SD cards are widely used in devices like cameras, smartphones, and dash cams for storing photos, videos, and other data. Yet many users are confused when they see the prompt “Format SD Card”.
What does formatting actually do? Will it delete all your data? In this article, I’ll explain what formatting an SD card means, why it’s sometimes necessary, and how to do it safely.
What Does Format SD Card Mean
A full format of an SD card erases all existing data on the card, including photos, videos, documents, applications, and music. It also re-establishes the file system, allowing devices like cameras, mobile phones, or computers to read from and write to the card properly.
Next, let’s understand the specific meaning of formatting in cameras, dash cams, and Android devices, respectively.
- Camera: Formatting a camera’s memory card erases all data, preparing it for storing new photos.
- Dashcam: Formatting a dashcam’s memory card erases old video recordings and prepares the card to continuously store new footage.
- Android: Formatting an Android device’s memory card rebuilds the file system, helping to fix errors and preparing it for storing apps and files.
Now that you understand what formatting an SD card means, you might be wondering why it’s necessary to do so. Let’s take a closer look at the reasons behind formatting your SD card.
Why Do You Need to Format Your SD Card
Here are a few key reasons why formatting is crucial:
- Device compatibility: Formatting an SD card helps you establish the required file system for specific devices (such as cameras, game consoles, and dashcams), ensuring proper operation.
- Resolving errors or corruption: Formatting may repair issues caused by improper removal or file system corruption, ensuring the health and reliability of the card.
- Setting the correct file system: You’ll need to set a specific file system (such as ExFAT or FAT32) on the card so that devices can properly store and retrieve data.
- Erasing card data: Before selling an old SD card, you should perform a full format to completely erase all data.
How to Format an SD Card
This section describes four methods for formatting an SD card on a computer. Whether your SD card is for a dash cam, camera, or other devices, you can format it using these methods.
Before we begin, let’s understand the difference between a quick format and a full format.
- Quick format: A quick format deletes files from a partition and rebuilds the file system, volume label, and cluster size. This means that a quick format doesn’t actually erase all data.
- Full format: A full format completely erases files from a partition, rebuilds the file system, volume label, and cluster size, and scans the partition for logically bad sectors.
First, you need to insert it into your computer’s SD card reader or a compatible adapter.
#1. Via Windows Explorer
It is a file manager application that is part of the Windows operating system. You can use it to format your SD card. Here’s how:
Step 1: Press the Windows key + E to open File Explorer.
Step 2: Find your SD card under This PC.
Step 3: Right-click on the SD card’s icon and choose Format.
Step 4: Choose the appropriate file system. FAT32 is often recommended for compatibility with various devices, while exFAT is suitable for larger cards (64GB and above).
Step 5: Click the Start button to begin formatting the SD card.
Step 6: A warning message will appear, and click OK to proceed.
#2. Via Disk Management
Disk Management is a built-in Windows utility that allows you to manage partitions and disks on your computer. Here are the steps to format an SD card:
Step 1: Press Windows Key + X, and select Disk Management.
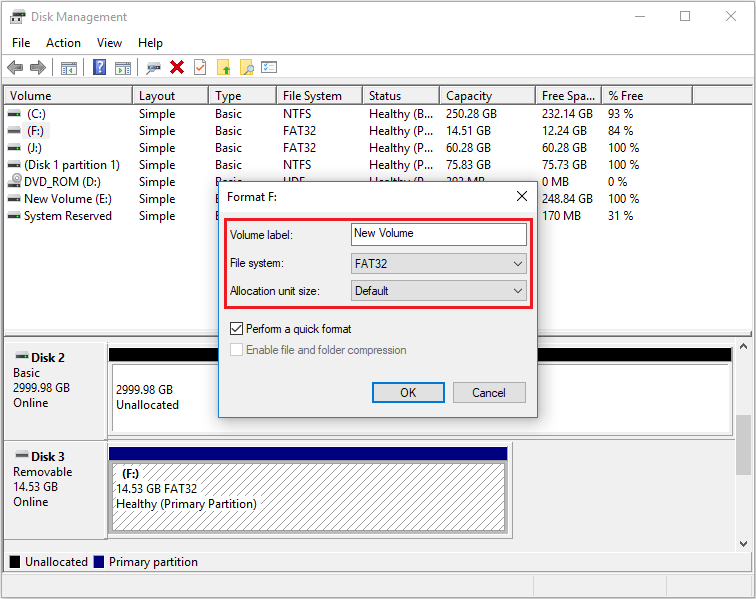
Step 2: In the Disk Management window, right-click on the SD card’s volume (partition) and select Format.
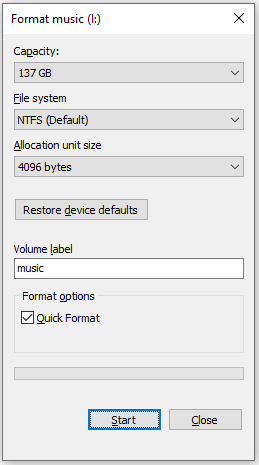
- Volume label: You can optionally enter a name for the SD card.
- File system: Select either FAT32 (compatible with most devices) or exFAT/NTFS (for larger files).
- Allocation unit size: Usually, the default setting is fine.
- Perform a quick format: By default, Quick format is selected by default, which will not rewrite data but only delete the index table, while Full format will scan for bad sectors and overwrite data.
Step 3: Click OK to begin the formatting process.
Step 4: A warning message will appear, and click OK to proceed.
#3. Via MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard lets you quickly format your drive to Windows-compatible file systems like NTFS, FAT32, or exFAT.
It also supports formatting drives larger than 32GB to FAT32, which Windows typically doesn’t allow.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Download and install MiniTool Partition Wizard on your computer, then open the program to access its main interface.
Step 2: Right-click the target partition and select Format from the context menu.
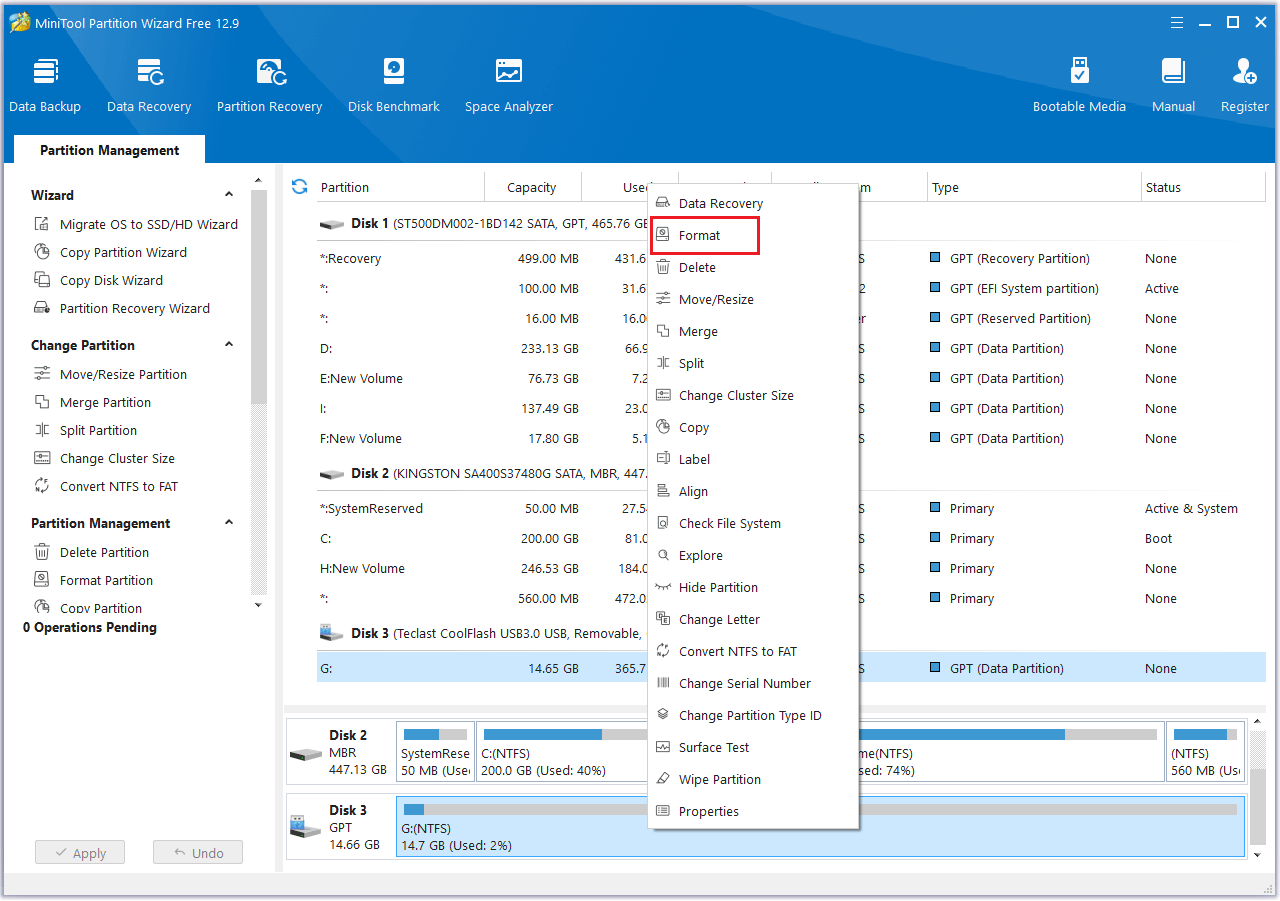
Step 3: In the new pop-up window, set the Partition Label, File System, and Cluster Size. Then click OK to continue.
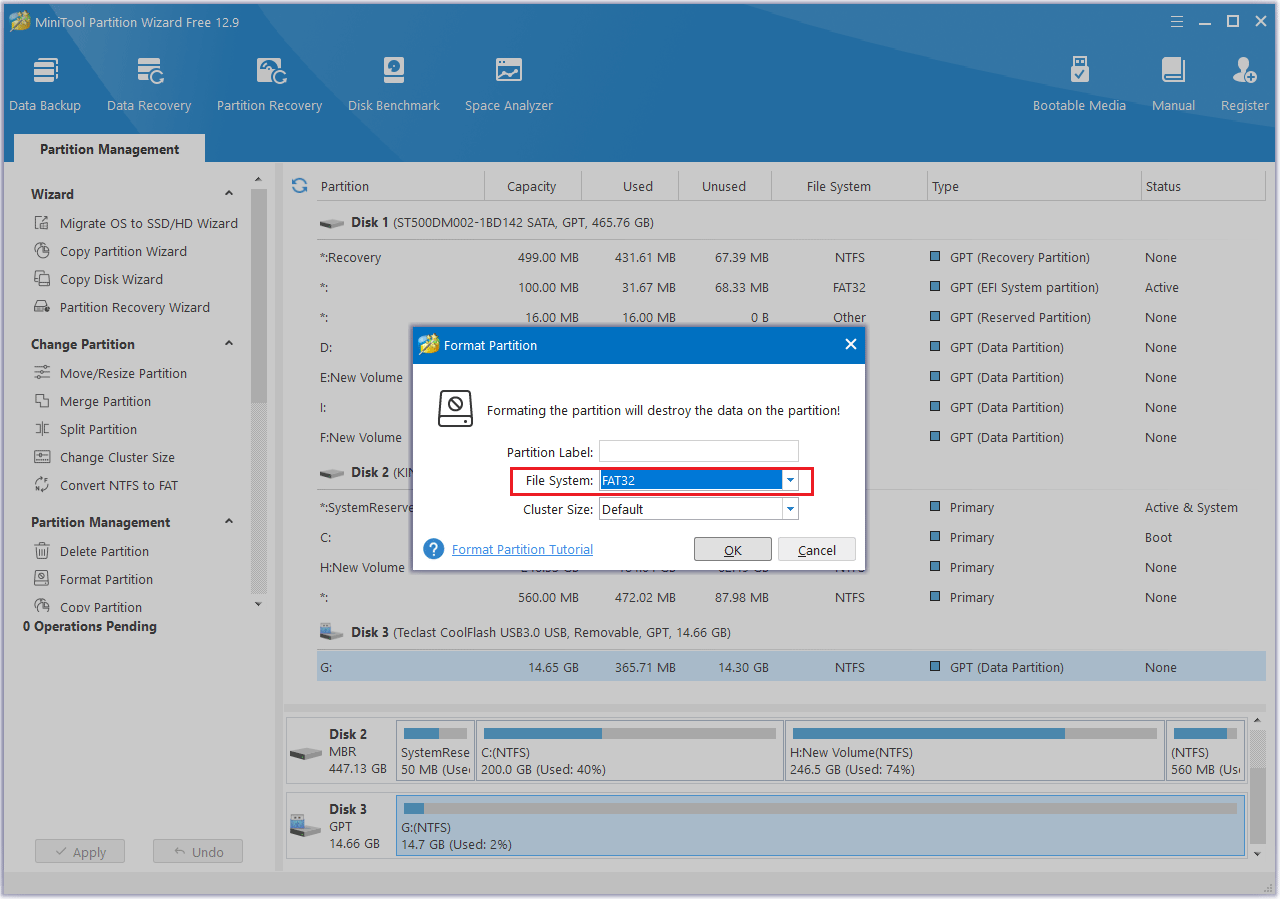
Step 4: Click Apply to execute the pending operation.
Besides this, it can also help you convert MBR to GPT without data loss, change cluster size, create/copy/extend partitions, clone HDD to SSD, etc.
#4. Via Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is another command-line tool built into Windows that can also be used to format an SD card. Although it may seem a bit complicated, it’s still worth a try. Here are the steps:
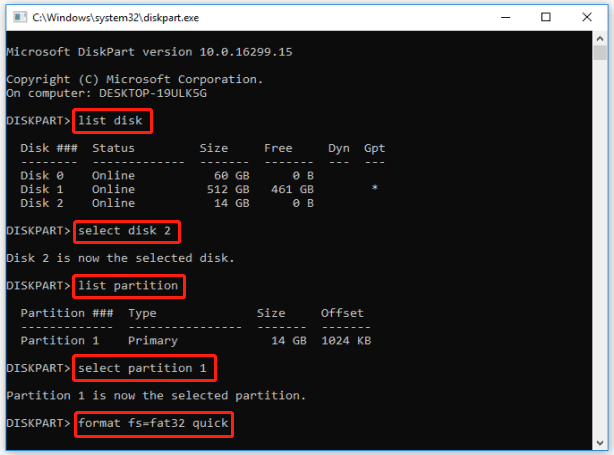
Step 1: Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, then type diskpart and hit Enter. When prompted, click Yes to launch the tool in Command Prompt.
Step 2: Type the following commands in order and press Enter after typing each one.
- list disk (This command displays all the disks recognized by your computer)
- select disk * (* represents the drive number)
- list partition (This command shows all the partitions on the selected disk)
- select partition * (* represents the partition number of the drive)
- format fs=fat32 quick (This command will quickly format an SD card to FAT32)
Step 3: Once formatting is complete, type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
Further reading:
1. How to format an SD card on a camera?
To format an SD card by using a camera, first make sure the camera is turned off and the SD card is properly inserted into the slot. Then turn on the camera and open the menu. Look for the “Format”, “Format Memory Card”, or a similar option, usually within the Setup menu. Select this option and confirm to start the formatting process, which will erase all data on the card.
2. How to format the SD card on the Dash Cam?
Step 1: Turn on your dash cam and find the settings menu. This is usually indicated by a gear icon or a similar symbol.
Step 2: Find an option like “Format SD Card” or “Card Formatting”. It might be under a “System” or “Storage” section.
Step 3: Select the format option and confirm the process.
Step 4: After formatting is finished, reboot the dash cam to make sure the changes are applied.
How to Recover SD Card Data Lost after Formatting
For some reason, many people forget to back up their SD card data, which leads to the loss of important files. Here’s an example:
So, I’m stupid, and formatted an SD card and thus lost a crucial video file. Been looking up ways to recover data, and have tried a few, not many, to any degree of workable avail. Has anyone had a similar problem and found a workable solution? Thanks a lot.--archinect.com
So, how can you recover data from a formatted SD card? You can use an SD card recovery program. I highly recommend MiniTool Partition Wizard.
It enables you to:
- Recover data from various storage devices, including HDD, SSD, USB drive, memory stick, SD card, etc.
- Recover data from a formatted partition, a deleted partition, RAW partition.
- Recover all kinds of files such as documents, photos, audio, music, videos, email archives, etc.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here is how to recover lost data from a formatted SD card with MiniTool Partition Wizard:
Step 1: Launch the MiniTool software to enter its main interface and click Data Recovery in the top toolbar.
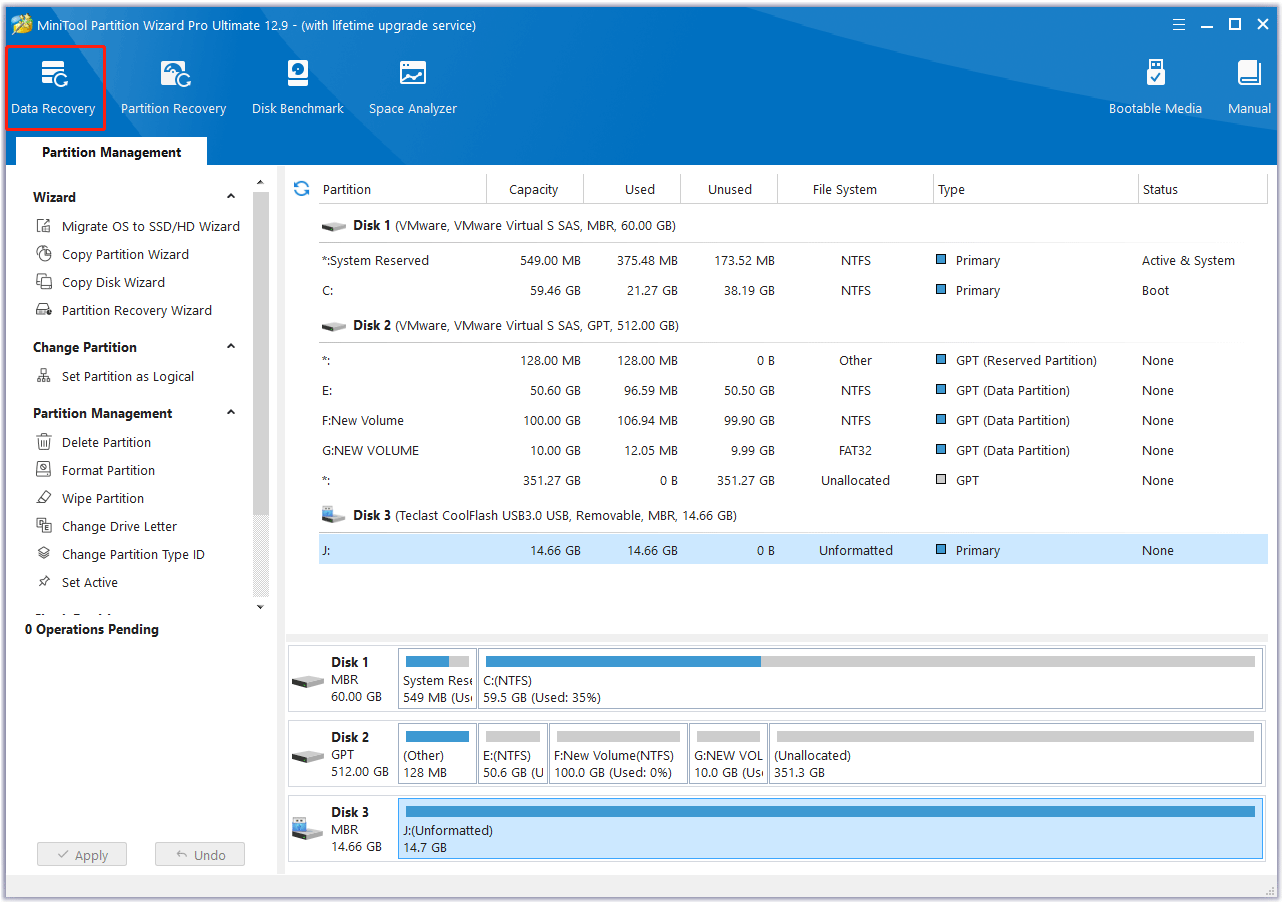
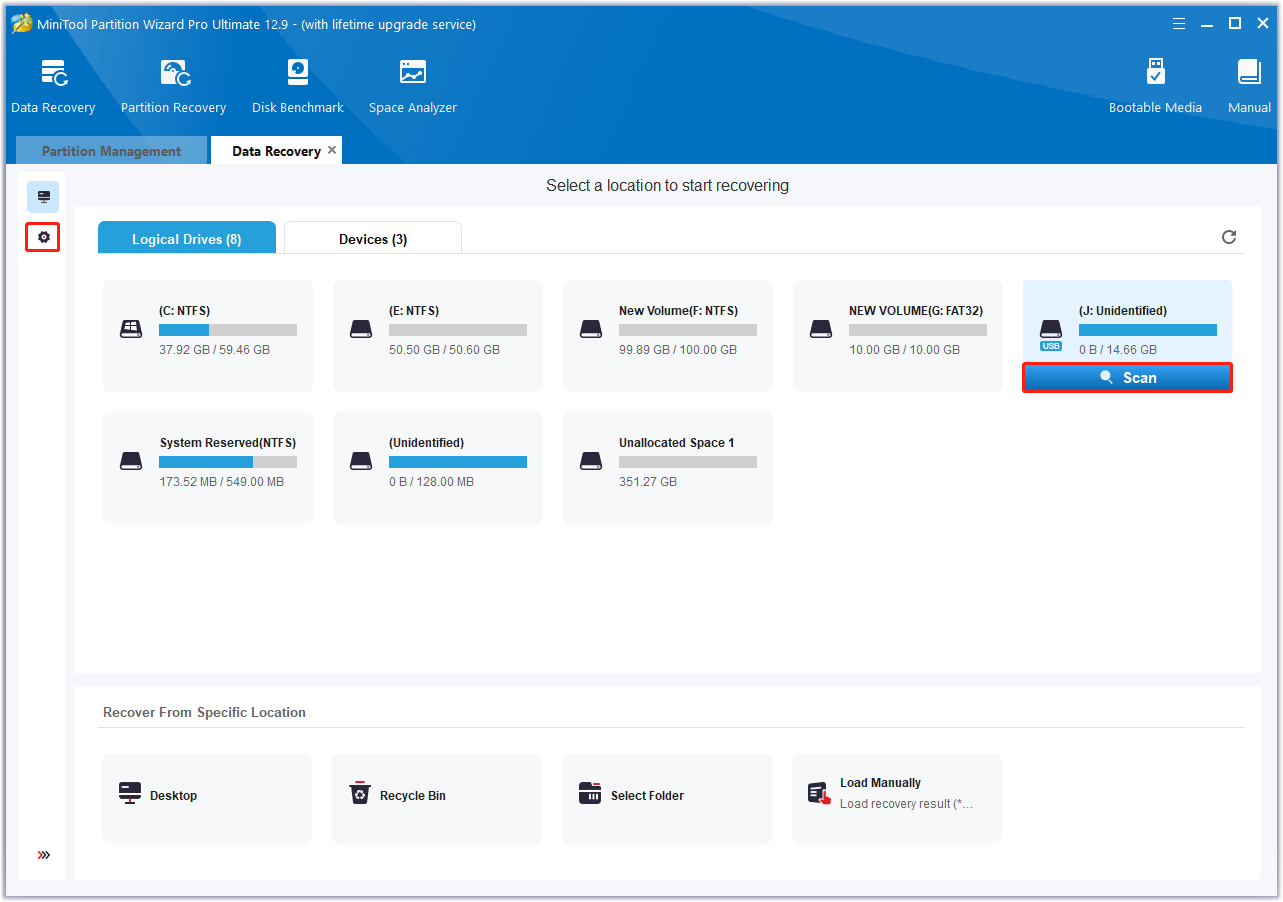
Step 2: In the window that appears, go to the Logical Devices tab, choose the SD card with data loss, and click on Scan.
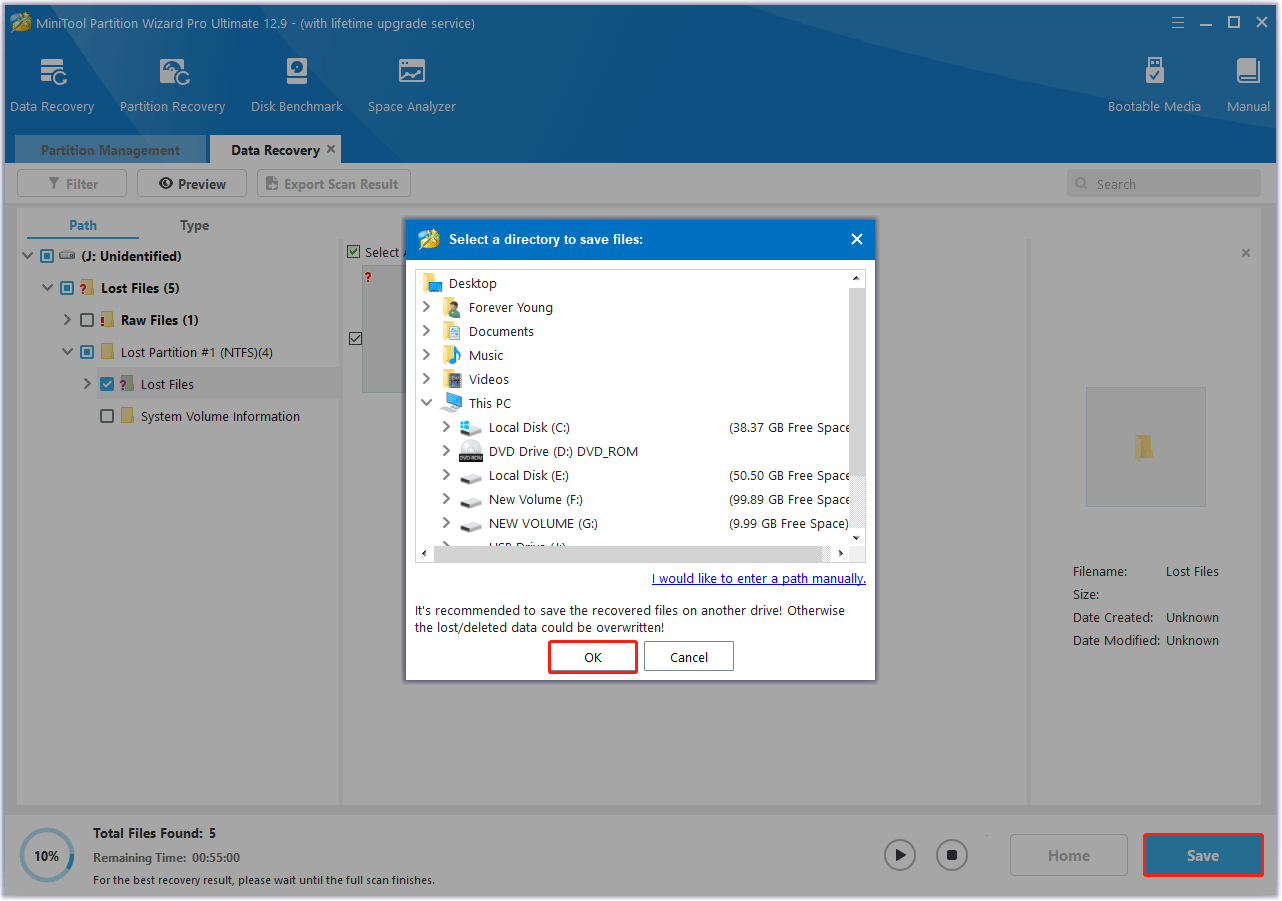
Step 3: Once the scan is complete, select the checkboxes next to the folders or files you wish to recover, then click Save.
Step 4: In the pop-up window, choose a destination to save the selected files or folders, then click OK to confirm.
Bonus Tip: Why Can’t Format SD Card
Here are some common reasons why an SD card may not format
Hardware Issues:
- Physical Damage: The card may be scratched, bent, or otherwise physically damaged, preventing it from being recognized or formatted.
- SD Card Write-Protected: SD cards have a physical write-protect switch. If this switch is enabled, the card cannot be formatted.
Storage Media Error:
- File System Error: The card’s file system (e.g., FAT32, exFAT) may be corrupted, preventing formatting. Or, the card may display as RAW, indicating it’s unreadable.
- Bad Sectors: Damaged sectors on the card can prevent formatting.
Other Issues:
- Incompatible Card Reader: The card reader may not be compatible with the SD card’s file system (such as exFAT or NTFS), especially on older card readers, which may not recognize cards in such formats.
- Low Battery: Some devices require a certain amount of battery power to format an SD card.
- Card in Use: If another program or device is accessing the card, formatting will fail.
- Virus Infection: Malware can interfere with formatting.
Bottom Line
This article addresses key questions such as what it means to format an SD card, why formatting is necessary, and how to perform the process safely.
Mastering this knowledge is crucial for protecting your SD card, extending its lifespan, and preventing data loss.
If you have any questions or suggestions while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can contact us via [email protected] to get a quick reply.
What Does Format SD Card Mean FAQ
2). Formatting, on the other hand, is a much more comprehensive operation. Full format erases all data on the SD card and rebuilds the file system (such as FAT32 or exFAT), essentially initializing the entire card.
1.2 exFAT: It is suitable for transferring large files and is compatible with newer devices.
1.3 NTFS: Primarily used on Windows computers, but not supported by some devices.

User Comments :