When you create or format a drive smaller than 4GB, the Windows system will offer you 3 file system options: FAT, FAT32, and NTFS.
If you want to know the difference between FAT32 and NTFS, you can read this post: NTFS vs. FAT32 vs. exFAT – Differences and How to Format to. Therefore, in this article, I only focus on FAT vs FAT32.
About FAT File System
FAT, short for File Allocation Table, is a file system originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks. And it was later adapted for use on hard disks and other devices.
The first FAT version is 8-bit FAT released in 1977 and it was only used in some terminal computer systems at that time. Therefore, it was not widely used. In 1980, FAT12 was released, along with the first version of DOS. It is the first widely used version of the FAT file system.
In 1984, FAT16 was released and in the next few years Microsoft released FAT16 improved versions (FAT16B and FAT16X). But all of them are called FAT16. In 1996, FAT32 was released for Windows 95 OSR2 / MS-DOS 7.1.
Please note that 8-bit FAT, FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32 are variants of the FAT file system. The reason why Microsoft releases new FAT file systems is that the old FAT file system can’t manage so large a disk as disk drive capacity increases.
Further Reading:
Why can’t the old FAT file systems manage large disk? To figure out this problem, you should learn how FAT file systems manage disk.
When you format a partition to FAT file system, an index table (the file allocation table) will be created to identify chains of data storage areas (clusters) associated with a file in the partition.
The table is a linked list of entries for each cluster. Each entry contains either the number of the next cluster in the file, or else a marker indicating the end of the file, unused disk space, or special reserved areas of the disk.
When you need to look for a file, the system will check root directory of the disk that contains the number of the first cluster of each file in that directory. And then the system can traverse the FAT, looking up the cluster number of each successive part of the disk file as a cluster chain until the end of the file is reached.
Therefore, you can see, the maximum size of partition/volume that the FAT file system can manage is the product of the maximum number of entries and cluster size (the number of entries determines the number of clusters that the file system can deal with).
When the disk drive capacity increases, the maximum number of clusters must increase as well, and so the number of bits used to identify each cluster has grown. 8-bit FAT means that it uses 8-bit entries; FAT12 means it uses 12-bit entries; FAT16 means it uses 16-bit entries; and FAT32 means it uses 32-bit entries.
FAT vs FAT32
There are 8-bit FAT, FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32. In a broad sense, FAT stands for all of them. But in Windows 10, FAT only stands for FAT12 and FAT16.
FAT12 vs FAT16 vs FAT32: Size Limit
When you create a partition, the FAT32 option only occurs when the partition is no more than 32GB and the FAT option only occurs when the partition is smaller than 4GB. If you have created a FAT partition, the partition is FAT16 when the volume size is no smaller than 16MB; and the partition becomes FAT12 when it is smaller than 16MB.
Please note that in Windows 10, the minimum volume size is 8MB and you can’t create a FAT8 partition.
Therefore, when it comes to FAT32 vs FAT, I must explain FAT12 vs FAT16 vs FAT32 actually. To understand FAT12 vs FAT16 vs FAT32 standards, please refer to the following chart:
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | |
| Max. Number of Files | 4,068 for 8 KB clusters | 65,460 for 32 KB clusters | 268,173,300 for 32 KB clusters |
| Max. File Size | N/A | 2GB without LFS or 4GB with LFS | |
| Min. Volume Size |
|
| |
| Max. Volume Size |
|
|
|
1. Most modern PCs have Large-file support (LFS).
2. The max. volume size and min. volume size vary depending on the sector size determined by disk manufacturers and cluster size allowed by system.
The specific minimum volume size and maximum volume may vary from computer to computer. In my PC (the system is Windows 10 and the disk sector size is 512 bytes), the boundary between FAT12 and FAT16 is 16 MB; the maximum size of FAT16 is 4 GB; and the minimum volume size of FAT32 is 36 MB.
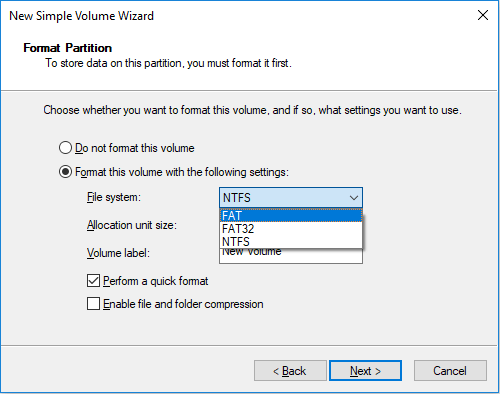
If I want to create a FAT32 partition smaller than 36MB, I will get error message “The volume size is too small for the selected file system” and then the partition becomes a RAW partition.
FAT16 vs FAT32: Which Should I Use?
In this part, I will not talk about FAT12, because its max. volume size is too small and many devices has abandoned the support for it.
When the drive is no more than 4GB, should you use FAT16 or FAT32? Actually, this depends on the cluster size that the two file systems use.
| Volume Size | FAT16 Cluster Size | FAT32 Cluster Size |
| 7 – 16 MB | 2 KB | Not supported |
| 17 – 32 MB | 512 bytes | |
| 33 – 64 MB | 1 KB | 512 bytes |
| 65 – 128 MB | 2 KB | 1 KB |
| 129 – 256 MB | 4 KB | 2 KB |
| 257 – 512 MB | 8 KB | 4 KB |
| 513 MB – 1 GB | 16 KB | |
| 1 – 2 GB | 32 KB | |
| 2 – 4 GB | 64 KB |
A disk consists of many sectors whose size is fixed to 512 bytes or 4096 bytes (4 KB) in most cases. When the PC writes and reads data, the unit is cluster (not sector), which is composed of 2n sectors (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, etc.).
In general, the larger cluster size you use, the fewer clusters the files will use, and then the faster the files are accessed by OS. But the disadvantage is space waste. On the other hand, when you use smaller cluster size, you can make use of disk space more fully but the data access speed will be slower.
According to IBM, FAT16 does provide excellent performance on small hard disk drives that are less than 1.2 GB. But if hard disk drives are larger than 1.2 GB, FAT16 becomes very inefficient in storing data because large amounts of hard disk drive space is unused but occupied by the file allocation table.
FAT vs FAT32: How to Tell Whether the Drive is FAT or FAT32?
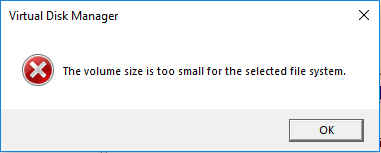
How can I tell if my USB stick is formatted as FAT16? Windows 7 Disk Management says that my USB stick is a FAT volume. But it doesn’t say whether it’s FAT16 or FAT32. I opened the Property window and it doesn’t tell between FAT16 and FAT32 either. — superuser.com
If you want to just tell between FAT16 and FAT32 in Windows, please do as follows:
- Press Windows key + R key.
- Type “msc” into the Run box and press Enter to open the Disk Management tool. This tool will show you the FAT32 and FAT file systems like the following picture:
But if you want to check whether the partition is FAT12 or FAT16, you can use MiniTool Partition Wizard. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
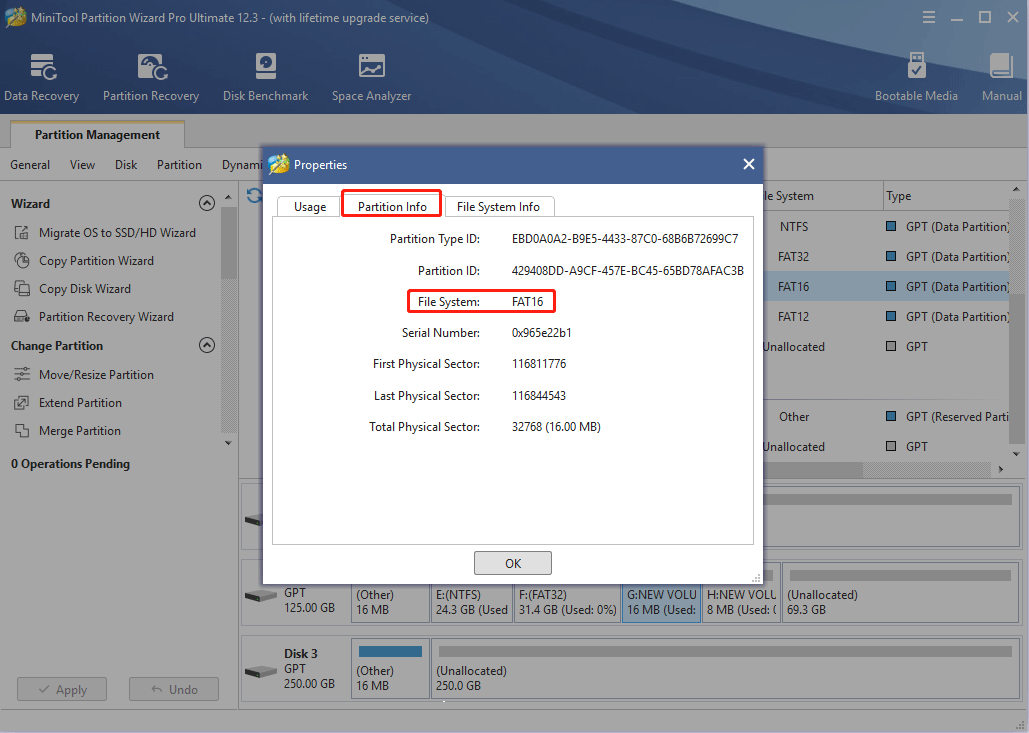
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click the FAT partition and choose Properties.
Step 2: Skip to Partition Info tab and check the File System information.
Can I Break Through FAT Volume Size Limit in Windows 10?
In Windows 10, the FAT12 volume size limit is 16MB; the FAT16 volume size limit is 4GB; and the FAT32 volume size limit is 32GB. To break through the FAT volume size limit, you can try third-party software.
MiniTool Partition Wizard can help you break through the FAT32 volume size limit and extend the FAT32 partition size up to 2TB. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
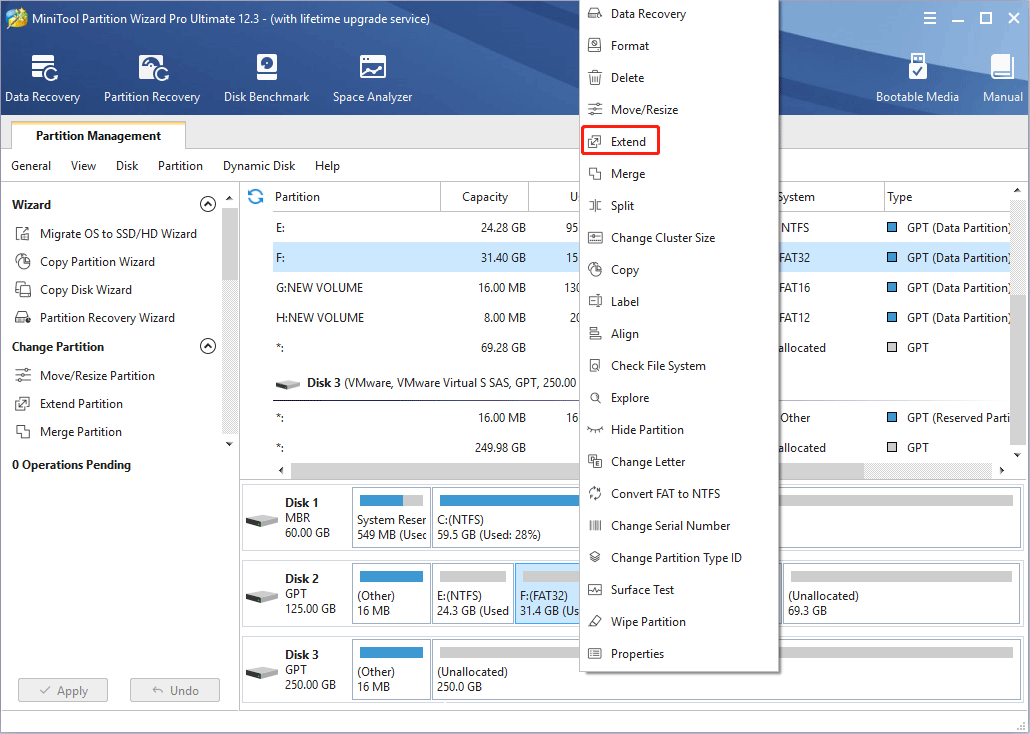
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click the FAT32 partition and choose Extend.
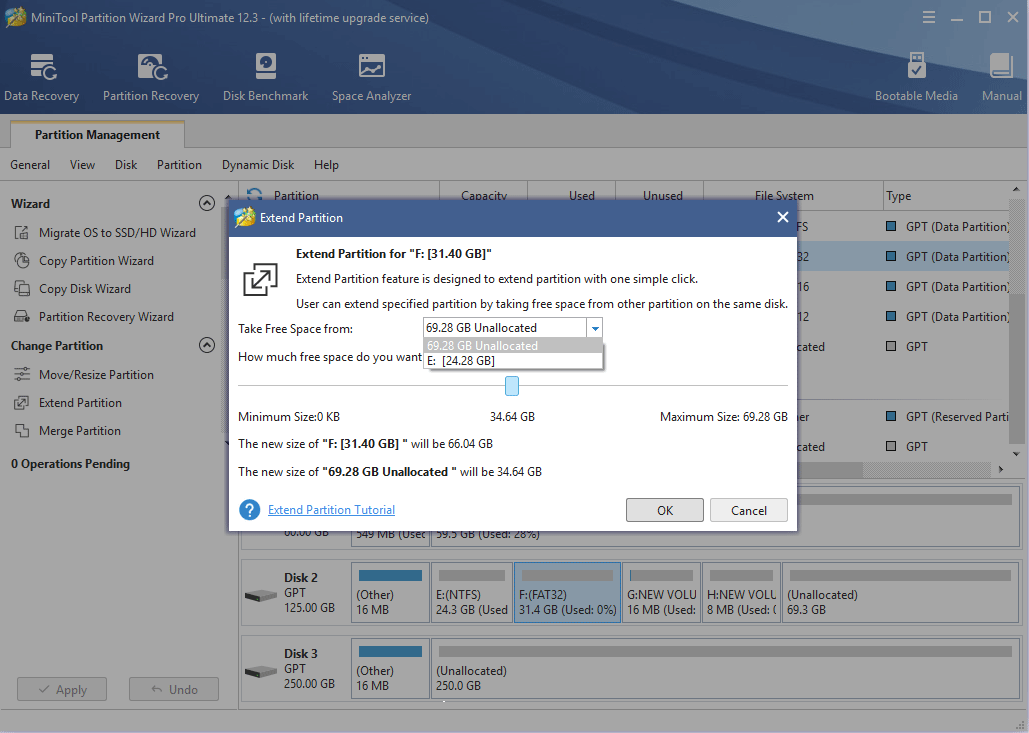
Step 2: Choose unallocated space or a partition to take free space from. Drag the blue block to determine how much free space you want to take and then click the OK button.
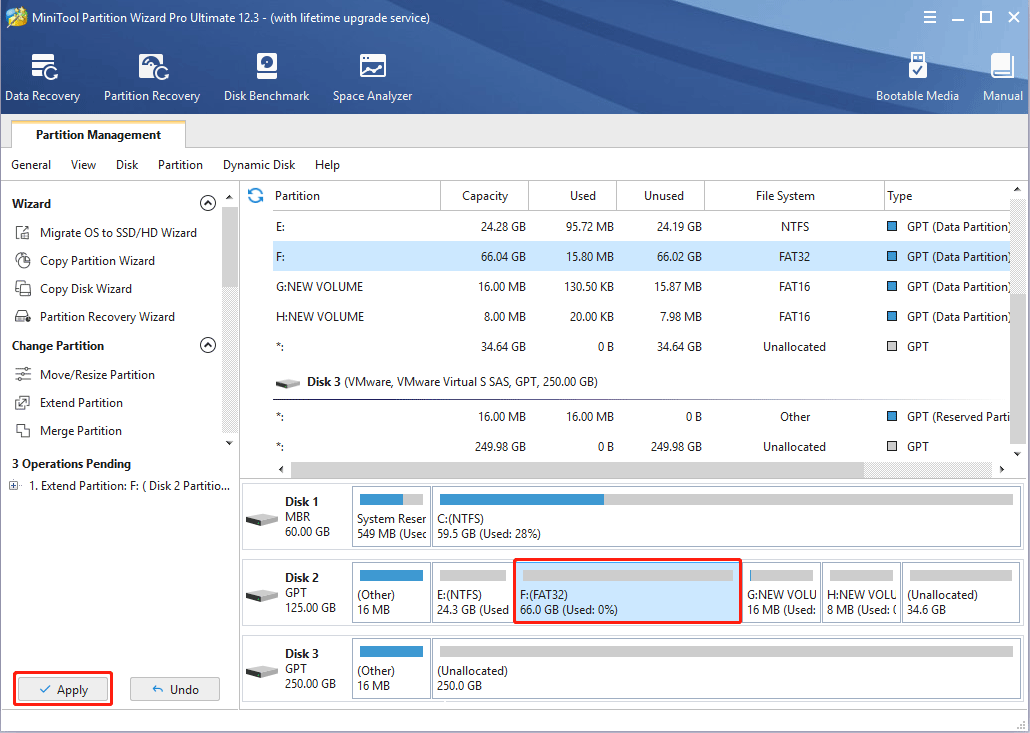
Step 3: Check the layout of the disk and click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
Bottom Line
Is this post useful to you? Do you have other ideas about FAT vs FAT32 or FAT 16 vs FAT32? Please leave a comment in the following zone. In addition, if you have difficulty in checking partition information or extending FAT32 partition, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible!

User Comments :