doesn’t have enough space, because it can move the location of partitions to gather the unallocated space together. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
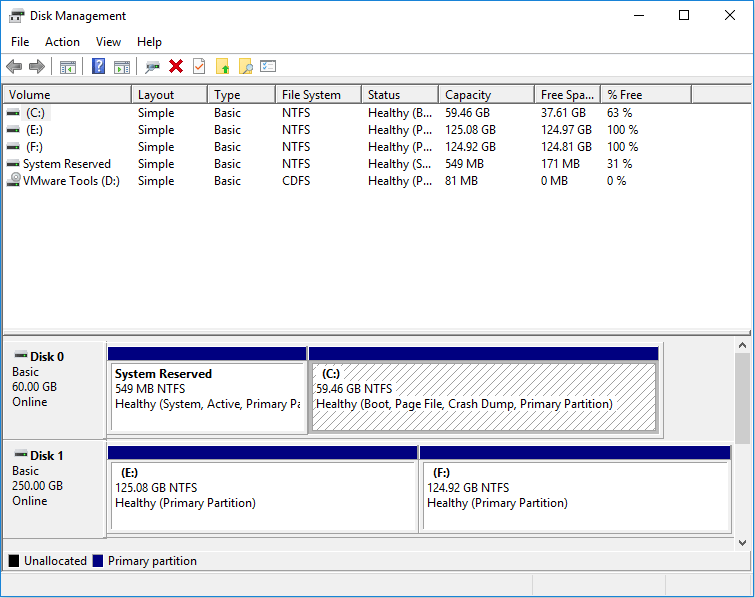
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click a partition and choose Move/Resize.
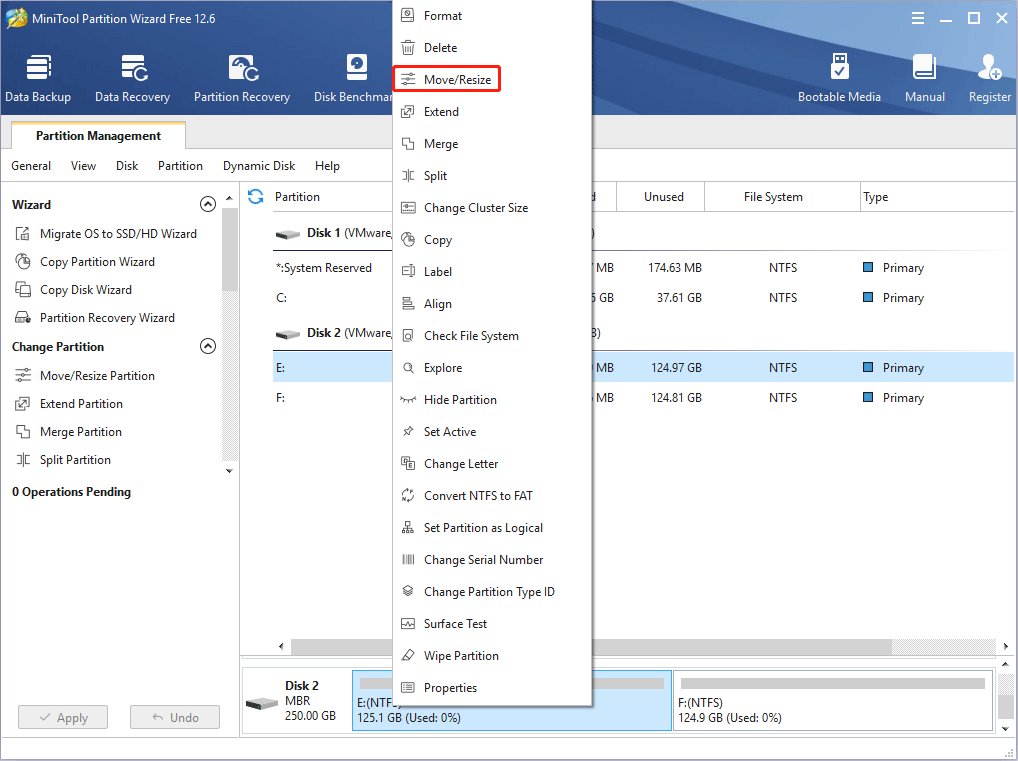
Step 2: Drag the two arrows on the two sides of the partition to shrink the partition, and then drag the block to move the location of the partition. Then, click the OK button. In this way, you can get unallocated space. Through the same method, you can gather the unallocated space together.
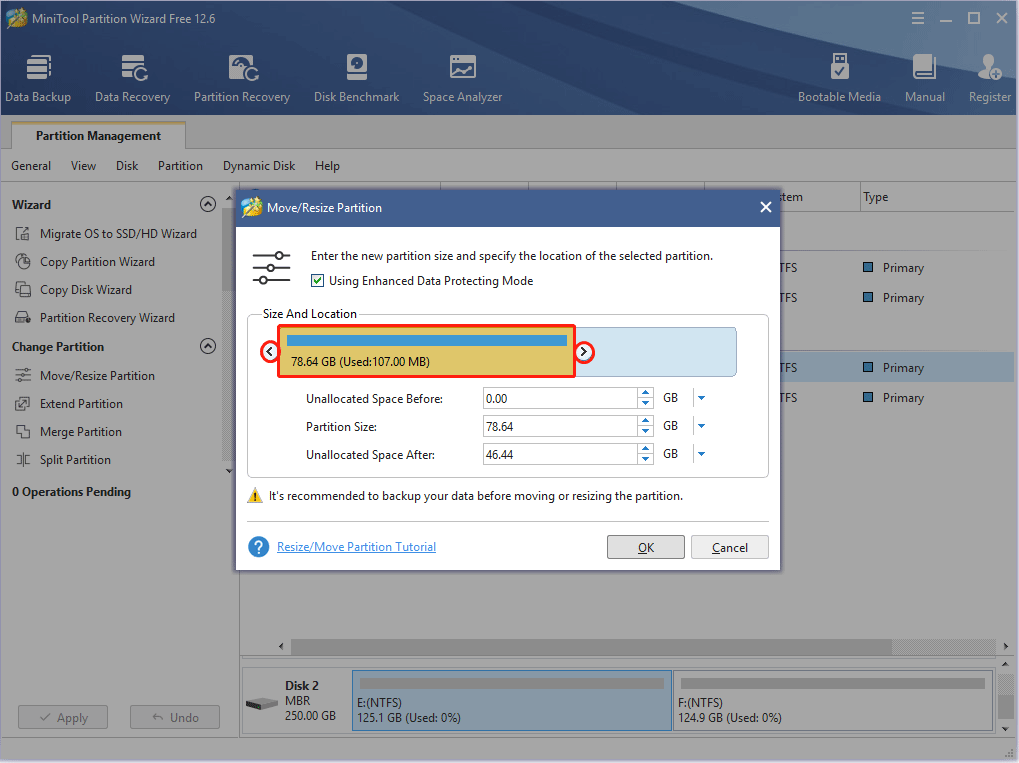
Step 3: Right-click the unallocated space and choose the Create button.
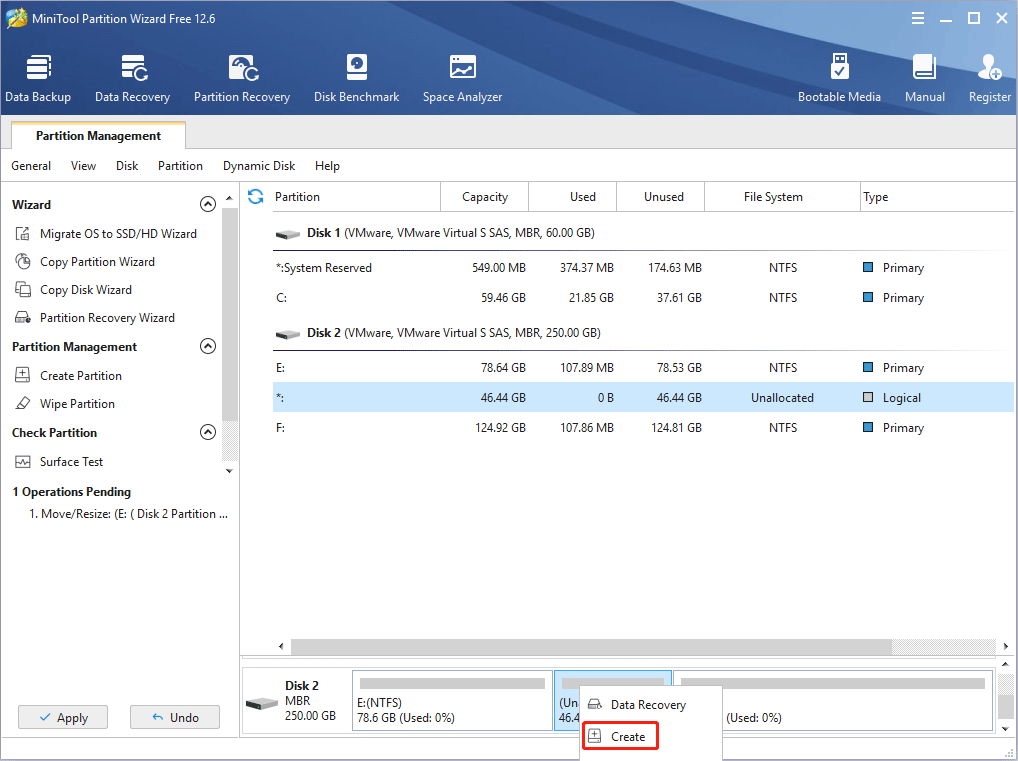
Step 4: Set parameters for the new partition. You can keep all of them to the default value if you don’t have specific demands. Then, click the OK button.
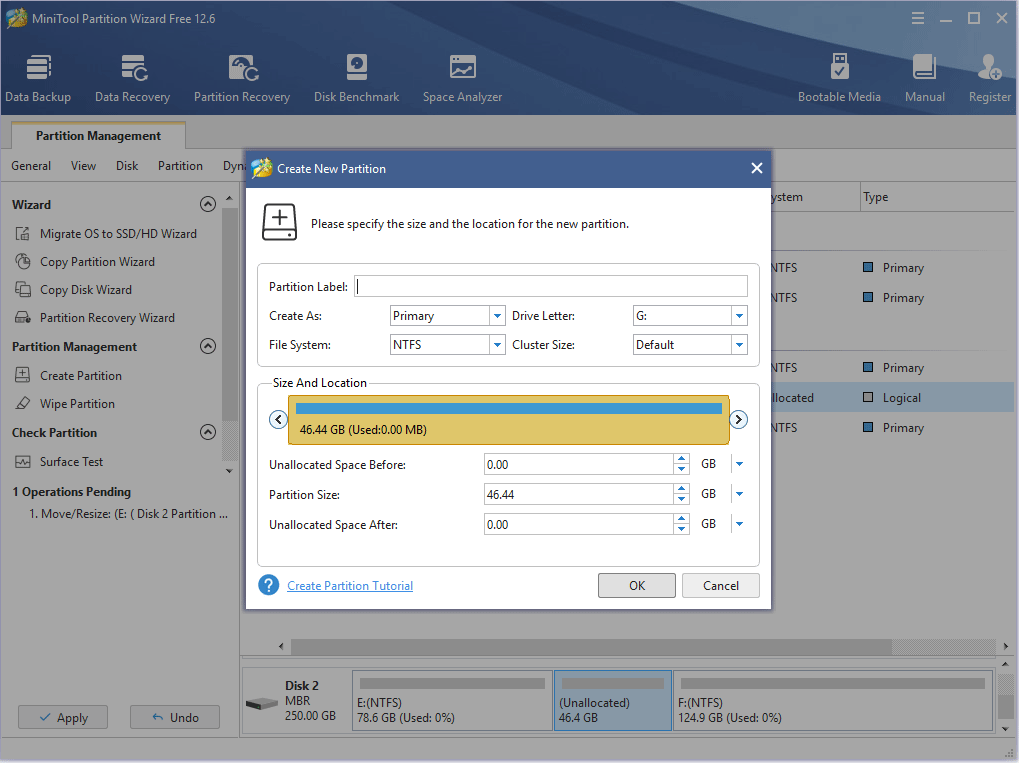
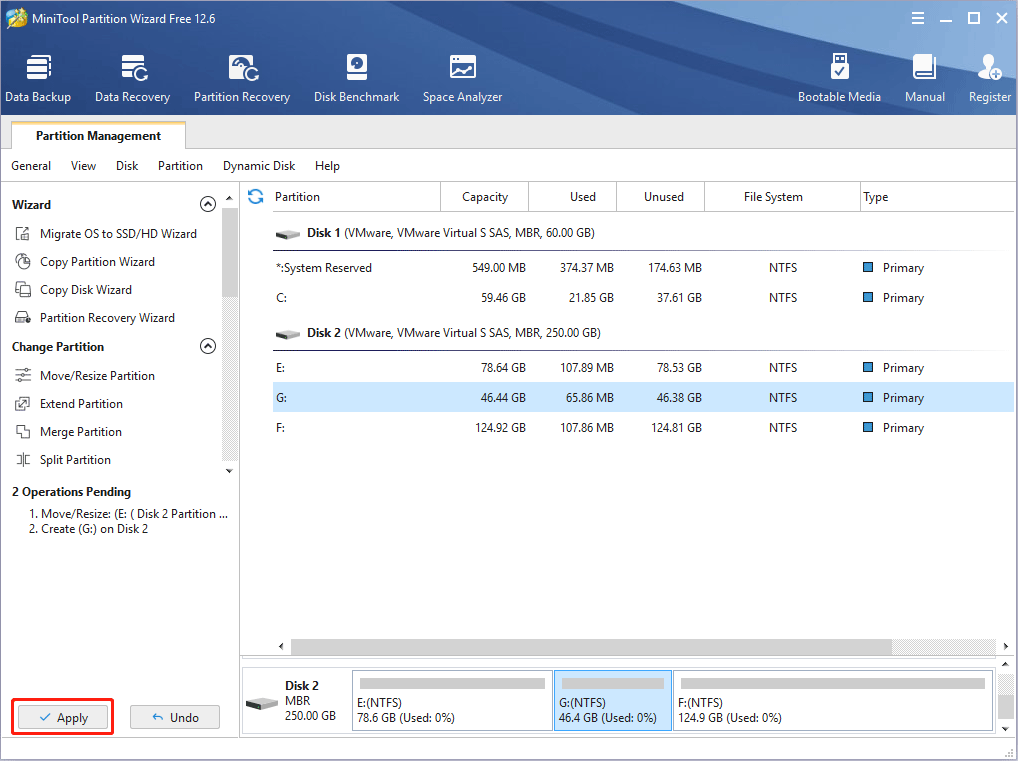
Step 5: Click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
Bottom Line
Is this post useful to you? Do you have other ideas about VM vs dual boot? Please leave them in the following comment zone for sharing. In addition, if you have any problems with MiniTool Partition Wizard, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.

![How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2020/02/install-linux-on-windows-10-thumbnail.png)



User Comments :