An Overview of TPM
TPM (Trusted Platform Module), also known as ISO/IEC 11889, is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor. This secure cryptoprocessor is usually soldered on motherboards or integrated into CPUs (the so-called discrete TPM and integrated TPM).
How does the TPM work? When the PC is powered up, the TPM will authenticate it. The TPM provides a cryptographic key to unlock the encrypted drive, and if the key is validated, the computer will boot up as normal. If the cryptographic key is tampered with, the computer won’t start. TPM is important to many security applications like BitLocker, Windows Hello, etc.
Discrete TPM vs Firmware-Based TPM
Discrete TPM and integrated TPM are hardware TPM. They are more secure, simply because they’re isolated from other components in the PC. If one component or area of the PC is compromised, the TPM can still function independently.
However, one defect is that the TPM version is hard to be changed once you buy a PC. If you want to upgrade the TPM, you need to replace the hardware. To solve this problem, Intel and AMD release firmware-based TPM (PTT in Intel and fTPM in AMD).
The firmware-based TPM still performs the same function as hardware TPM, but it runs on the main CPU, so a separate chip is not required. However, this also means that the firmware-based TPM doesn’t have its own dedicated storage. Instead, it stores the key in the trusted execution environment (TEE), the secure area of a main processor.
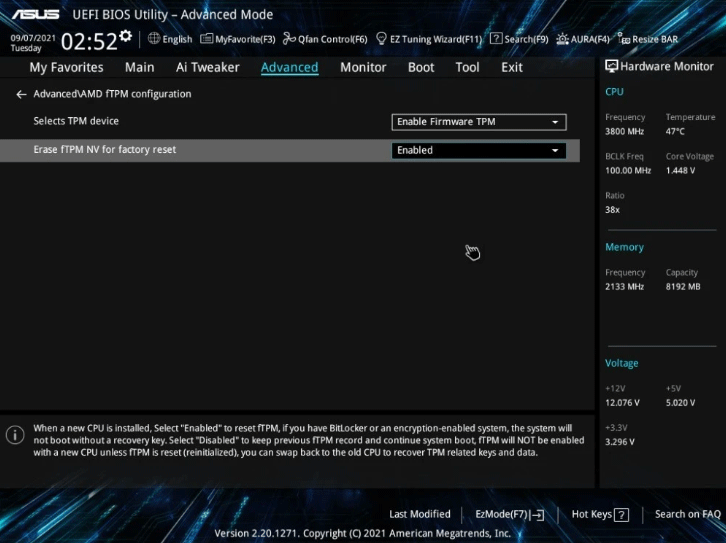
Therefore, compared to the hardware TPM, the firmware TPM is more prone to tampering. In addition, if you replace the CPU or upgrade the BIOS program, the motherboard will automatically perform fTPM initialization by default. In this case, if you have BitLocker or encryption enabled, the system will not boot without a recovery key.
To avoid this issue, you just need to disable the Erase fTPM NV for factory reset feature in BIOS.
What Is A TPM 2.0 And Why Does Windows 11 Require It
TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 Features
Windows 11 is the latest Windows version released in 2021. It requires TPM 2.0 for installation. Fortunately, Windows 11 doesn’t care about the type of TPM you’re using, so long as it adheres to the TPM 2.0 standard.
Why does Windows 11 require TPM 2.0, instead of TPM 1.2, the last popular TPM version? The reason lies in the difference between TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0. In this part, I will explain TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 from the algorithm, supported OS, and supported Windows features.
TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 Algorithm
| Algorithm Name | TPM 1.2 | TPM 2.0 |
| RSA 1024 | √ | Optional |
| RSA 2048 | √ | √ |
| ECC P256 | × | √ |
| ECC BN256 | × | √ |
| AES 128 | Optional | √ |
| AES 256 | Optional | Optional |
| SHA-1 | √ | √ |
| SHA-2 256 | × | √ |
As you can see, TPM 2.0 supports newer algorithms. For example, TPM 1.2 only allows for the use of RSA and the SHA-1 hashing algorithm. However, some entities are moving away from SHA-1 for security reasons. In addition, TPM 2.0 enables greater crypto agility by being more flexible with respect to cryptographic algorithms.
TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 Supported OS
TPM 1.2 supports Windows 7/8/8.1/10, RHEL, and Ubuntu, while TPM 2.0 supports Windows 8/8.1/10/11, RHEL, and Ubuntu. However, even though both TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0 support the same OS, they have some differences:
- Windows 8 launched with support for TPM 2.0 but only supports SHA-1.
- TPM 2.0 only supports Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3, Ubuntu 16.04, and later versions, because they have the Linux upstream kernel version 4.4 or newer.
TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 Supported Windows Features
Both TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0 support the following features:
- Measured Boot
- BitLocker
- Windows Defender Application Control (Device Guard)
- Credential Guard
- Device Health Attestation
- Windows Hello/Windows Hello for Business
- UEFI Secure Boot
- TPM Platform Crypto Provider Key Storage Provider
- Virtual Smart Card
- Certificate storage
However, because TPM 1.2 only supports the deprecated SHA-1 algorithm, most of the above features recommend you use TPM 2.0. In addition, Windows 10, version 1507 (End of Life as of May 2017) only supported TPM 2.0 for Credential Guard.
The features supported only by TPM 2.0 are as follows:
- Device Encryption
- Windows Defender System Guard (DRTM)
- Autopilot
- SecureBIO
Does Your PC Use TPM 1.2 or 2.0?
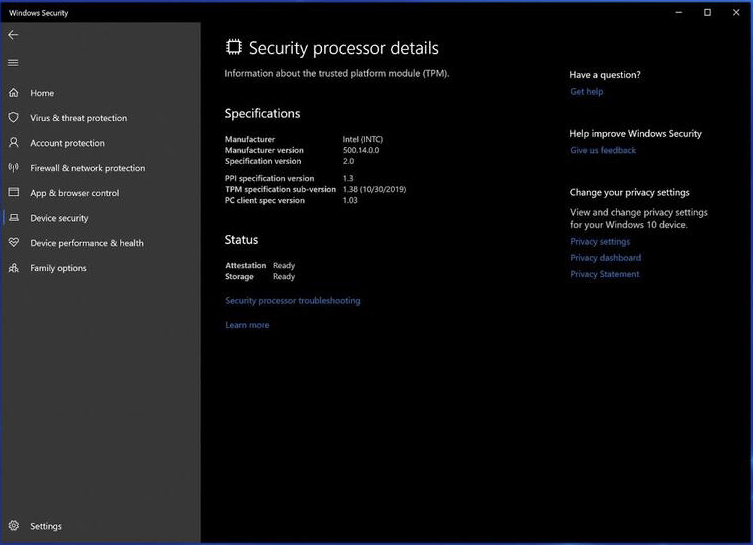
Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0. Does your PC meet the requirement? What version of TPM does your PC use? You can check the TPM version through the following steps:
- Open Windows Security from the Windows Search bar.
- Go to Device security.
- On the right pane, under the Security process section, click the Security process details
- Then, you can check if the Specification version is 2 or 2.0.
If you do not see a Security processor section, your PC may have no TPM or the TPM feature is disabled.
How to Check if Your PC Has TPM for Windows 11? How to Enable It?
How to Upgrade the TPM Version from 1.2 to 2.0
If your PC’s TPM version is 1.2, to install Windows 11, you may want to upgrade the TPM from 1.2 to 2.0. You need to follow the guide below.
Stage 1. Whether Your PC Can Upgrade the TPM Version to 2.0
You need to contact your PC manufacturer first to ask whether your PC can upgrade the TPM version from 1.2 to 2.0. In general, there are 2 ways to upgrade the TPM version.
#1. Upgrade the Hardware.
If you use the discrete TPM or integrated TPM, you need to use this method. To use this method, you need to make sure your PC has a TPM 2.0 header and check if the header has 14 pins or 20 pins. You need to check this information from your PC manufacturer.
If you use the integrated TPM, you may just need to replace the CPU. Anyway, contact your PC manufacturer to know what you should do.
Then, buy a TPM 2.0 with the corresponding amount of pins. If you’re still not feeling confident, try buying from the same manufacturer as your motherboard.
#2. Install the TPM Upgrade.
This method only works when you use the firmware-based TPM. In addition, this method only works for some specific PC models.
At the time of writing, only Dell and HP offer the tools to help you upgrade the TPM version from 1.2 to 2.0. They also list PC models that can be upgraded from TPM version 1.2 to 2.0. Here are the lists.
Dell PCs
- Dell Edge Gateway 5000/5100 (OEM Ready)
- Dell Precision Tower 3420/3620/T5810/5810XL/T7810/T7910
- Latitude 7370/E5270/E5470/E5570/E7270/E7470
- OptiPlex 3040/3240 All-in-One/5040/7040/7440 AIO/5050
- Precision 3510/7510/7710
- XPS 15 9550
HP PCs
- HP ProBook 430/440/450/455/470 G3/G4
- HP ProBook 640/645/650/655 G2/G3
- HP EliteBook 725/745/755/820/840/850 G3
- HP EliteBook 725/745/755/820/828/840/848/850 G4
- HP Elite x2 1012 G1
- HP Elite x2 1012 G2 Tablet
- HP EliteBook Folio (1030) G1
- HP EliteBook Folio 1040 G3/G4
- HP EliteBook x360 1030 G1
- HP EliteBook x360 G2
- HP ZBook Studio/15/15u/17 G3
- HP ZBook Studio/14u/15/15u/17 G4
- HP Pro x2 612 G2
- HP ProDesk 400/600 G2 DM
- HP ProDesk 400/480/600/680 G3 MT
- HP ProDesk 400/600 G3 SFF
- HP ProDesk 490/498 G3
- HP ProDesk 600 G2
- HP ProDesk 400/600 G3 Desktop Mini
- HP ProDesk 400 G4 MT/SFF
- HP ProOne 400 G2/G3 AiO 20T & NT
- HP ProOne 600 G3 AiO 21.5″ T
- HP ProOne 600 G2 AiO
- HP ProOne 800 G3 AiO 23.8″ T/NT GPU
- HP EliteDesk 705/800 G2 DM
- HP EliteDesk 800 G3 DM
- HP EliteDesk 800 G2/G3 TWR/SFF
- HP EliteDesk 705 G3 SFF/MT
- HP EliteDesk 705 G3 Desktop Mini
- HP EliteDesk 800 G3 AiO T/NT
- HP EliteOne 800 G2 AiO 23T & NT
- HP RP9 G1 Retail System
- HP Elite Slice
Stage 2. Make Your System Disk and BIOS Mode Ready for TPM 2.0
TPM 2.0 is not supported in Legacy and CSM Modes of the BIOS. Devices with TPM 2.0 must have their BIOS mode configured as Native UEFI only. However, if your PC uses the legacy mode (it means that the system disk is MBR style), it won’t boot when the BIOS mode is changed to UEFI.
To avoid this issue, you need to make sure your PC is ready for the TPM 2.0 upgrade. You can follow the steps below:
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
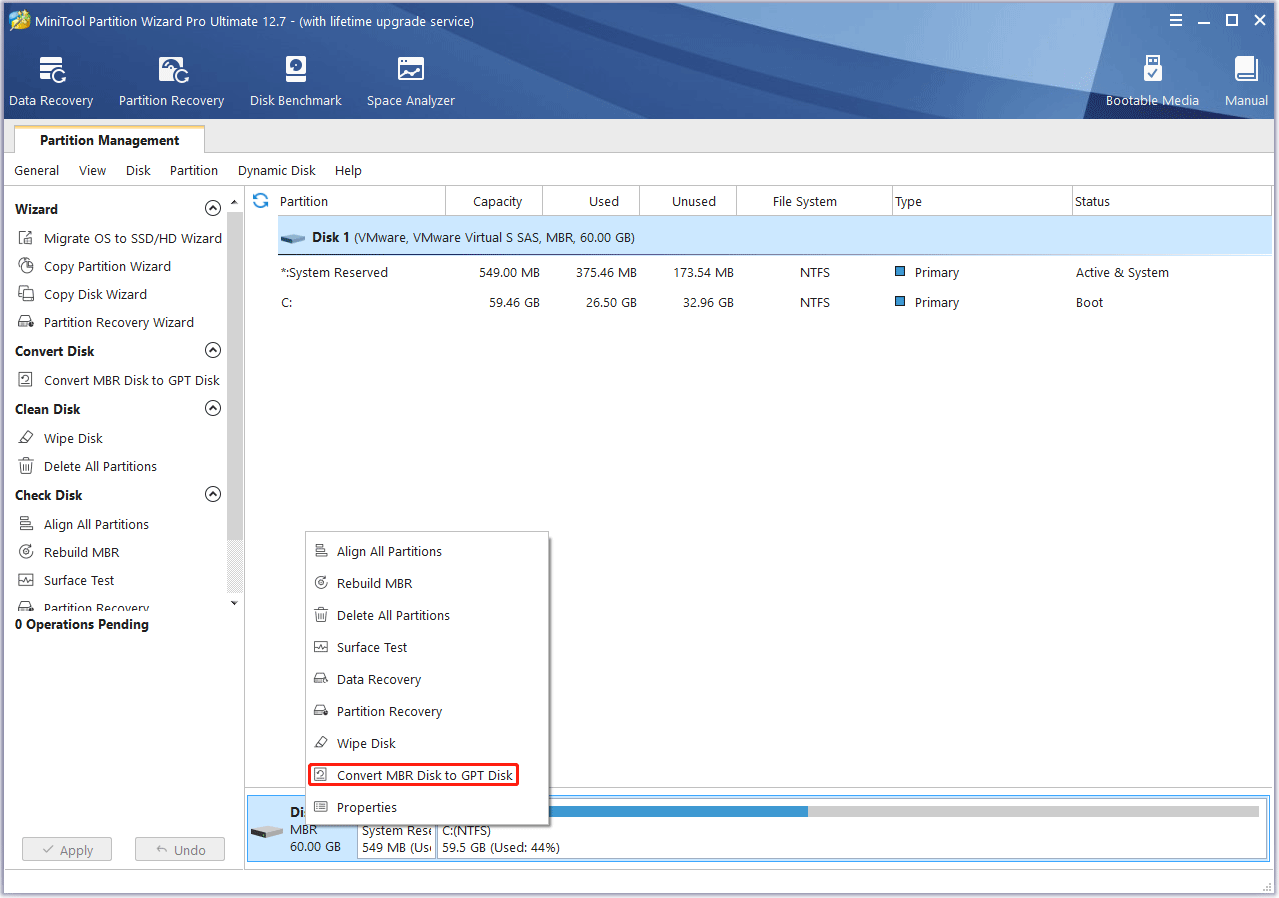
Step 1: Use MiniTool Partition Wizard to convert the system disk from MBR to GPT without data loss. Only if the system disk is GPT style, the PC can boot normally in the UEFI boot mode.
- Launch this software on your PC.
- Right-click on the system disk and click on Convert MBR Disk to GPT Disk.
- A warning window will pop up. Click OK.
- Click the Apply button to execute the operation. After that, you need to wait until the conversion is completed.
Step 2: After the conversion is completed, your PC won’t boot. You need to power on your PC and press the BIOS key to enter the firmware. Then, you need to go to the Boot tab to change the Boot Mode to UEFI. Save changes and exit the firmware. After that, your PC can boot up normally.
Stage 3. Install the TPM 2.0 Upgrade
If you use the hardware TPM and you bought the new hardware (like the new TPM chip), you just need to insert the hardware component into your PC. If necessary, you may need to update your BIOS.
Before you install the TPM 2.0 upgrade, you need to unlock the BitLocker encrypted drive first (if there is one).
#1. Dell TPM 2.0 Upgrade
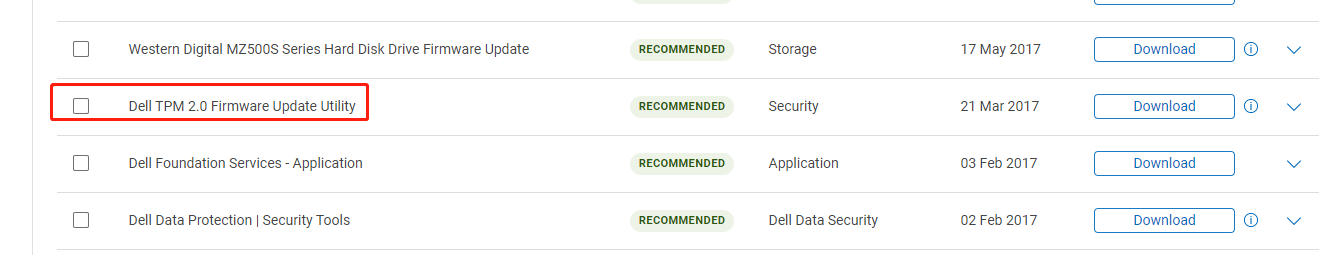
Step 1: Find your PC model. Then, go to the Dell Support page and enter the model number into the search box.
Step 2: On the new page, select the Drivers & Downloads tab. Expand the Find drivers link. Show all the drivers. Find Dell TPM 2.0 Firmware Update Utility and download it.
Step 3: The Dell TPM 2.0 download is an executable file. You just need to run it. After the upgrade is completed, you can check your TPM version again to see if the upgrade is successful.
Note: If you want to upgrade to the TPM to 2.0 on Precision systems, you need to first update BIOS to the latest version A14 (as of 15 August 2016), and apply the TPM FW patch/update 1.3.0.1.
#2. HP TPM 2.0 Upgrade
To install HP TPM 2.0 upgrade, you need to use HP TPM Configuration Utility. In addition, upgrading an HP PC to TPM 2.0 is much more complicated than upgrading a Dell PC. You can read this post to know the detailed steps.
Bottom Line
Is this post useful to you? Do you have other opinions about TPM 1.2 vs 2.0? Do you know other ways to upgrade the TPM version from 1.2 to 2.0? Have you encountered problems when upgrading the TPM version? Leave your comments in the following zone.
In addition, if you encounter problems when using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.

![How to Install Win11 Without TPM [A Step-by-Step Guide]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2022/07/install-windows-11-without-tpm-thumbnail.png)
User Comments :