If you’re looking for a professional and detailed explanation of MBR vs GPT, you have come to the right place. This post also tells you how to choose between MBR and GPT, how to check if a disk is MBR or GPT, and how to convert between them using professional disk partition software.
When you install a new disk, the first thing to do is partition it. Disk partitioning will divide the disk into one or more regions (so-called partitions). Only after the partitions are created, can the disk be used to install operating systems or apps, store data, etc.
To partition a new disk, you must first choose a partition style for it. That is the disk initialization process that occurs when you connect a brand-new internal disk.
There are two types of partition styles: MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table). What’s the difference between them? How to choose or convert between them? Keep reading to get the answers.
MBR vs GPT Partition Structure
MBR and GPT partition style organize disk partitions into different structures. The following picture shows MBR vs GPT partition structure.
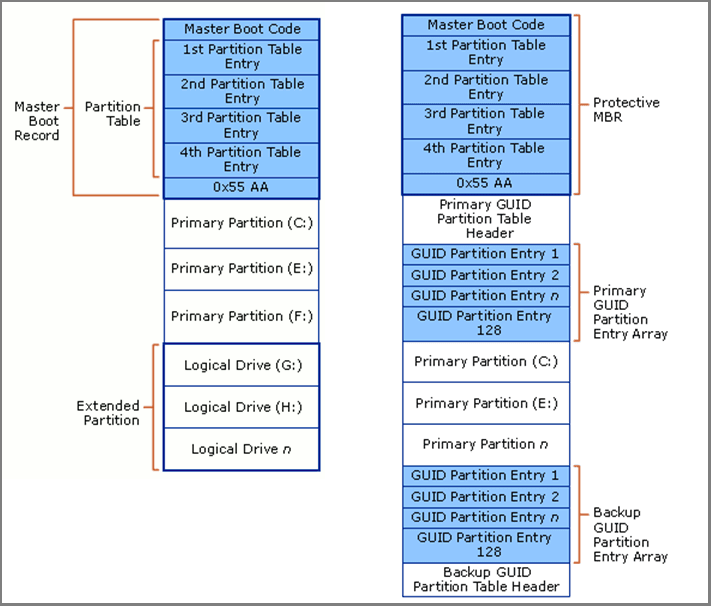
Read the following content to learn about the picture.
MBR Partition Structure
An MBR disk is composed of Master Boot Record and partitions (primary and extended). Master Boot Record is located in the first sector (512 bytes) of the disk, and it is composed of the following 4 parts.
- Master Boot Code: It takes up the first 440 bytes of the MBR sector, storing the first-stage system bootloader, which will find the active system to run the second-stage boot loader (like Windows Boot Manager). Then, the kernel operating system can be loaded. If the bootstrap code is corrupt, the system will not boot.
- Windows Disk Signature: It is the unique disk ID number that Windows writes during the disk initialization process, taking up 4 bytes after the bootstrap code. If this signature is corrupt, Windows will prompt you to initialize disk. Following Disk Signature, there are 2 bytes of null values. Many people may view Windows disk signature as part of Master Boot Code.
- MBR Partition Table: It occupies 64 bytes of data and every 16 bytes record a partition information. Therefore, MBR disks can only have 4 primary partitions, or 3 primary partitions plus 1 extended partition.
- MBR Boot Signature: It is the last 2 bytes of the MBR sector. Their values are always 0x55 and 0xAA.
Following the MBR, there are primary partitions and the only one extended partition that can be divided into many logical drives.
GUID Partition Structure
A GPT disk is composed of the following 6 parts.
- Protective MBR: Located in the first sector of the disk, it is functionally equivalent to a normal MBR, but has no boot code and only one partition. This partition is of type 0xEE (EFI_GPT_DISK). The purpose of protective MBR is to provide compatibility with legacy tools that do not understand the GPT format.
- GPT Header: Located in the second sector of the disk, it records the location of the GPT Partition Table, CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) checksum, etc.
- GPT Partition Table: Taking up a total of 32 sectors, it can accommodate 128 partition table entries. Hence, a GPT disk can hold up to 128 partitions. Each partition table entry records the partition’s GUID (Globally Unique Identifier), start and end positions, partition type, partition name, etc.
- GPT Partitions: GPT supports up to 128 partitions and all of them are primary partitions. You can use any of them to install OS.
- GPT Header Backup: Located in the last sector of the disk, it offers the details about the GPT Partition Table Backup.
- GPT Partition Table Backup: It is a complete backup of the GPT partition table. If the original partition table is corrupt, the system will read the backup to recognize partitions.
MBR vs GPT Key Differences
| Comparison Options | MBR | GPT |
| Max Disk Size | 2TB | 8ZB or 64ZB |
| Partition Number | 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions plus 1 extended partition | 128 primary partitions |
| Partition Table Security | No safety measures | Backup + CRC check |
| Supported Boot Mode | Legacy BIOS | UEFI |
| Supported OS | Older systems | Newer systems |
GPT vs MBR Disk Size
For MBR, the available size for block addresses and related information is limited to 32 bits. Therefore, for hard disks with 512‑byte sectors, the MBR partition table entries allow a maximum size of 2 TiB (2³² × 512 bytes).
As shown in the picture below, Disk 0 is an MBR disk, and the portion exceeding 2TB is unusable.
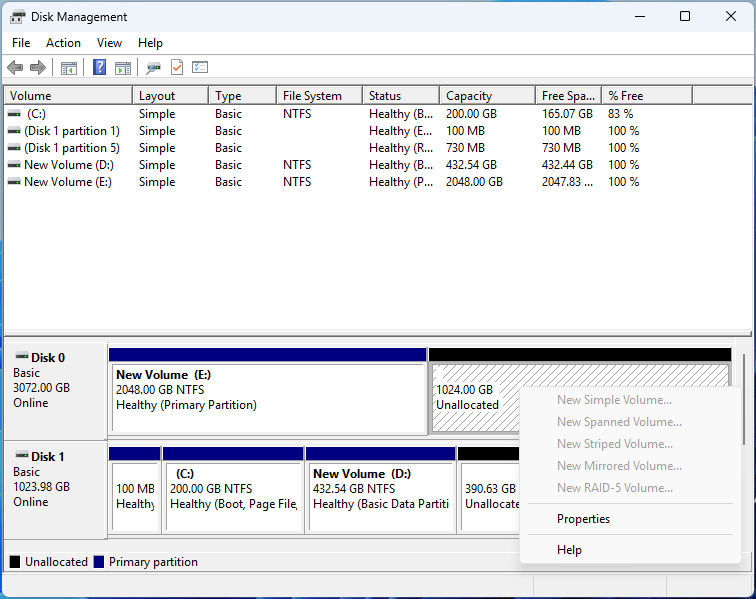
On the other hand, GPT uses 64 bits for logical block addresses, allowing a maximum disk size of 264 sectors. For disks with 512‑byte sectors, the maximum size is 8 ZiB (264 × 512 bytes). For disks with 4,096‑byte (4K) sectors, the maximum size is 64 ZiB (264 × 4,096‑bytes).
Further Reading:
Can MBR break through the 2TB limit if we apply it on 4K disks? This depends on whether the 4K disks have an emulation technology (512e).
If the 4K disks use 512e, the MBR size limit is 2TB still. If the 4K disks are native (without 512e), the max size can be up to 16TB theoretically.
In 2010, hard-disk manufacturers introduced drives with 4K sectors (Advanced Format). For compatibility with legacy hardware and software, those 4K drives use the 512e technology that presents 512‑byte sectors to the computer, despite their underlying 4K physical sectors.
Since April 2014, 4K native drives have been available on the market. However, applying MBR on native 4K disks may encounter compatibility issues.
GPT vs MBR Partition Number
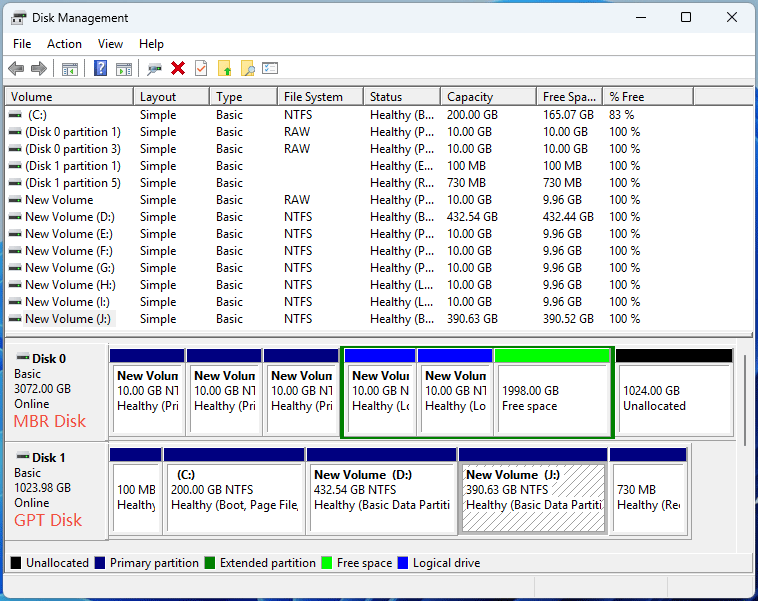
Another main difference between MBR and GPT is the number of partitions, which is determined by the partition table.
According to the partition table structure, an MBR disk can only has 4 primary partitions, or 3 primary partitions plus 1 extended partition, while a GPT disk can be divided into up to 128 primary partitions.
Besides, only the primary system can serve as a system partition.
GPT vs MBR Security
The GPT has a backup of the header and the partition table. If the header or partition table is corrupt, the computer can read the backup to access the disk partitions or system. MBR doesn’t have a backup. Therefore, if the MBR is corrupt, the partitions or the system may be inaccessible.
In addition, GPT has CRC check, which can recover GUID partition table automatically.
GPT vs MBR Boot Mode
If you want to use an MBR or GPT disk as a system disk, the boot mode should be changed in the firmware. In general, MBR system disks use BIOS boot mode while GPT system disks use UEFI boot mode. Click BIOS vs UEFI to know more.
If you clean install Windows on disk, ignoring the boot mode, you may encounter error “The selected disk is of the MBR/GPT partition style.” If you have changed the system disk’s partition style, you should also change the boot mode. Otherwise, the system won’t boot.
GPT vs MBR OS Support
The following Windows versions can boot from MBR or GPT disks:
- Since MBR is a traditional partition style, all Windows systems support booting system from MBR disks except for Windows 11 and Windows Server 2025 (or later versions).
- All 64-bit Windows systems support booting from GPT disks except for Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Server 2003.
- For 32-bit Windows systems, only Windows 8, 8.1, and 10 support booting from GPT disks.
The following Windows versions can read and write on MBR or GPT disks:
- All Windows versions, including Windows 11 and Windows Server 2025, support reading and writing data on MBR disks.
- All Windows systems support reading and writing data on GPT disks, except for Windows 9x/XP 32-bit and Windows Server 2003 32-bit.
How to Choose Between MBR and GPT
What about MBR vs GPT SSD? Should I choose MBR or GPT for SSDs?
Actually, the storage medium of the drive doesn’t affect the choice between MBR and GPT. GPT is obviously better than MBR. Therefore, if your computer supports GPT disks, choosing GPT always.
Does my computer support GPT disks? This depends on the OS and the motherboard.
- From the perspective of operating system compatibility, for Windows 7 and older operating systems, it’s best to use MBR on the system disks, which can avoid boot and compatibility issues. For Windows 8 and later systems, GPT is recommended.
- From the perspective of boot mode, booting form GPT disks usually requires UEFI. However, older motherboards usually do not have UEFI, and most motherboards before 2011 only support traditional BIOS boot mode. Although some older motherboards may support UEFI through a BIOS update, this is not common.
- From the perspective of disk capacity, if a disk is larger than 2TB, GPT is recommended.
- For USB drives, MBR is recommended so that you can use them in more systems.
How to Check Disk Partition Style
Is your disk GPT or MBR? You can check that using Windows Disk Management or some commands.
#1. Use Disk Management
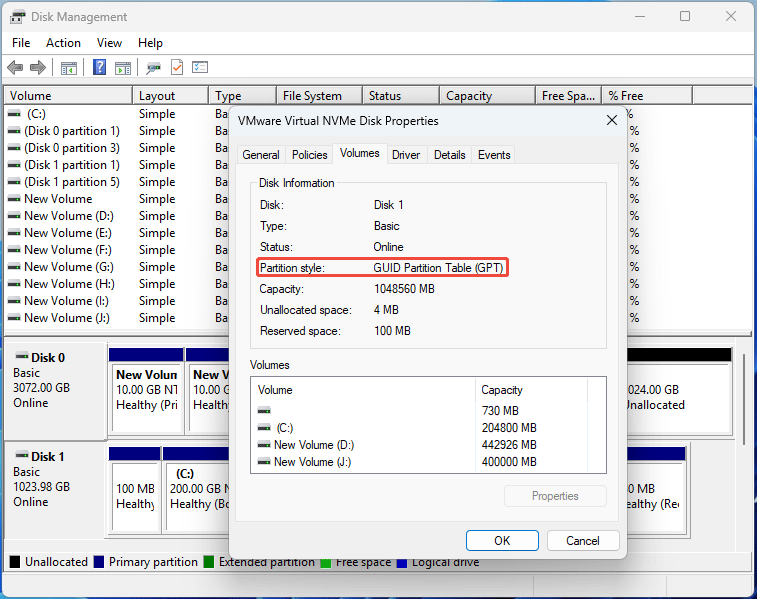
Disk Management is a Windows GUI tool for managing disks and partitions. You can also use it to check the status and properties of the disks and partitions. Here is how to use it to check the disk partition style:
- Press the Windows logo key + X and select Disk Management from the menu.
- Right-click on the disk and choose Properties.
- Go to the Volumes tab and you will see the Partition style information.
#2. Use DiskPart Commands
DiskPart is a Windows command tool used to manage disks and partitions. It can check the disk partition style easily and the steps are as follows:
- Press the Windows logo key + R to open Run.
- Type “diskpart” and press Enter to open the DiskPart tool.
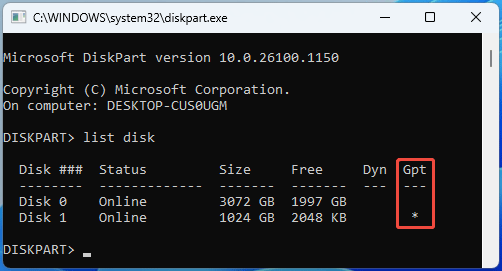
- On the command prompt window, type “list disk” and then press Enter.
- Check the Gpt column. An asterisk symbol indicates that this disk is a GPT disk. Otherwise, the disk is uninitialized or a MBR disk.
#3. PowerShell
PowerShell comes pre-installed on all modern versions of the Windows operating system. It is an easy-to-use command-line shell and scripting environment for automating management tasks on Windows-based systems. Disk and partition management is one of the many features you can perform with it.
Here is how to check if the disk is GPT or MBR using it:
- Press the Windows logo key + X and select Terminal or Windows PowerShell from the menu.
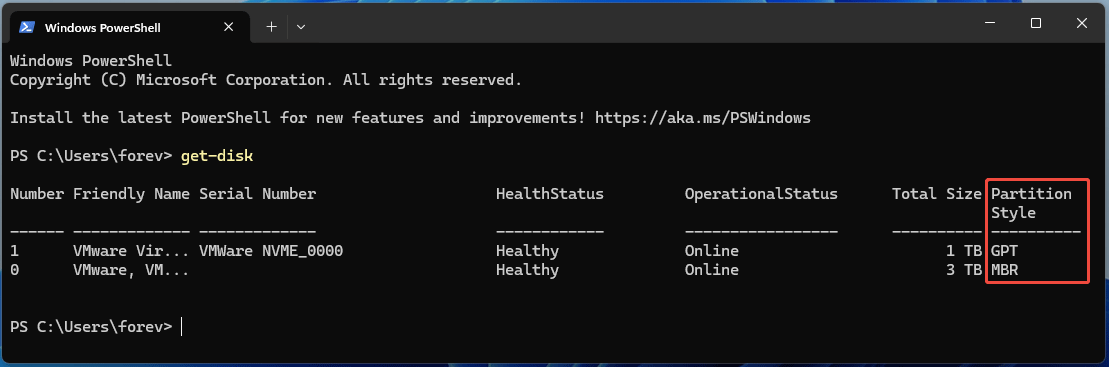
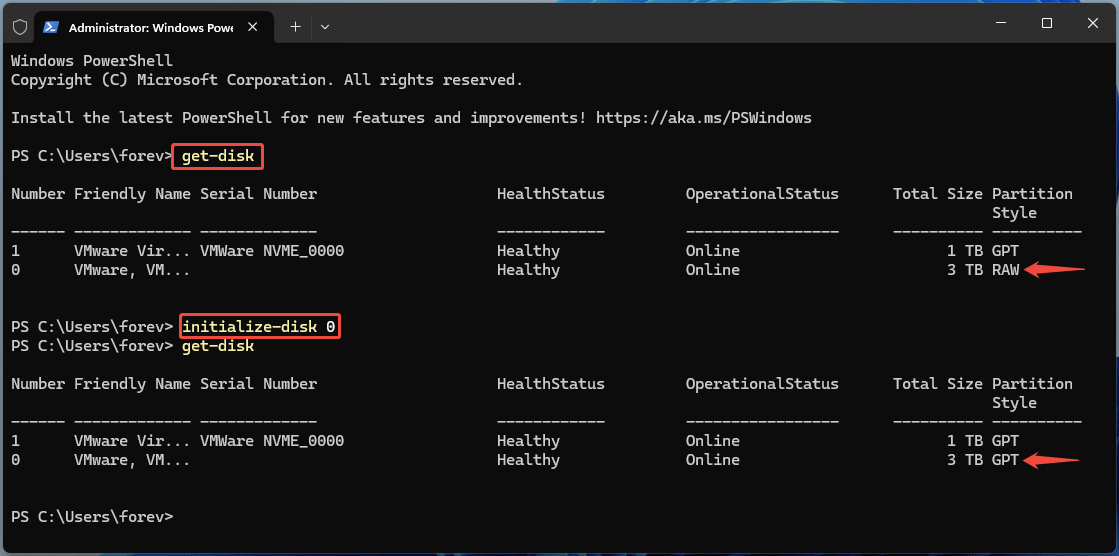
- Once PowerShell opens, type “get-disk” and press Enter.
- Check the Partition Style column. It will tell you if the disk is MBR or GPT.
Initialize Disk to MBR or GPT
If you connect a brand-new internal disk to your computer, you need to initialize it for use. Here, I will show you how to initialize disk MBR or GPT using Disk Management, DiskPart, and PowerShell.
#1. Use Disk Management to Initialize Disk
The steps are simple. You just need to:
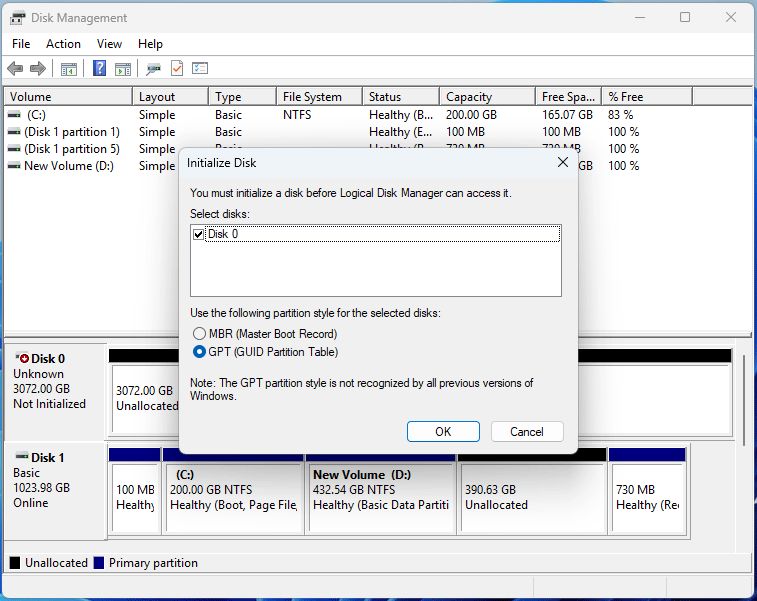
- Open Disk Management.
- Right-click the Unknown disk and choose Initialize Disk.
- On the pop-up window, select a partition style and then click OK.
#2. Use DiskPart to Initialize Disk
To initialize a new disk using DiskPart commands, you need to open the DiskPart tool and then execute the following commands one by one.
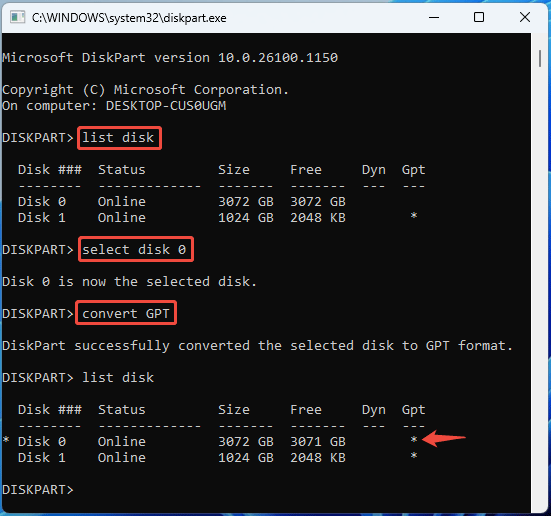
- List disk (it will list all disks so that you can check the disk number)
- Select disk * (* is the number of the disk you want to initialize)
- Convert GPT/MBR (choose GPT or MBR according to your need)
#3. Use PowerShell to Initialize Disk
To use PowerShell to initialize a disk, you need to run it as administrator. Then, use the following commands.
- Get-disk (use it to check the number of the disk you want to initialize)
- Initialize-disk disknumber (this command will initialize the disk to GPT. If you want to initialize the disk to MBR, you need to add “-PartitionStyle MBR”)
How to Convert to MBR or GPT
Sometimes, you need to convert MBR to GPT or vice versa. In this part, I will show you how to do that in different approaches.
#1. Use MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a professional disk and partitioning management tool. It can do partition and disk conversions without data loss. For example:
- Convert partitions between FAT32 and NTFS.
- Convert a primary partition to a logical drive and vice versa.
- Convert a disk between MBR and GPT.
- Convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk.
How to convert MBR to GPT or vice versa with MiniTool Partition Wizard? Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
2. If you want to convert the system disk to GPT or MBR, for system safety, you need to back up the system or make a bootable USB drive with MiniTool Partition Wizard before the conversion.
3. After converting the system disk, you need to change the boot mode.
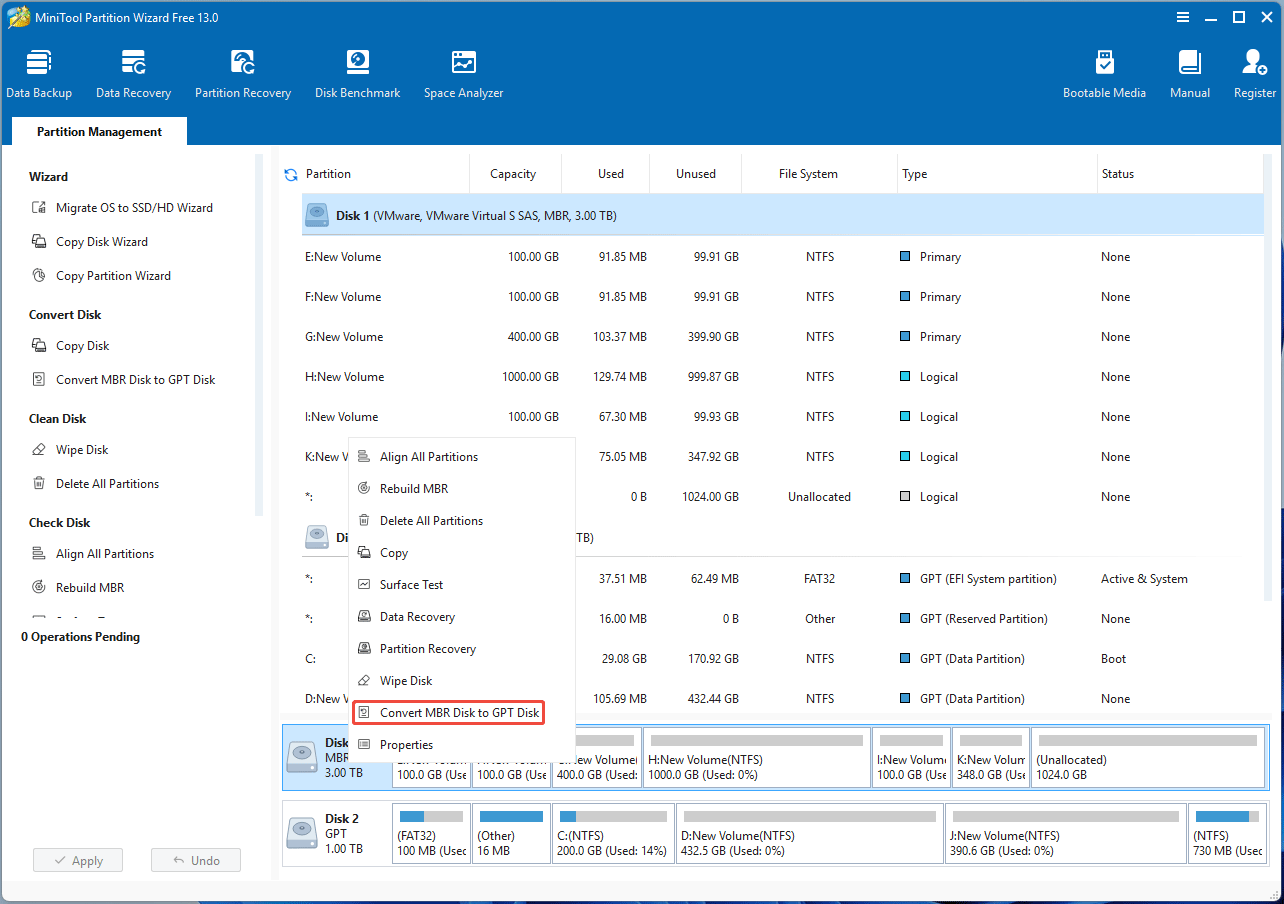
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and right-click an MBR disk. Then, select Convert MBR Disk to GPT Disk.
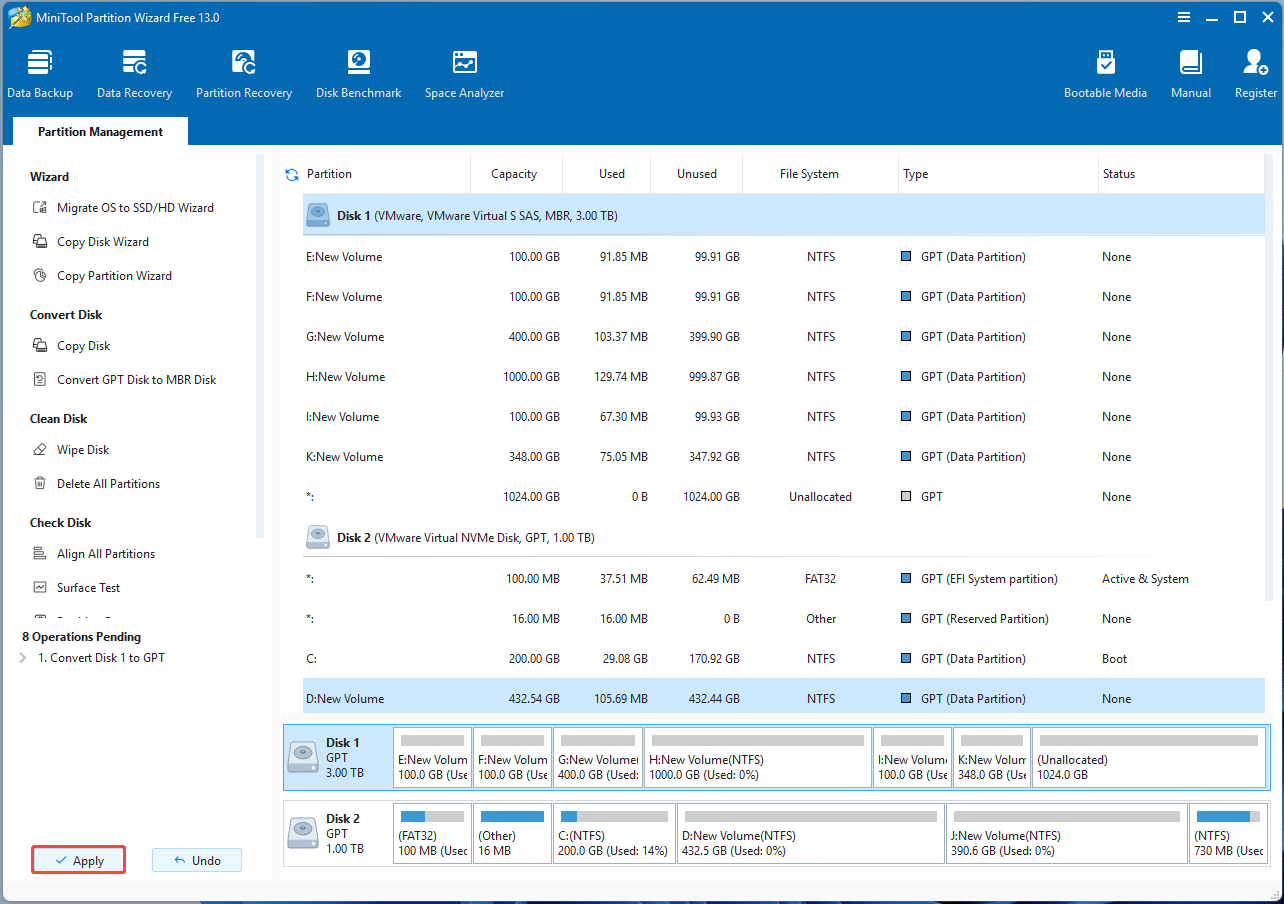
Step 2: Click the Apply button to start the conversion.
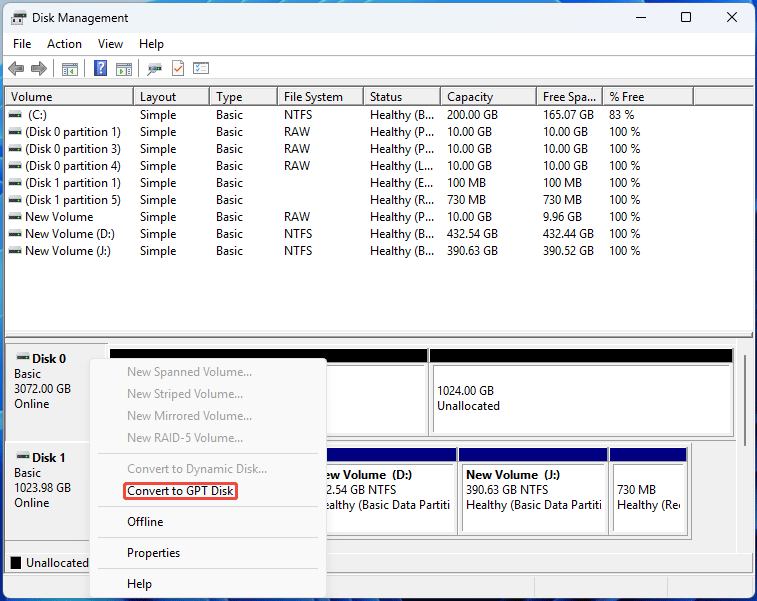
#2. Use Disk Management
Disk Management can convert disks to GPT or MBR. However, this conversion requires you to delete all partitions on the disk. In addition, the system disk in use cannot be converted.
Here is the guide:
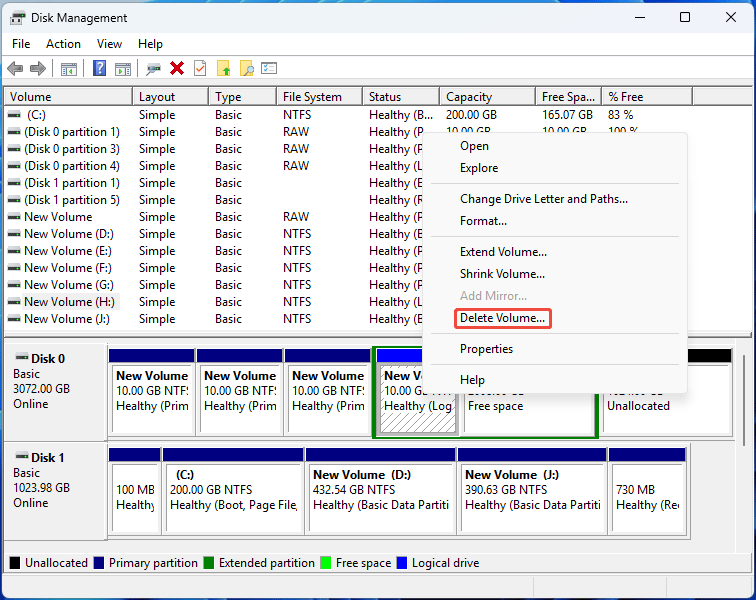
Step 1: Delete all partitions on the disk.
- Open Disk Management.
- Right-click a partition and then select Delete Volume.
- Repeat this operation to delete all partitions.
Step 2: Once all partitions have been deleted, right-click the disk and then choose the Convert to GPT Disk or Convert to MBR Disk option.
#3. Use DiskPart
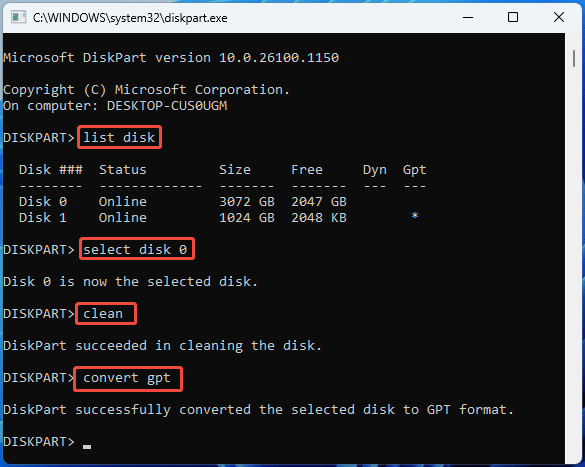
Like Disk Management, DiskPart also requires you to delete all partitions on the disk and the system disk in use cannot be converted.
The commands to convert disk are the same to disk initialization, except that you need to clean the disk first. Open DiskPart and apply the following commands one by one:
- List disk
- Select disk *
- Clean
- Convert GPT/MBR
#4. Use MBR2GPT
Windows 10 version 1703 64-bit or later 64-bit systems include a tool called MBR2GPT, which can convert the system disk from MBR to GPT without data loss. However, to make sure the conversion is successful, the system disk should meet the following requirements:
- The system disk is an MBR disk and can work normally.
- The system disk is not in dual boot.
- The disk has at most 3 primary partitions and has no extended/logical partition.
- All partitions on the MBR disk can be recognized by Windows.
- The system disk is not encrypted by BitLocker or the BitLocker has been suspended.
- The disk has enough free space at the front and end of the disk (16KB + 2 sectors at the front and 16KB + 1 sector at the end).
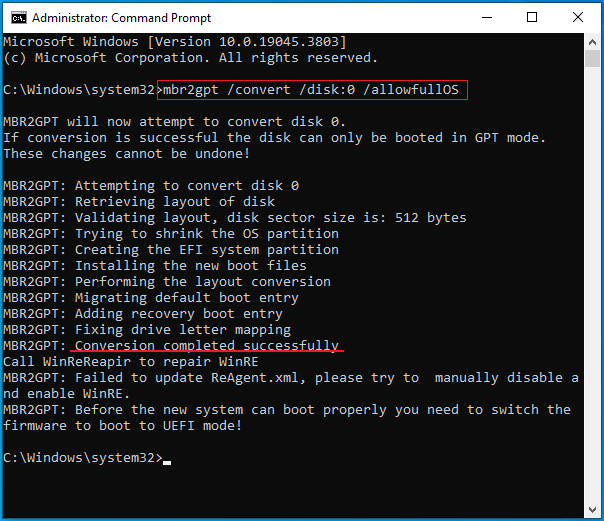
To convert the system disk from MBR to GPT with MBR2GPT, you can follow the steps below:
- On the Windows Search bar, type “cmd”.
- From the result list, right-click Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
- On the Command Prompt window, type “mbr2gpt /convert /disk:* /allowfullOS” and press Enter. * is the number of the system disk.
FAQ
Bottom Line
Does this post answer your questions about MBR vs GPT? Do you have problems with MiniTool Partition Wizard? Feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will reply you soon.



User Comments :