As we all know, an SSD is a storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies (DRAM, NAND flash, 3D XPoint) to store data persistently. However, if you search on Amazon, most SSDs' storage medium is NAND flash. Then, what about NAND SSD? Read this post, in which MiniTool explains to you what NAND flash is and what it brings to SSD.
What Is NAND Flash
NAND flash is a type of non-volatile flash memory. It relies on electric circuits to store data, but it does not require power to retain data, which is also one of the reasons why SSDs mostly use NAND flash as their storage media rather than DRAM (another reason is that NAND flash is cheaper than DRAM).
Further Reading:
3D XPoint is a non-volatile memory technology jointly developed by Intel and Micron Technology in July 2015. Intel names Optane for storage devices that use the technology and Micron calls them QuantX. It’s said that Optane’s performance is better than NAND SSD and the price is lower than DRAM.
NAND memory cells are made with two types of gates: control and floating gates. Both gates help control the flow of data. When you program one cell (write data), a voltage charge is sent to the control gate, making electrons enter the floating gate. Through this charge manner, data can be stored in each NAND memory cell.
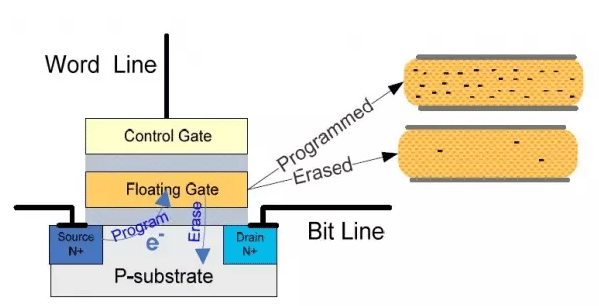
But when power is detached from NAND flash memory, the floating-gate transistor will provide an extra charge to the memory cell, keeping the data.
NAND Flash’s Defects
NAND flash also has its inherent disadvantages like the following ones:
1. Block Erase
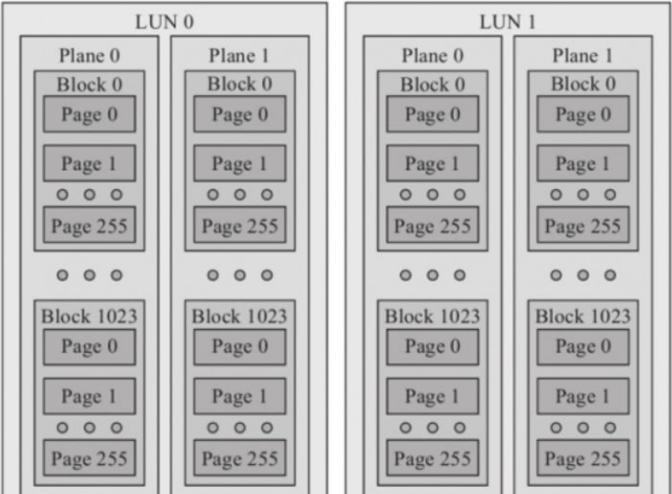
In general, a NAND flash chip has multiple LUNs (Logic Unit Number); each LUN has multiple planes; each plane has thousands of blocks; each block has hundreds of pages. When you write or read data, the unit is page. However, when you erase data, the unit is block.
On the other hand, data is usually written at random and non-continuous locations; whether to modify or write data, erasure is required. Therefore, write amplification cannot be avoided.
2. Limited P/E (Program/Erase)
Each NAND block has a limit on the number of times that it can be erased. When this number is exceeded, the block may become unusable. Because once the number of P/E cycles is exceeded, the following situations are most likely to occur:
- Electrons can’t enter the floating gate (write failure).
- The electrons in the floating gate can easily come out (data retention issue).
- The electrons in the floating gate cannot come out (erase failure).
If you worry about your SSD’s life, you can read the following post to know how to prolong your SSD’s life.
3. Read Disturb
As the flash memory is read multiple times, the contents of adjacent memory cells in the same block will change (become a write operation). The principle is as follows:
Each page has a space around 4KB or 8KB. Within a page, there are many cells. Each cell usually stores one bit of data (a cell can also store more than one bit of data and I will explain to you later).
When a page is read, a voltage Vref is applied to the control electrodes of cells on the page while the control electrodes of the cells on other pages is applied with a relatively larger voltage Vpass, which may create a stronger electric field to draw some electrons into the floating gate of the cells on the pages that are not read (program data), resulting in data error.
On the other hand, the more times you erase blocks, the worse the insulation effect, and the easier it is for electrons to enter the floating gate.
4. Program Disturb
When a page is written, a higher voltage will be applied to the control electrodes of cells on the page while a lower voltage will be applied to the control electrodes of the cells on other pages that are not written. Thus, electrons can be easily injected into the floating gates of the cells on the written page.
However, if the higher voltage and the lower voltage are close, especially when too many erasing times lead to poor insulation performance, it is very likely that electrons enter adjacent memory cells. This will also cause data error.
Technology Progress: Process Technology
Since the invention of the NAND flash in 1986, the manufacturers have made a lot of great progress in NAND flash technology, such as the improvement of the process technology, 3D NAND, MLC, TLC and QLC. In this part, I will explain the process technology to you.
In order to reduce the cost per bit and expand the capacity of SSD, manufacturers first think of improving the process technology, for example, from the early 50nm to the current 16/15nm process nodes.
The number in the process technology represents the distance from source to drain. The shorter the distance, the faster the electrons enter, and the smaller the size of the transistor, meaning that a chip of the same size has a larger capacity and faster speed.
However, when the process technology reaches 15nm nodes, it is approaching the limit. On the one hand, the continuous improvement of process technology will make the cost increase sharply, which cannot be offset by the cost reduction brought by the increase in capacity.
On the other hand, when the process technology is below 20nm nodes, the charge leakage (data retention issue) and charge interference (read disturb and program disturb) are more obvious.
Therefore, if the process technology goes further, the reliability and performance will decrease.
Technology Progress: SLC vs MLC vs TLC vs QLC
In order to increase capacity and reduce costs further, manufacturers proposed MLC, TLC, and QLC. In this part, I will explain SLC vs MLC vs TLC vs QLC to you.
In general, one memory cell stores only one bit of data, which is so-called SLC (Single-Level Cell). If you increase the number of bits that can be stored in each memory cell, for example, increasing to 2 (MLC, short for Multi-Level Cell), to 3 (TLC, short for Triple-Level Cell), or to 4 (QLC, short for Quad-Level Cell), the storage capacity of NAND flash will also increase accordingly.
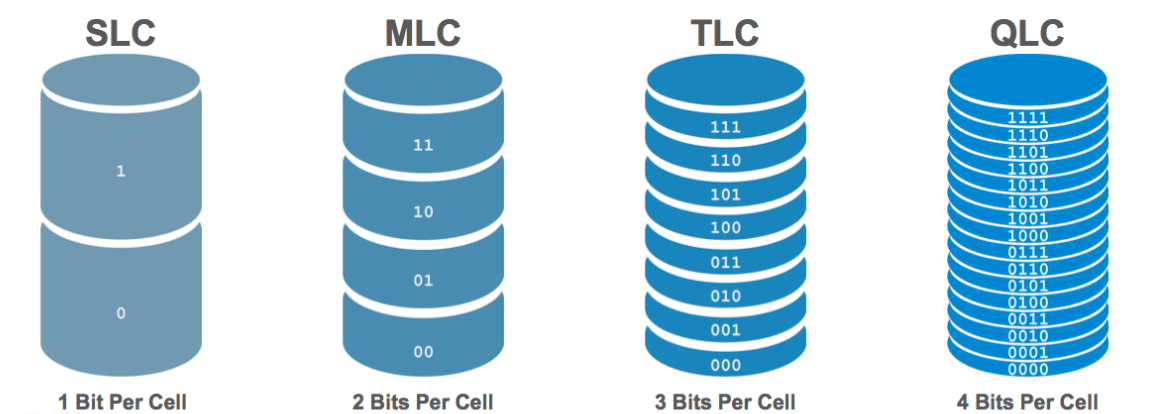

For example, an ordinary flash memory created by SLC has a capacity of 128 GB; then, MLC will make it have a capacity of 256 GB (double); TLC will triple it to 384 GB; and QLC will quadruple it to 512 GB. And sequentially, costs are reduced.
However, the capacity increase and cost reduction come at the cost of reduced performance, reliability, and life.
As mentioned above, the NAND flash completes data reading and writing through applying voltage. In this process, there is one or multiple threshold voltages (Vth).
In SLC, there is only one threshold voltage, because it stores only one bit of data: 0 or 1. If the voltage in the cell exceeds the threshold voltage, it means 0. Conversely, if the voltage in the cell is below the threshold voltage, it means 1. Therefore, the read and write is very simple and fast.
However, if one memory cell stores more bits of data, there will be more threshold voltages. For example, an MLC NAND flash memory stores two bits of data, namely, 00, 01, 10, or 11. Hence, it needs 3 threshold voltages to distinguish them.
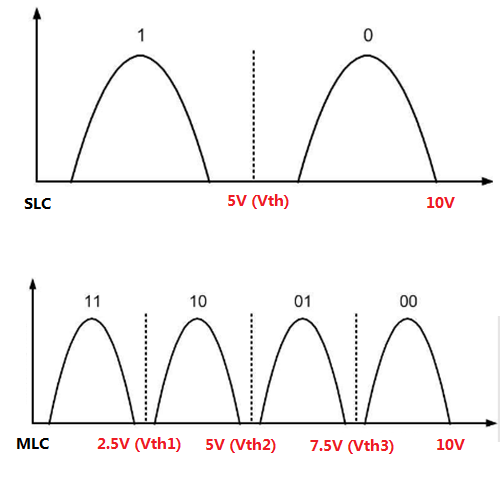
The more bits of data stored in the cell, the more threshold voltages it needs, the more time it takes to identify the voltage signal, so the longer it takes to read and write data.
On the other hand, if there are multiple threshold voltages, the assignable voltage for each bit of data will become less, and therefore the possibility of charge interference (read and program disturbs) increases.
Technology Progress: 2D NAND vs 3D NAND
Unlike the above two technologies, 3D NAND provides different ideas for increasing capacity and reducing costs.
Traditional 2D NAND Flash (planar NAND flash) is composed in a two-dimensional manner. It is mainly composed of word lines (WL) and bit lines (BL), as shown in the figure below. A word line represents a page. The bit line represents the memory cells on the word line (page). There are as many memory cells on the word line as there are bit lines.
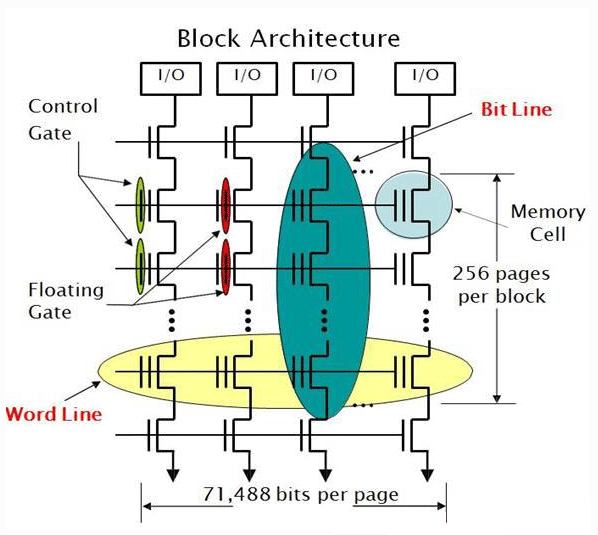
The word lines and bit lines intersect to form a block. Then tile the blocks to form the 2D NAND flash.
As for 3D NAND flash, it stacks the planar NAND flash like buildings. It increases more transistors per unit area by stacking more layers of flash.
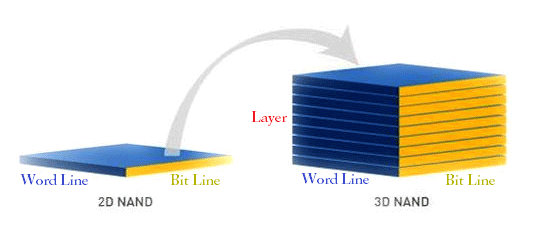
Just through this way, manufacturers can increase NAND capacity and reduce costs and they don’t need to make efforts on improving the process technology or storing more bits of data in one cell. As a result, capacity, performance, and reliability are guaranteed.
Precautions for Using NAND SSD
If you decide to use a NAND SSD, here are some notes about using it:
1. Installing OS on the NAND SSD: It is the only way that can make the most of the advantages of an SSD and greatly boost the performance of a computer.
2. Running OS version above Windows 7: Operating systems above Windows 7 will automatically detect whether the disk system is an SSD and will decide to how to optimize it accordingly. For example, in Windows 7, you can only defrag a hard drive, which will hurt an SSD and shorten its life. However, OS above Windows 7 will recognize SSD and optimize it with a special method.
3. Enabling AHCI or NVMe mode: AHCI mode can allow your storage device with SATA III interface to perform better. As for NVMe mode, if your SSD has an M.2 interface, PCI interface, etc., this mode will allow your SSD to perform at its highest speed. To know more about AHCI and NVMe, please read this post: M.2 SSD vs. SATA SSD: Which One Is Suitable for Your PC?
4. Keeping 4K alignment: 4K misalignment will not only greatly reduce the data write and read speed, but also increase the number of unnecessary writes of the SSD, affecting its life.
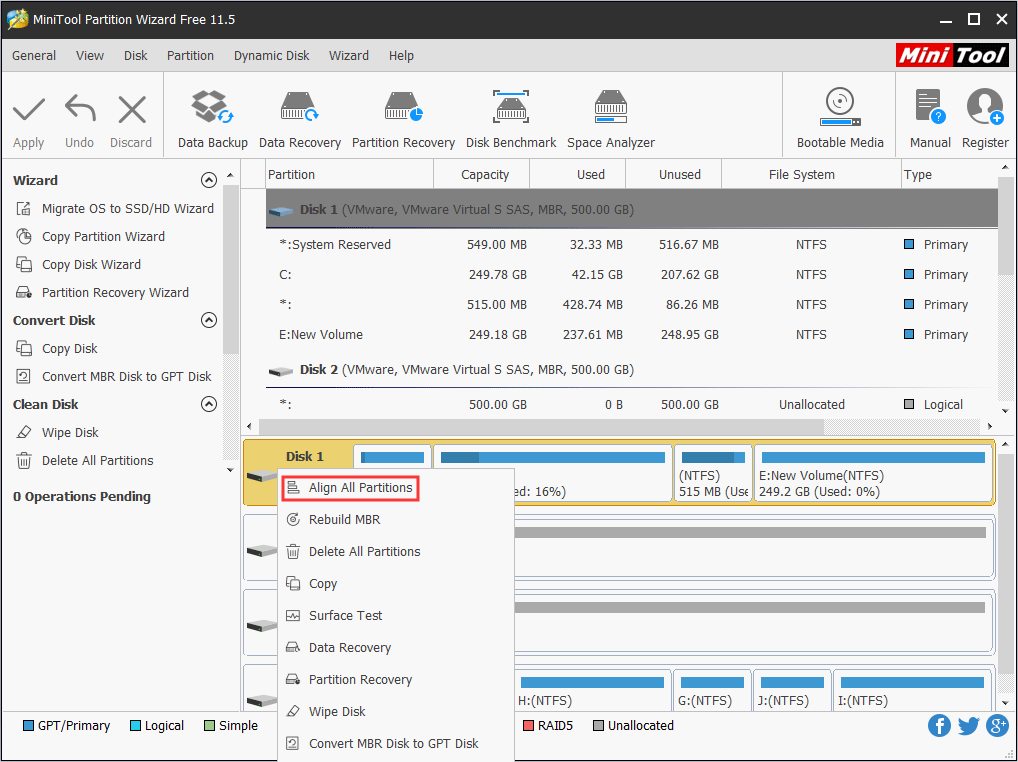
To keep 4K alignment of the SSD, you can use the MiniTool Partition Wizard, whose Align All Partitions feature can help you. All you need to do is just clicking the following button to free download this tool, launching it, right-clicking the drive to choose Align All Partitions, and finally click the Apply button to execute operations.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
5. Reserving enough free space: The more data a solid-state drive stores, the slower the performance. If a partition has been in a state of over 90% usage for a long time, the probability of SSD crash will be greatly increased. Therefore, it is very important to clean up useless files in time and store large files like movies or music on a mechanical hard disk.
Of course, there are other methods to prolong SSD life and boost the performance of your SSD. I have mentioned a post on how to prolong the life of your SSD before. Hence, here I will recommend you: How to Get Best Performance from SSD in Windows 10/8/8.1/7.
Bottom Line
Have this post answered all your doubts doubt about the NAND SSD? Please leave a comment below. In addition, if you have any problem in aligning SSD partitions, installing OS on SSD, or cleaning up useless files, please leave your questions below or email us at [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.




![How to Move Files from SSD to HDD [Step-by Step Guide]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/06/how-to-move-files-from-ssd-to-hdd-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :