Are you looking for a disk speed test tool for Windows? Now, you've come to the right place. This post from Partition Magic offers a complete hard drive speed test guide and discusses other relevant topics.
Why You Need a Hard Drive Speed Test
As we all know, the hard drive speeds play an important role in boosting the overall performance of a computer. A faster drive or SSD has more excellent performance at accessing larger files and applications. If your computer is becoming slow or runs into disk performance issues, you may want to test hard drive speeds with a benchmark utility.
A disk speed test can measure the read and write speeds of the data you transfer from the disk to the computer, which can help determine whether the disk affects your computer’s performance. Is there a free HDD/SSD benchmark tool for Windows? Of course, yes. Let’s keep reading to learn more details.
Understand the Key SSD/HDD Speed Metrics
Here, I summarize some relevant questions that you’d better know before the disk speed test Windows, including types of hard drive speeds, and HDD vs SSD speeds.
Types of Hard Drive Speeds
Most people should know hard drives have read and write speeds, but may not understand the two types of hard drive speeds: sequential and random write/read speeds. There are differences between them.
- Sequential write and read speeds reflect how quickly your data is accessed or stored in continuous and long strings without interruption, one block after another. These speeds have a great impact on transferring large files, streaming media, installing applications, or other tasks where your data is read and written in a continuous stream.
- Random write and read speeds indicate how quickly your data can be accessed or stored at scattered and various locations on your hard drive. It mainly influences the operating system startup speed, application loading, database operations, and other tasks involving frequent access scattered and small files.
HDD vs SSD Speeds
SSDs are faster than HDDs, especially in terms of boot time. A traditional HDD usually has a data transfer speed of 30 MB/s to 150 MB/s, while an SSD can reach speeds up to 3500 MB/s, especially with the newer NVMe interface. In addition, SSDs have faster data transfer speeds and better application performance compared to HDDs.
How to Test Hard Drive Speeds on Windows 11/10
Now, it is high time to test the hard drive speed on Windows 11/10. I highly recommend you use the expert HDD/SSD benchmark program: MiniTool Partition Wizard. Alternatively, you can choose the other three methods based on your preference.
Way 1. Disk Speed Test via MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a comprehensive disk partition manager that can easily perform the HDD/SSD speed test on Windows, including sequential and random write/read speeds. What’s more, the tool can partition hard drives, change cluster size, migrate Windows OS to SSD, convert FAT32 to NTFS without data loss, convert MBR to GPT without data loss, and so on.
Here’s how to check the HDD/SSD speeds using the software.
Step 1. Click the Download button below to get MiniTool Partition Wizard, run the executable file, and follow the on-screen instructions to install it on Windows.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2. Once installed, run the software to enter the main interface and click Disk Benchmark from the top ribbon area.
Step 3. Select a partition on the disk, like drive C, from the drop-down menu, and then set parameters to test the disk performance. For that:
- Transfer size: The data transfer size ranges from 1 KB to 2048 KB.
- Total Length: The total amount of transferred data ranges from 100 MB to 4096 MB.
- Queue Number: Queue up several read and write tasks on the drive, ranging from 1 to 512.
- Thread Number: Set up how many threads to be used to test the disk, ranging from 1 to 64.
- Test Mode: There are 3 modes for users to choose: Sequential, Random, and Sequential & Random.
- Cool Down Time: This option is used to reduce the HDD/SSD temperature before starting the next test.
Step 4. Click Start and wait for a minute to get the read and write speeds of the drive.

Way 2. Disk Speed Test via Task Manager
Task Manager is a Windows built-in utility that provides information about computer performance, including disk read and write speeds. Here you can perform the disk speed test on Windows using the tool.
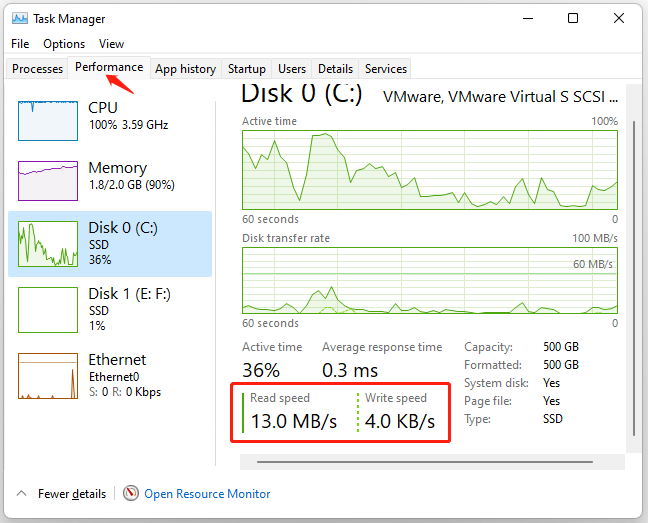
Step 1. Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys at the same time to open Task Manager.
Step 2. Navigate to the Performance tab and select the Disk you want to check from the left panel. Then you can find the read speed, write speed, Average response time, and other information at the bottom.
Way 3. Disk Speed Test via Command Prompt
Command Prompt is a built-in command line tool that can perform a disk speed test on Windows as well. Here’s how to check an SSD speed using the Command Prompt window.
Step 1. Press the Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, type cmd in the box, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys altogether. Then click Yes in the User Account Control window to run Command Prompt with admin rights.
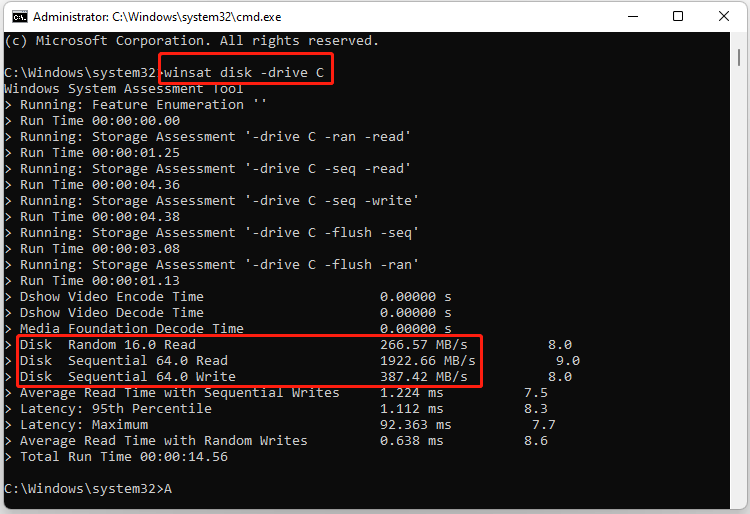
Step 2. In the elevated Command Prompt window, input the following command and hit Enter to test the HDD/SSD speed. Here you can also replace C with your needed drive letter.
winsat disk -drive C
Way 4. Disk Speed Test by Transferring a Large File
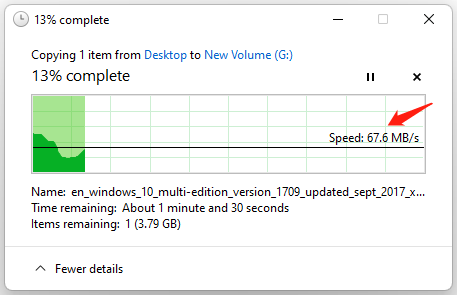
If you are a technical novice and don’t want to install any third-party software, you can try a simple method: transferring a large file manually. This provides a rough estimate of your disk’s performance.
To do that, right-click the large file and select Copy, go to another location for the file, right-click the empty space, and select Paste. Then you can get an overall approximation of the disk transfer speed. If you want to know more detailed information about the disk performance, the test won’t be enough. So, you’d better use a professional tool.
How to Increase HDD/SSD Speeds on Windows 11/10
If your HDD or SSD runs slowly on Windows, try the following solutions to improve its performance.
Solution 1. Clean Up the Disk Space
An HDD/SSD will run slower if it is running out of space. In this case, you need to clean up the storage space by deleting unnecessary files or uninstalling some programs.
If you don’t know what large files are taking up space, use MiniTool Partition Wizard. It can easily check large file sizes and choose to delete them permanently with the Space Analyzer feature.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1. In the main interface, click Space Analyzer from the top ribbon area, select the drive you want to clean up, like C, and click Scan.
Step 2. When the disk scanning is complete, you can check the file size in three ways: Tree View, File View, and Folder View.
Step 3. Expand the category that takes up huge disk space, right-click the large and unnecessary file, then select Delete (permanently).

Solution 2. Update the Disk Driver
An outdated disk driver can slow down your disk performance. To avoid that, you’d better check the update and install it regularly. Here’s how:
Step 1. Press the Win + X keys and select Device Manager.
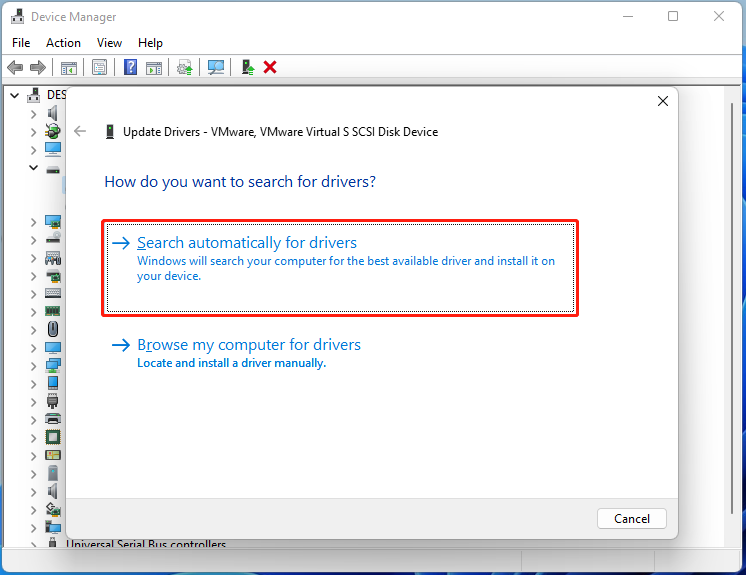
Step 2. Expand the Disk drives category, right-click the driver, and select Update driver.
Step 3. In the pop-up window, select Search automatically for drivers and follow the on-screen prompts to install the driver. Alternatively, you can visit the official website of your disk manufacturer, download the latest driver, and install it manually.
Solution 3. Check Disk Errors
If there are bad sectors or other errors on the HDD/SSD, it will slow down the speed of the disk. In this case, you can try checking and repairing the disk errors via CHKDSK.
Step 1. Open the elevated Command Prompt window as we showed above.
Step 2. In the elevated Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter.
chkdsk D: /f /r

Solution 4. Enable Trim
TRIM plays an important role in boosting the SSD’s performance. If the SSD is running slowly, you can check if the option is enabled. To do that:
Step 1. Open the Command Prompt window again, type the following command, and press Enter.
fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify
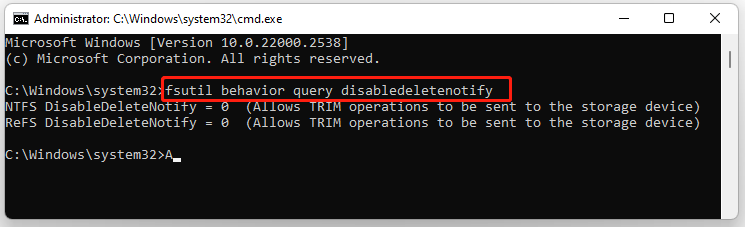
Step 2. If the Command Prompt displays NTFS DisableDeleteNofity = 1, it means TRIM is disabled on the SSD. Then you can run the fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 0 command to enable TRIM.
Of course, the slow HDD/SSD issue can be caused by other factors, like disk fragments, improper settings, outdated BIOS, faulty port or cable, etc. Under these situations, you can defrag the disk, update the BIOS, or check your USB port/cable.
Wrapping Things Up
Simply put, this post focuses on how to test hard drive speed on Windows 10/11. You can use an expert HDD/SSD benchmark tool – MiniTool Partition Wizard, or try Windows tools as we discussed above. Besides, you can try the methods in the post to speed up your HDD or SSD.
If you have any suggestions or feedback about MiniTool Partition Wizard, don’t hesitate to contact us via [email protected], and we will reply to you as soon as possible.
Hard Drive SSD Speed Test FAQ
In addition, I summarize some frequently asked questions related to the disk speed test in Windows. Hope they can help you.
What Affects the Hard Drive Speed?
Hard drive speed can be affected by several factors, including RPM, cache size, storage capacity, data fragmentation, file system, and interface type. If you want to speed up your hard drive, you can take measures related to these factors.
Best Disk Speed Test Software for Windows?
MiniTool Partition Wizard is the best free hard drive benchmarking program on Windows. Aside from enabling you to easily test sequential and random write/read speeds, it can help you manage hard drive partitions, clone hard disks, recover deleted files, rebuild MBR, convert disk between MBR and GPT without losing data, and more.
What’s a Normal Disk Speed?
A normal disk speed depends on whether you are using an HDD or an SSD. The average speed for a modern HDD is 30-150 MB/s, while an SSD can range from 500 MB/s to 3,500 MB/s, or more, with newer interface technology.
How RPM Affects Hard Drive Speed?
In terms of HDDs, RPM (Rotations Per Minute) directly influences the read and write speeds. A higher RPM means the drive spins faster, leading to faster data transfer and access. For instance, a 7200 RPM hard drive is at least 15% faster than a 5400 RPM hard drive.

User Comments :