How much SSD do I need? Actually, the SSD storage space you need depends on how you use your computer. For beginners, 256GB is sufficient. For intermediate users, 512GB-1TB is enough, while advanced users may need a 2TB or even larger SSD. The following content from Partition Magic will tell you in detail.
How much SSD storage do I need? This question may linger in your mind whenever you are ready to buy a new solid-state drive for your computer. Before understanding this question, let’s first know the SSD capacity and SSD form factors.
Common SSD Sizes and Form Factors
SSD capacity ranges widely, from 128GB to 30TB. The most commonly used capacity for general users is 256GB to 2TB. There are 4 common SSD form factors: 2.5-inch SATA, M.2 SSD, mSATA SSD, and U.2 SSD.
The following is a detailed introduction to SSD capacity and size.
SSD Sizes
- 128GB: Suitable for users who only install the system and a few programs.
- 256GB: Suitable for users who install lightweight games and multiple applications.
- 512GB: Provides ample space for application games and media files, suitable for ordinary users.
- 1TB: Suitable for gamers and users who handle large files.
- 2TB or more: Suitable for users with higher storage requirements.
SSD Form Factors
- 2.5-inch: The 2.5-inch SSD is the most widely used form factor. Measuring around 100 mm by 70 mm, with a typical thickness of either 7 mm or 9.5 mm, it is compatible with the majority of laptops and desktop computers.
- M.2 SSD: M.2 SSD has two protocol versions: SATA and NVMe. M.2 SSD based on NVMe protocol has faster performance.
- mSATA: mSATA stands for mini-SATA and uses the mSATA interface. It is only one-eighth the size of a 2.5-inch SSD and is commonly used in laptops and tablets.
- U.2: U.2 looks like a 2.5-inch hard drive, but is slightly thicker. It is usually used in high-end workstations and servers that require more storage space.
After a preliminary understanding of the capacity and size of the SSD, let’s take a look at the factors that need to be considered when choosing an SSD.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an SSD Storage
When choosing SSD storage, you should consider the operating system space occupied, the use of cloud storage and external hard drives, future expansion requirements, and your budget.
Here is an explanation of these 5 points:
- Operating system: The operating system itself takes up a certain amount of storage space, typically around 20 to 30GB for Windows. Over time, system updates and cache files can consume even more space. So, when choosing an SSD, be sure to leave enough space for the operating system.
- Cloud storage: If you primarily use cloud storage for your files, photos, and videos, an SSD with a smaller capacity may be sufficient.
- Future Requirements: When purchasing an SSD, you should consider long-term usage, future needs, and how many programs you may install.
- Budget: The price of an SSD generally increases with its capacity. Be sure to consider your budget and select a capacity that meets your specific needs.
- External drive: If you plan to store most of your data on an external drive, you might consider a smaller SSD.
- Game storage: Today’s games take up a lot of space, so be sure to account for your game library size when selecting an SSD.
- File storage: Storing large files such as videos, photos, or music requires more storage capacity.
Now that we understand SSD size, capacity, and the key factors to consider when buying one, let’s take a look at how much storage space you might need.
How Much SSD Do I Need
Whether you’re buying a laptop or building your PC, choosing an SSD with the right capacity is essential. It not only helps reduce costs but also improves performance and prevents issues with insufficient storage space.
So, how much hard drive do I need? Let’s find out.
As a matter of fact, choosing the right SSD capacity is quite simple. It mainly depends on your personal needs. Below, I’ve summarized the recommended SSD capacities for basic use, as well as for moderate use and advanced use.
#1. Basic Use
256GB:
For beginners, a 256GB SSD is generally sufficient. However, if you install a lot of applications or store large files, the drive can fill up quickly.
This capacity is best suited for basic tasks like web browsing, streaming videos, working with Word or Excel documents, and managing emails.
If you’re only considering your current needs, 256GB is a reasonable entry-level option.
512GB:
For basic web browsing and office work, 256GB is generally sufficient. However, if you plan to store large video files or install games, you’ll need more storage space.
Indeed, 512GB is a cost-effective choice for average users. It provides enough storage for the operating system, office software, games, and some multimedia files, without the need to frequently free up space.
#2. Moderate Use
512GB:
For users who perform basic tasks, play casual games, and manage digital media, a 512GB SSD is a solid choice. It‘s ideal for running smaller, indie, or niche titles.
However, if you’re a heavy gamer who frequently plays AAA titles, you may need at least a 1TB SSD to accommodate larger game installations.
1TB:
A 1TB SSD will hold more games than a 512GB SSD. Perfect for storing larger games, movies, and other media files without running out of space.
#3. Advanced Use
1TB:
For the majority of users, a 1TB SSD strikes an ideal balance between performance, storage space, and cost. It handles everyday tasks with ease while delivering the fast speeds typical of SSDs.
It’s ideal for gamers, content creators, and professionals working with large files. It provides ample space for games, software, and multimedia content.
2TB and More:
For tasks such as handling large files, playing AAA games, video editing, installing multiple operating systems, or running virtual machines, a 2TB or larger SSD is likely the better option.
For gamers, many AAA titles now exceed 100GB in size, with a few even reaching several hundred gigabytes. For video editors, 4K and 8K footage can be enormous, often tens of gigabytes per file.
That’s why a high-capacity SSD is a better fit for your needs.
Well, some users still hesitate between 256GB, 512GB, 1TB, and 2TB SSDs. It depends on your specific needs and budget. Here are some brief overviews to help you make a decision:
If the following conditions are met, choose a 256GB SSD:
- You only install basic software such as Windows, Office, and browsers.
- PPT and PDF files are not large.
- Your data is mainly stored in the cloud.
- Your budget is insufficient.
If the following conditions are met, choose a 512GB SSD:
- There needs to be a lot of free space after installing daily office software.
- It can meet the needs of light image processing and document editing.
- You can install 3 to 6 3A games and multiple independent games.
- Store a small amount of high-quality photos and high-definition video materials.
If the following conditions are met, choose a 1TB SSD:
- You have medium storage needs for games, photos, videos, and files.
- You are looking for a balance between capacity and budget.
- You often use cloud storage or external drives to store larger files.
If the following conditions are met, choose a 2TB SSD:
- You frequently work with large files, such as 4K video editing.
- You have an extensive media library or game collection.
- You run multiple virtual machines.
- You want your system to be able to handle growing storage needs in the future.
- You have enough budget.
How to Upgrade the SSD After Purchase
After purchasing a new SSD, you may want to migrate data from your old hard drive to the new one. In this case, I recommend using third-party software such as MiniTool Partition Wizard.
The software’s Copy Disk, Migrate OS to SSD/HD, and Copy Partition features can help you perform different types of disk migration.
- Copy Disk: Copy Disk usually refers to the process of copying the entire hard disk (including the system, data, partition structure, etc.) to another hard disk.
- Migrate OS to SSD/HD: Migrate OS to SSD/HD means migrating the operating system (OS) from the current hard disk to another hard disk (SSD or HDD) instead of copying the entire disk.
- Copy Partition: Copy Partition is a partition-level clone that only migrates the data of a selected partition.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
#1. Use Copy Disk
Step 1: Connect the new SSD to your PC, then launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to its main interface.
Step 2: Right-click the disk and then select Copy from the menu. Also, you can click the Copy Disk feature from the left action panel.
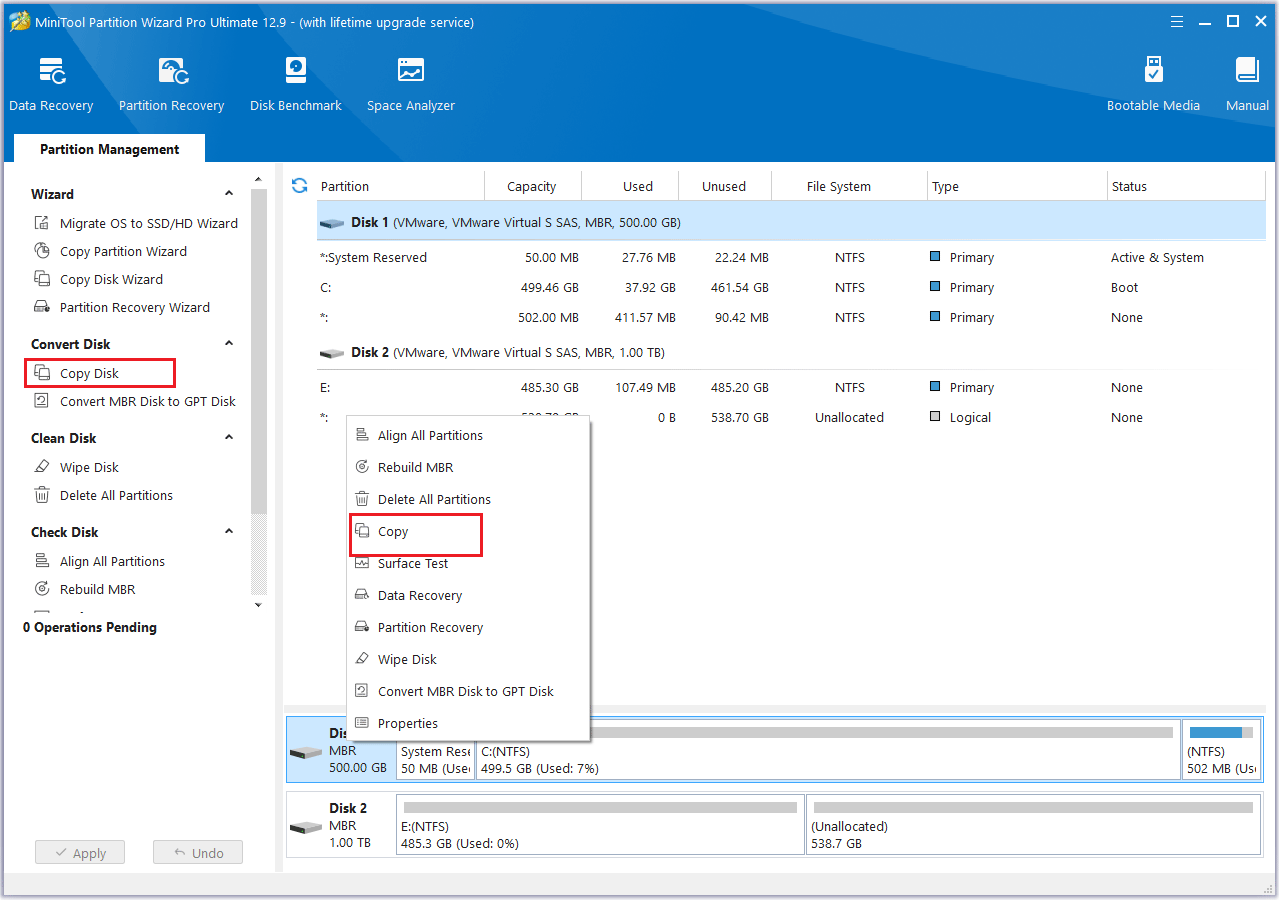
Step 3: In the pop-up window, choose the new SSD as the target disk, then click Next. When prompted to confirm, click OK to proceed.
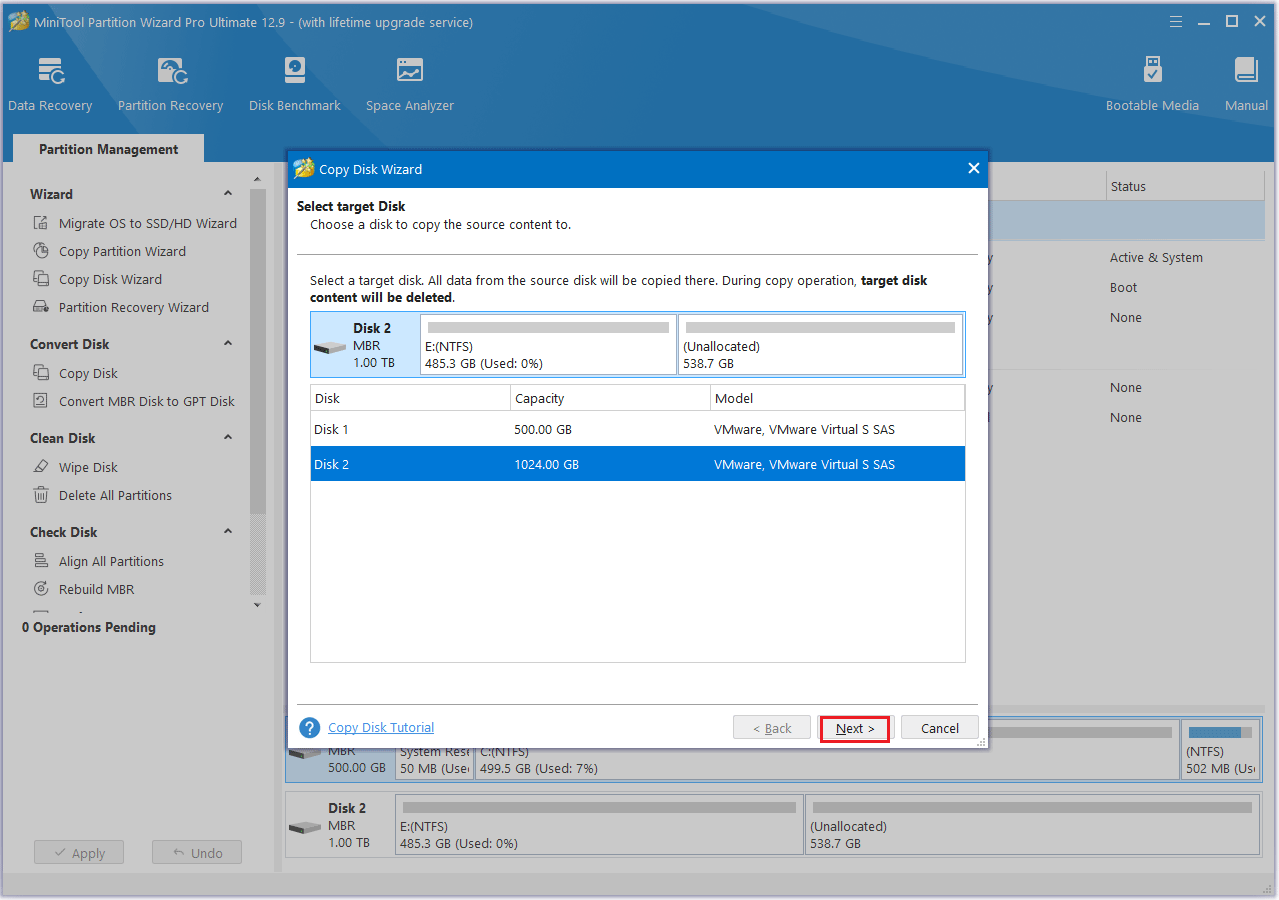
Step 4: On the next window, set Copy Options and adjust Target Disk Layout. Then click Next to proceed.
- Fit partitions to entire disk: If you choose this option, the target disk partition size will be adjusted automatically to fit the entire disk.
- Copy partitions without resizing: If you choose this option, the size of the source disk partitions will be used.
- Align partitions to 1MB: This option could help improve performance for SSD and advanced format disks, so please keep it checked if users are using such devices.
- Use GUID Partition Table for the target disk: This option allows you to use all the space on a hard disk larger than 2TB, but UEFI boot should be enabled in the BIOS.
- Change Selected Partition: You can resize or move the partition according to your needs.
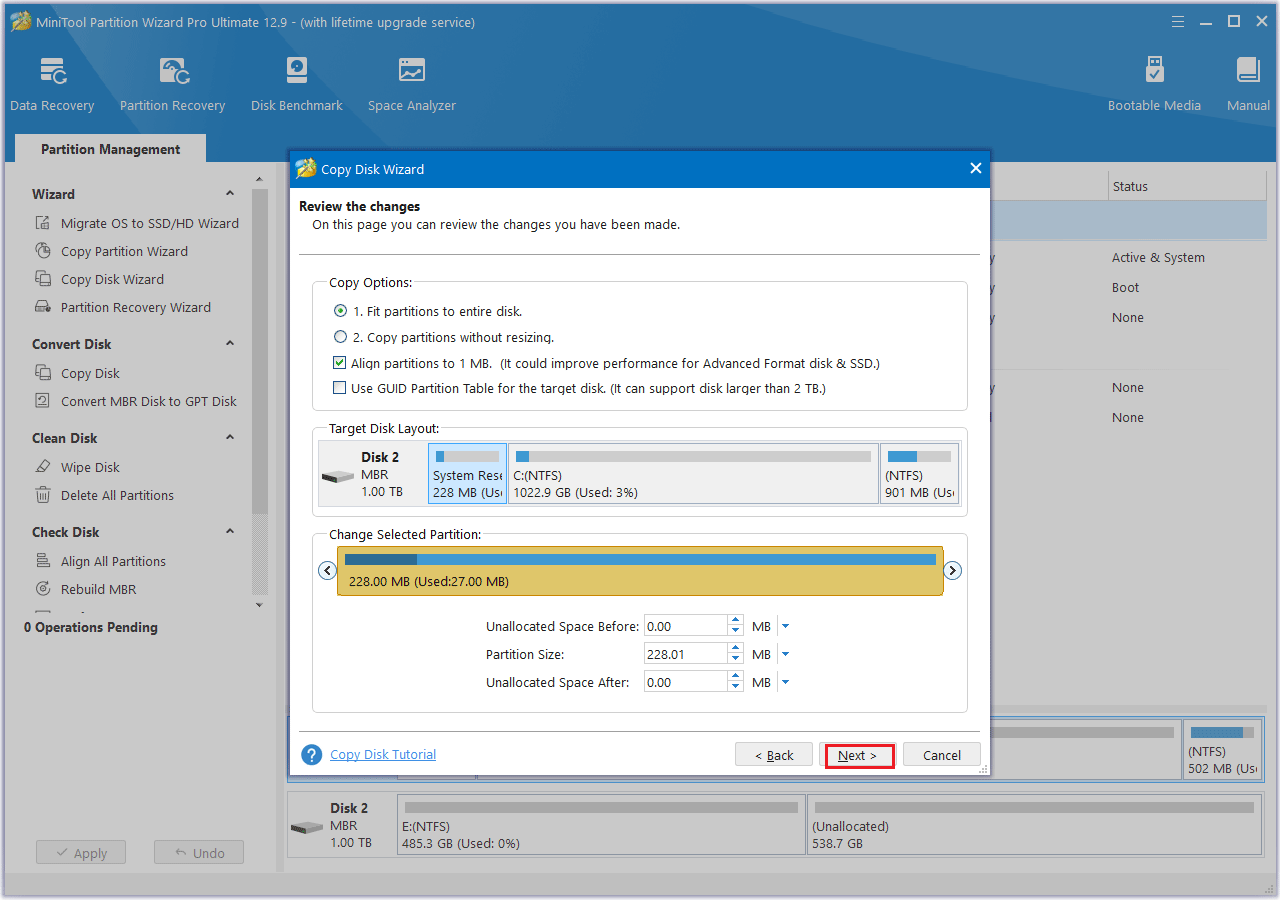
Step 5: A warning message “How to boot from the Destination disk?” will pop up, and click Finish to continue.
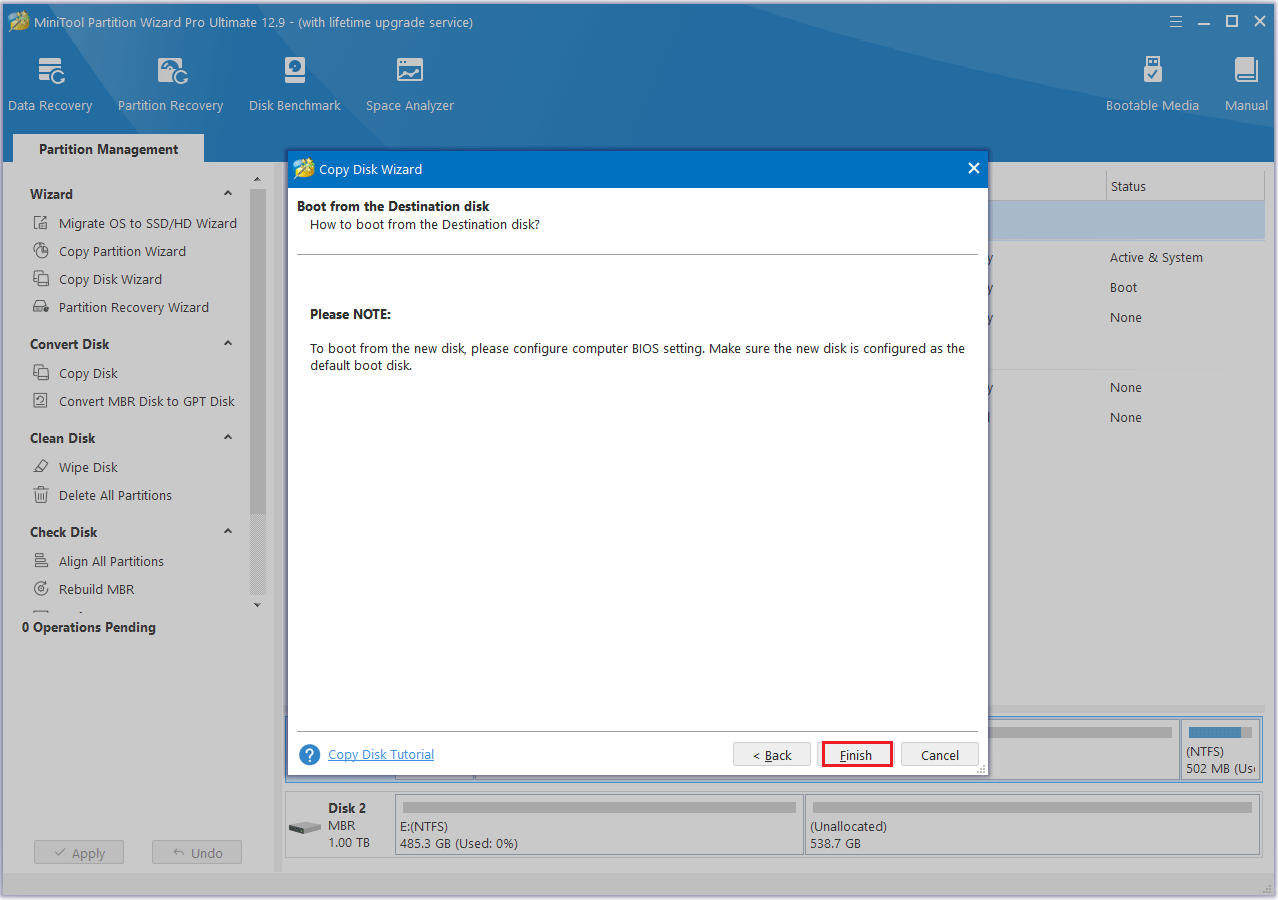
Step 6: Next, click the Apply button to carry out the pending operation.
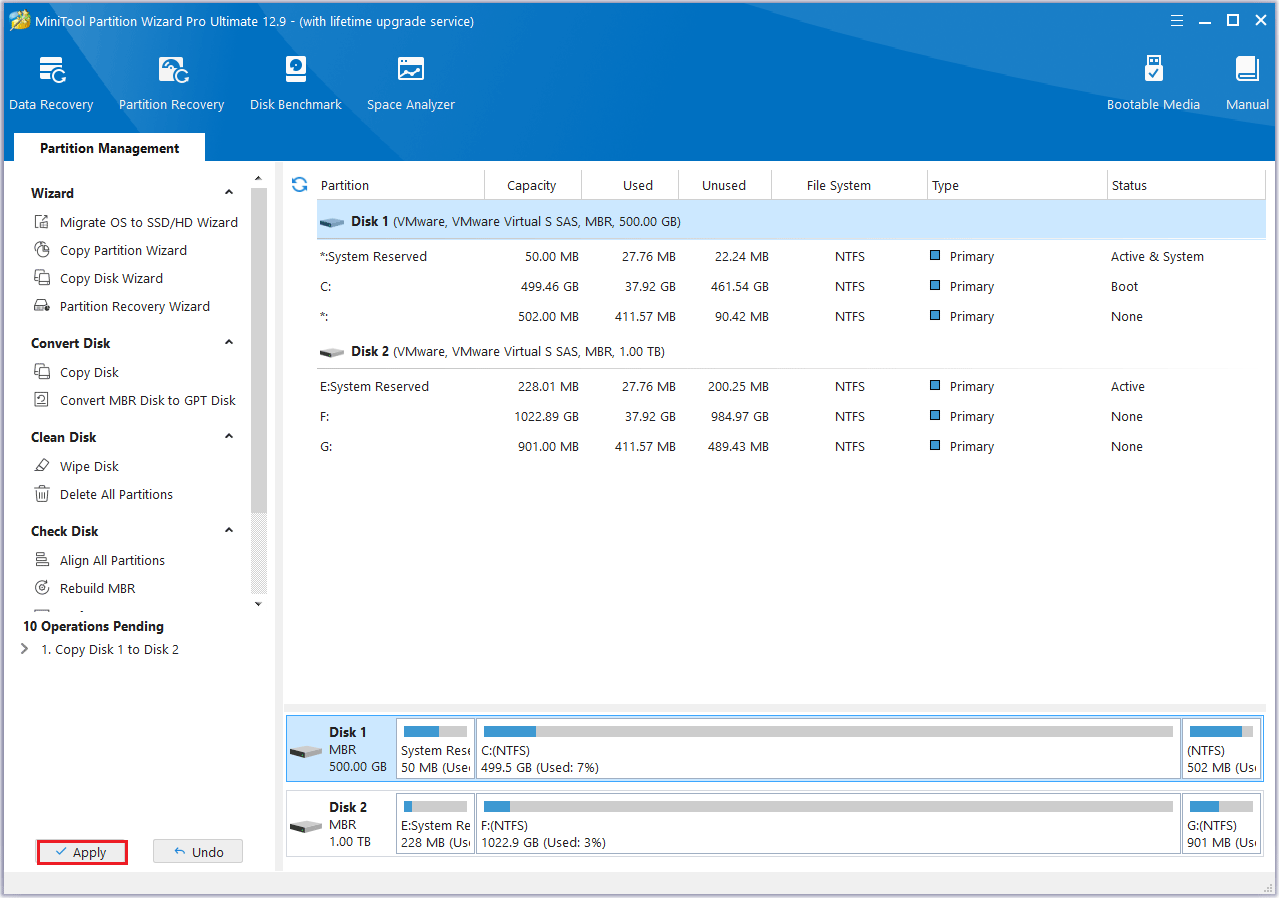
#2. Use Migrate OS to SSD/HD Wizard
Step 1: Connect the new SSD to your computer and launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to its main interface. Click on the Migrate OS to SSD/HD Wizard feature from the left action panel.
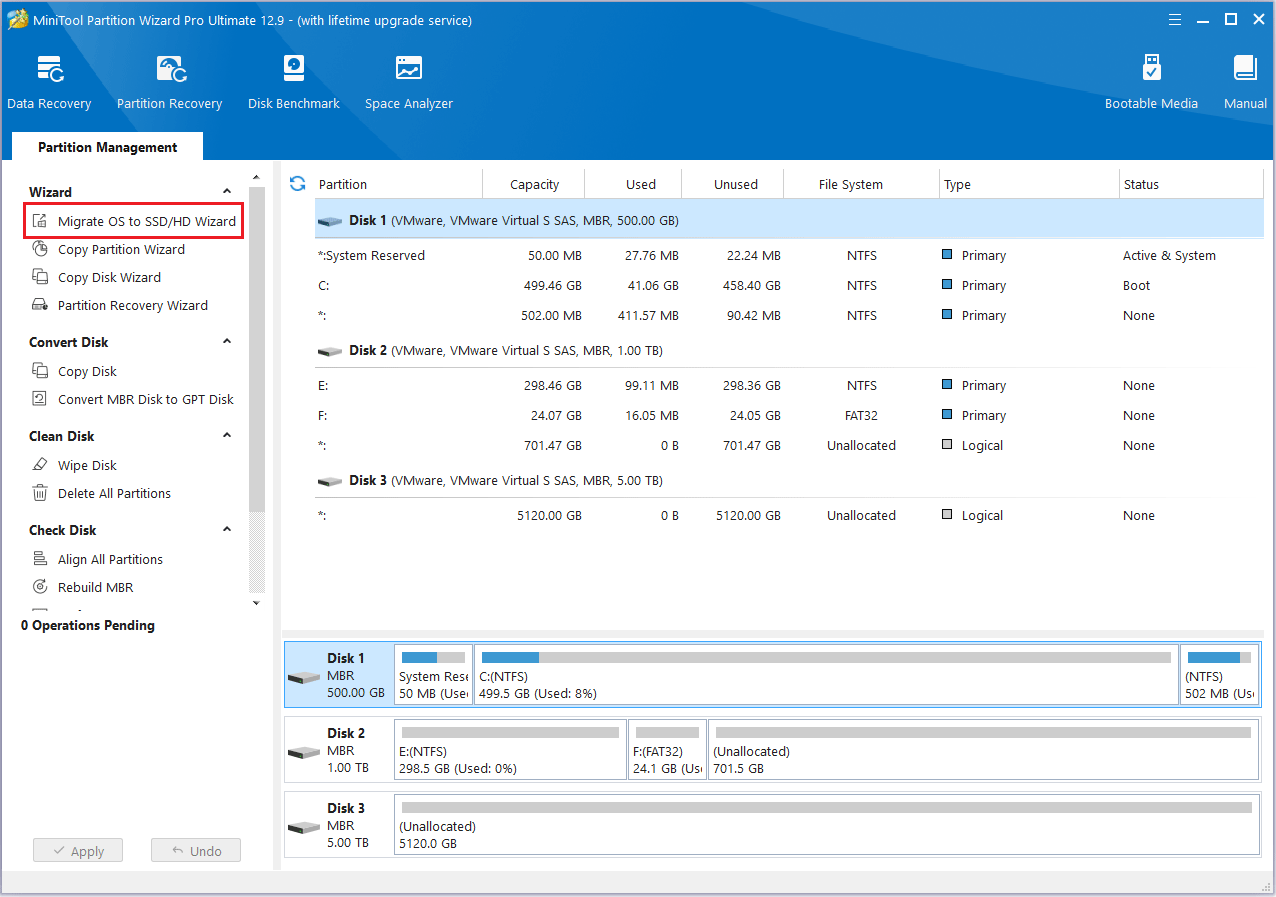
Step 2: Choose option B to migrate your OS to the SSD and click Next.
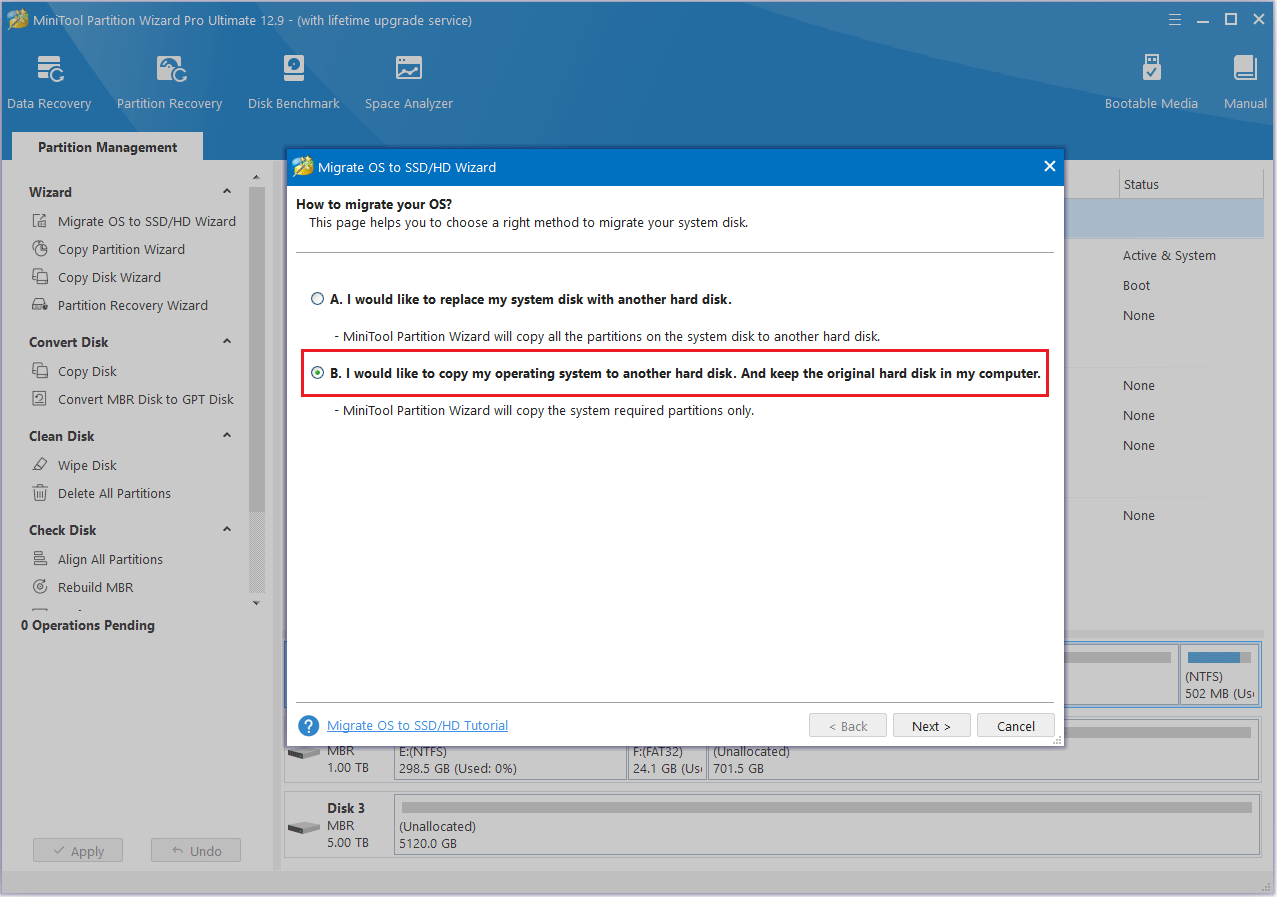
Step 3: Choose the SSD as the target disk and then click the Next button.
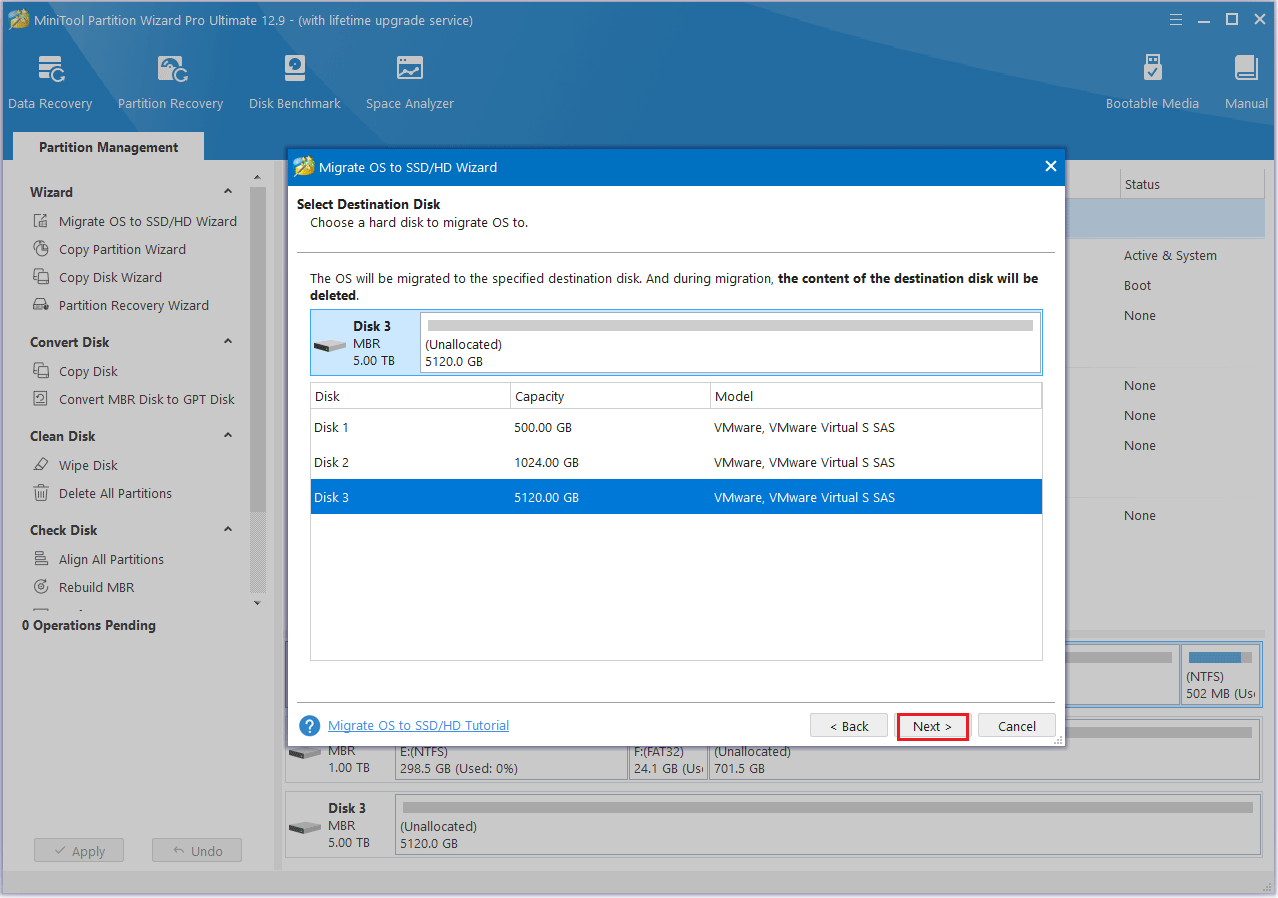
Step 4: Choose a copy option and then click the Next button.
Step 5: Review the pop-up message, then click the Finish > Apply button.
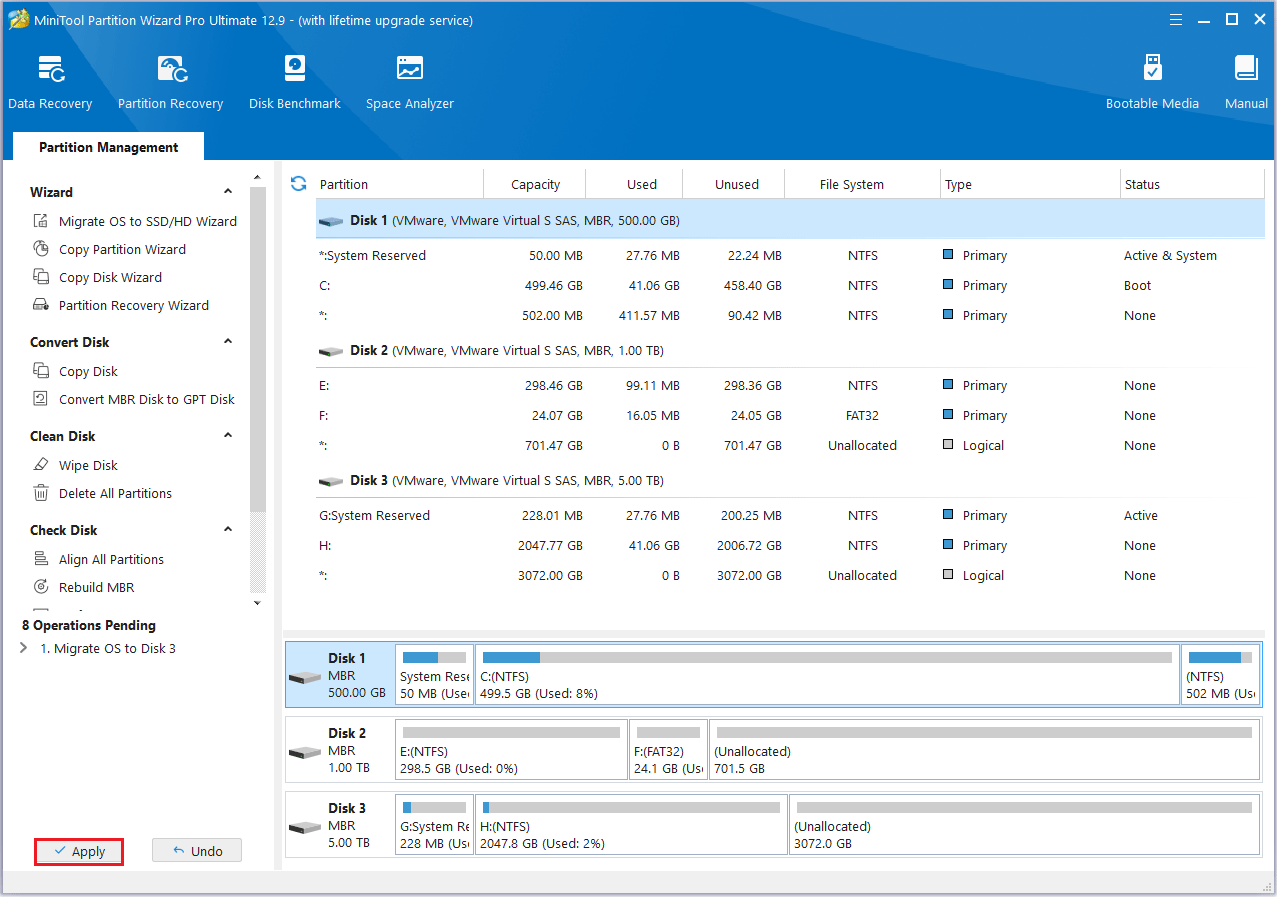
#3. Copy Partition
Step 1: Go to the MiniTool Partition Wizard main page.
Step 2: Click the disk you want to copy and choose the Copy Partition in the left action panel.
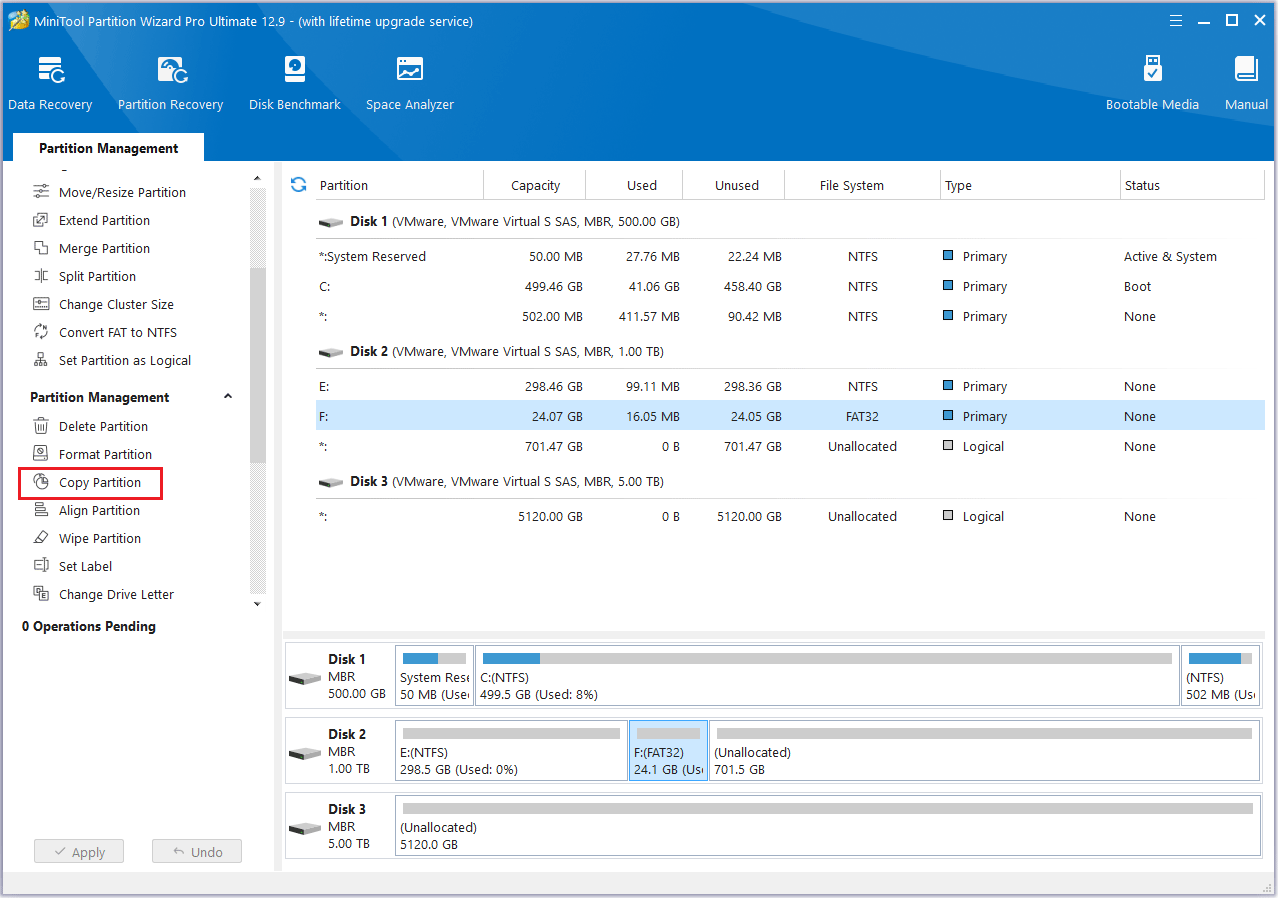
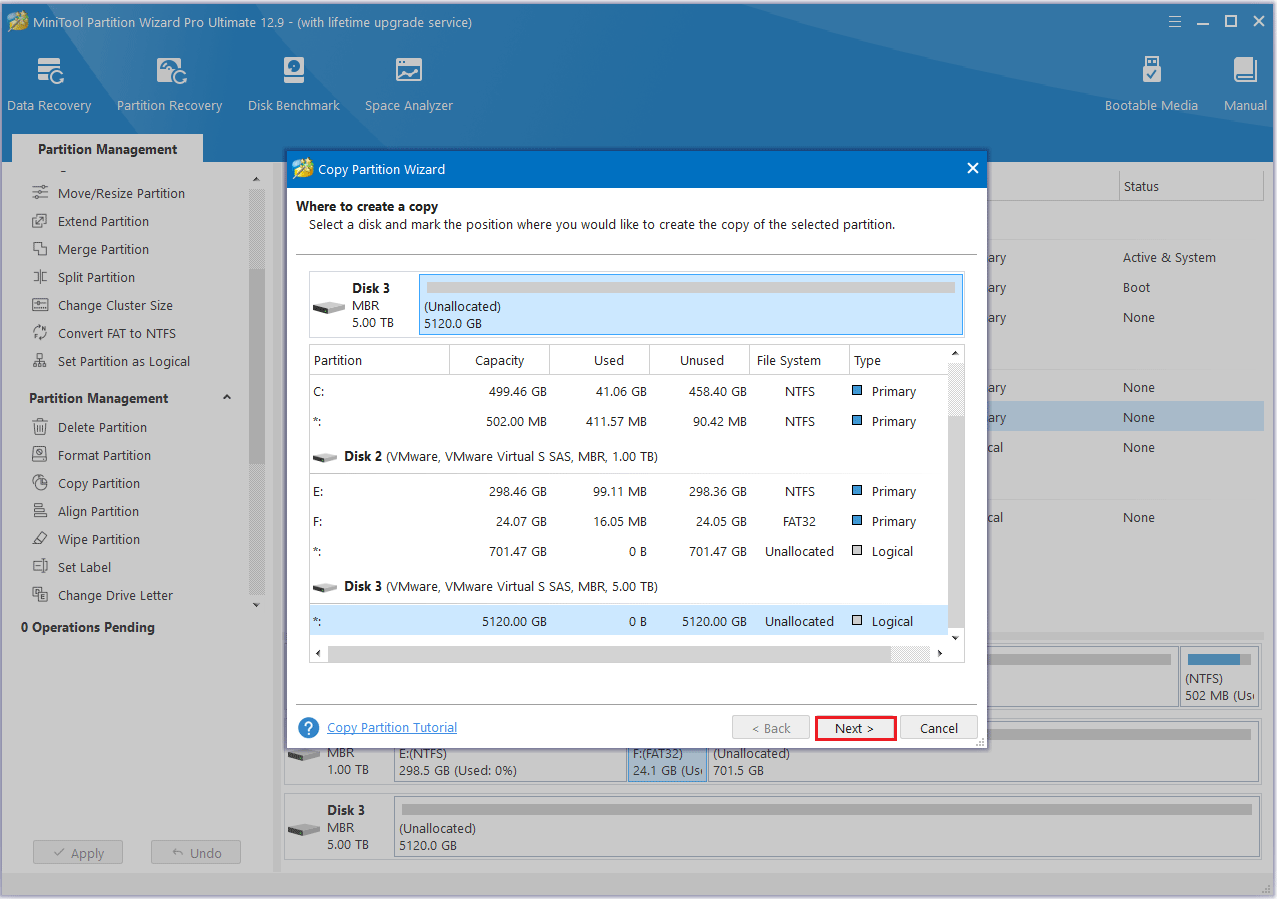
Step 3: Choose an unallocated space from the partition list to save a copy of the selected partition, and then click Next.
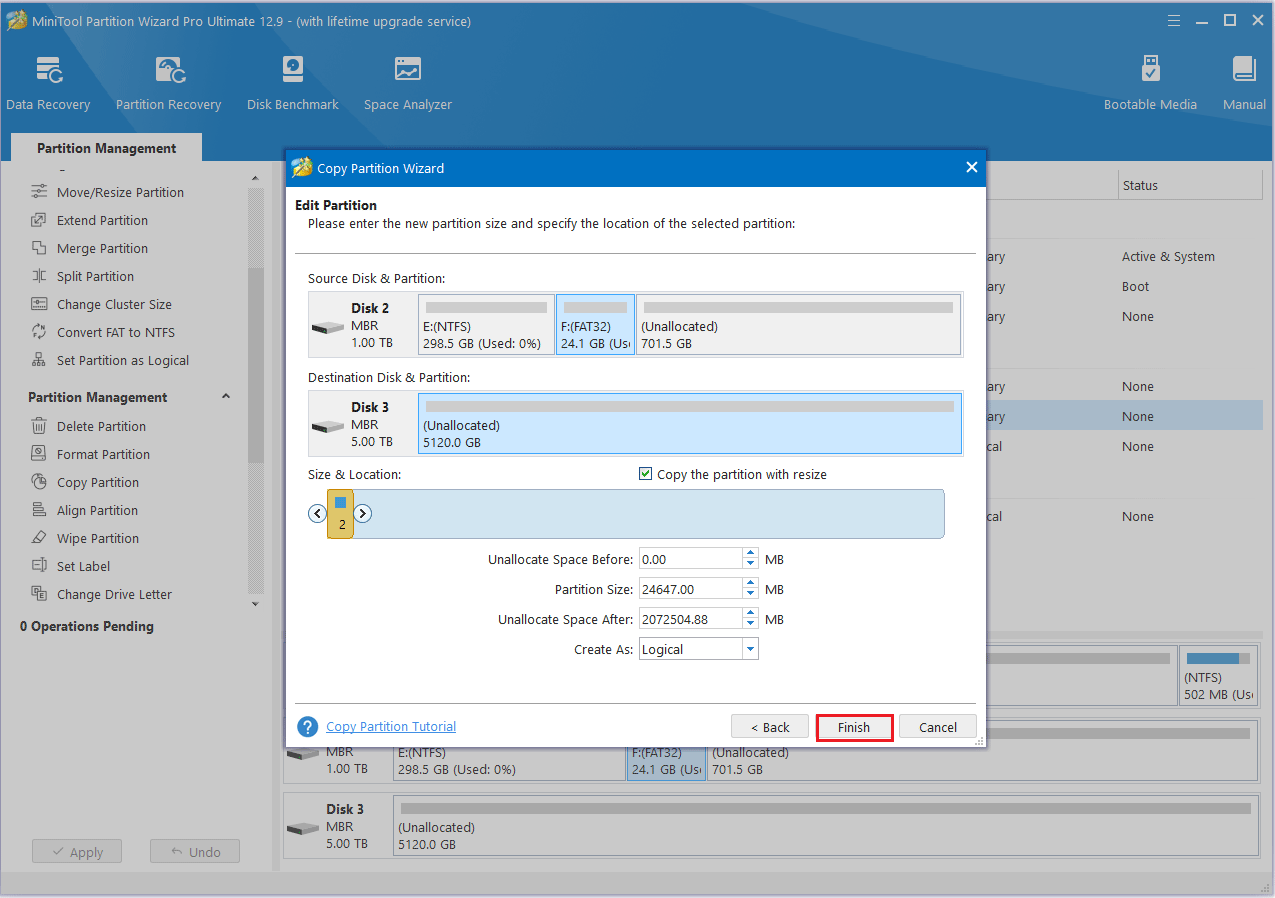
Step 4: Move the handle to enlarge or shrink the new partition. Alternatively, users can type the exact partition size in MB. Then, click Finish.
Step 5: Click the Apply button to finish the process.
How to Manage Your Old SSD
What are the best ways to manage your old SSD? Whether you plan to sell it, reuse it, or give it away?
Before taking any of these steps, it’s important to properly manage the SSD by clearing all data, removing existing partitions, and setting up new ones as necessary.
What software can help you?
MiniTool Partition Wizard is a great tool. It not only helps you migrate disk data, but also lets you expand or delete SSD partitions, and erase or format old SSDs.
In the following section, I will demonstrate how to extend partitions, delete partitions, format, and securely erase data from old SSDs.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
If you want to reuse the SSD, you can delete the partition first and then create the partition you want. The following are the detailed steps.
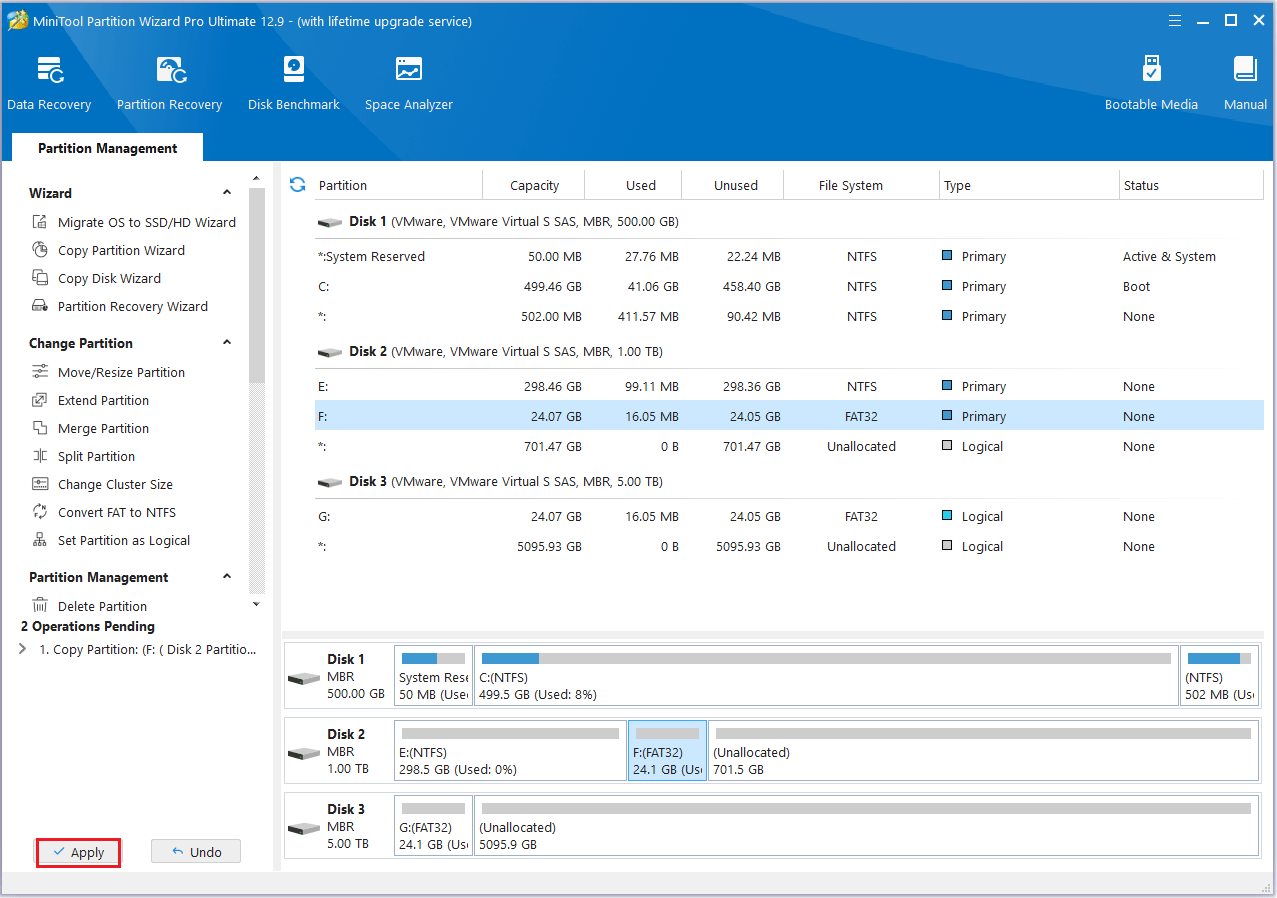
#1. Delete Partition
Step 1: Start by opening MiniTool Partition Wizard. Then, right-click the partition you no longer need and choose Delete.
Step 2: The original partition will now appear as unallocated space.
Step 3: Click the Apply button to perform all changes.
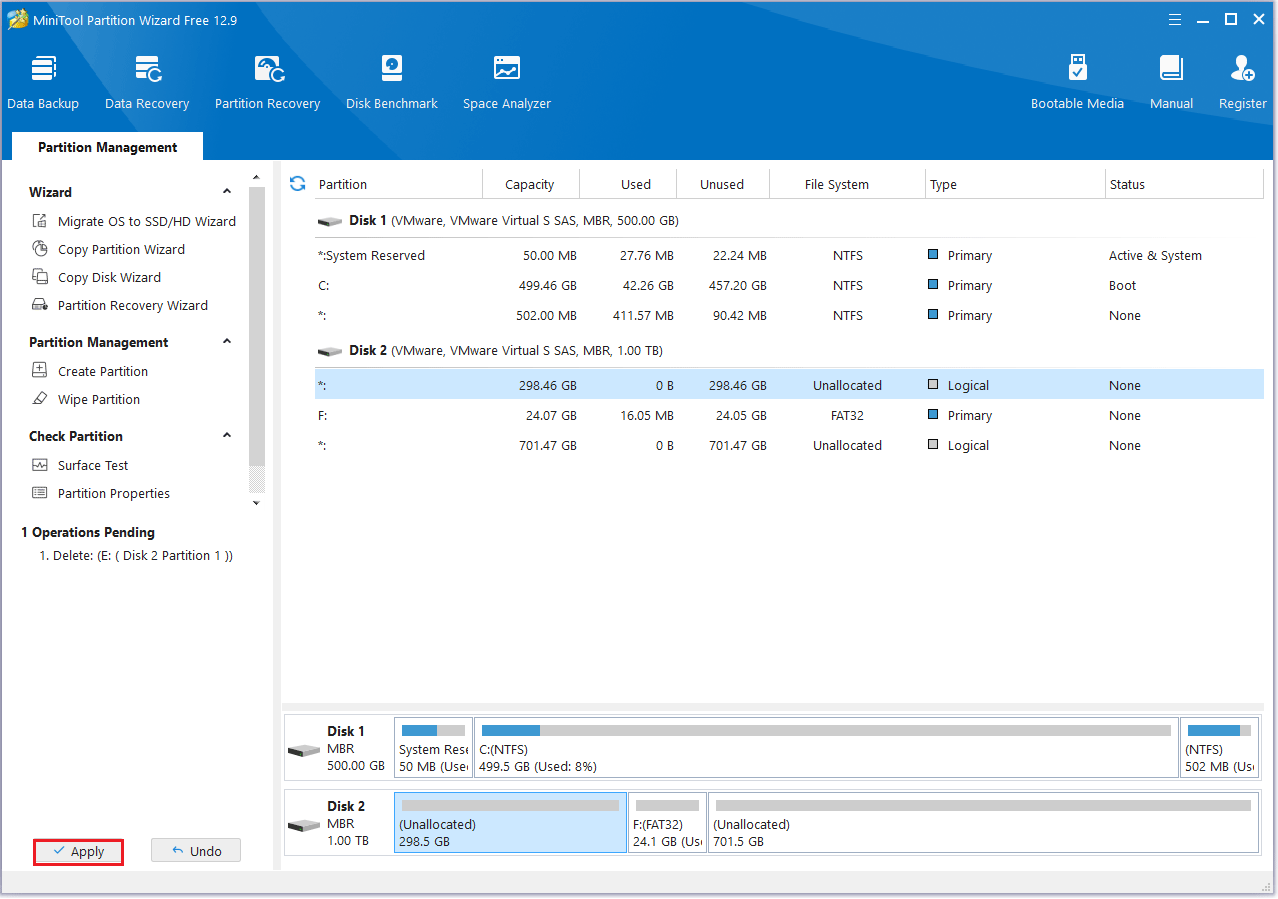
Now you can create your partitions according to your needs.
#2. Extend Partition
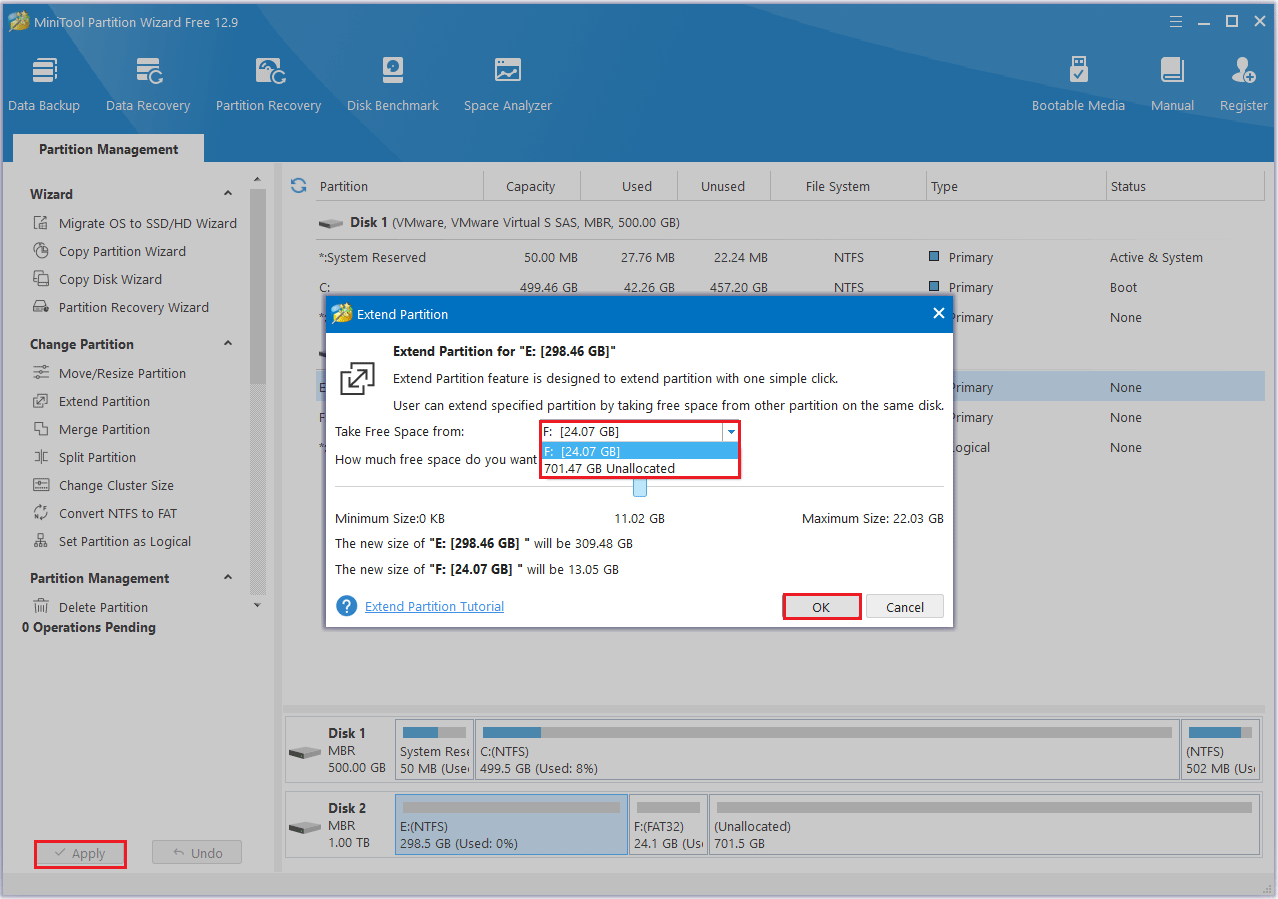
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to its main interface. Then right-click the partition to be extended and select Extend.
Step 2: Click the dropdown menu next to “Take Free Space from” and choose the partition to borrow space from. Then, drag the slider to select how much space to allocate. Finally, click OK to go back to the main interface.
Step 3: Click the Apply button to perform all changes.
#3. Wipe Disk
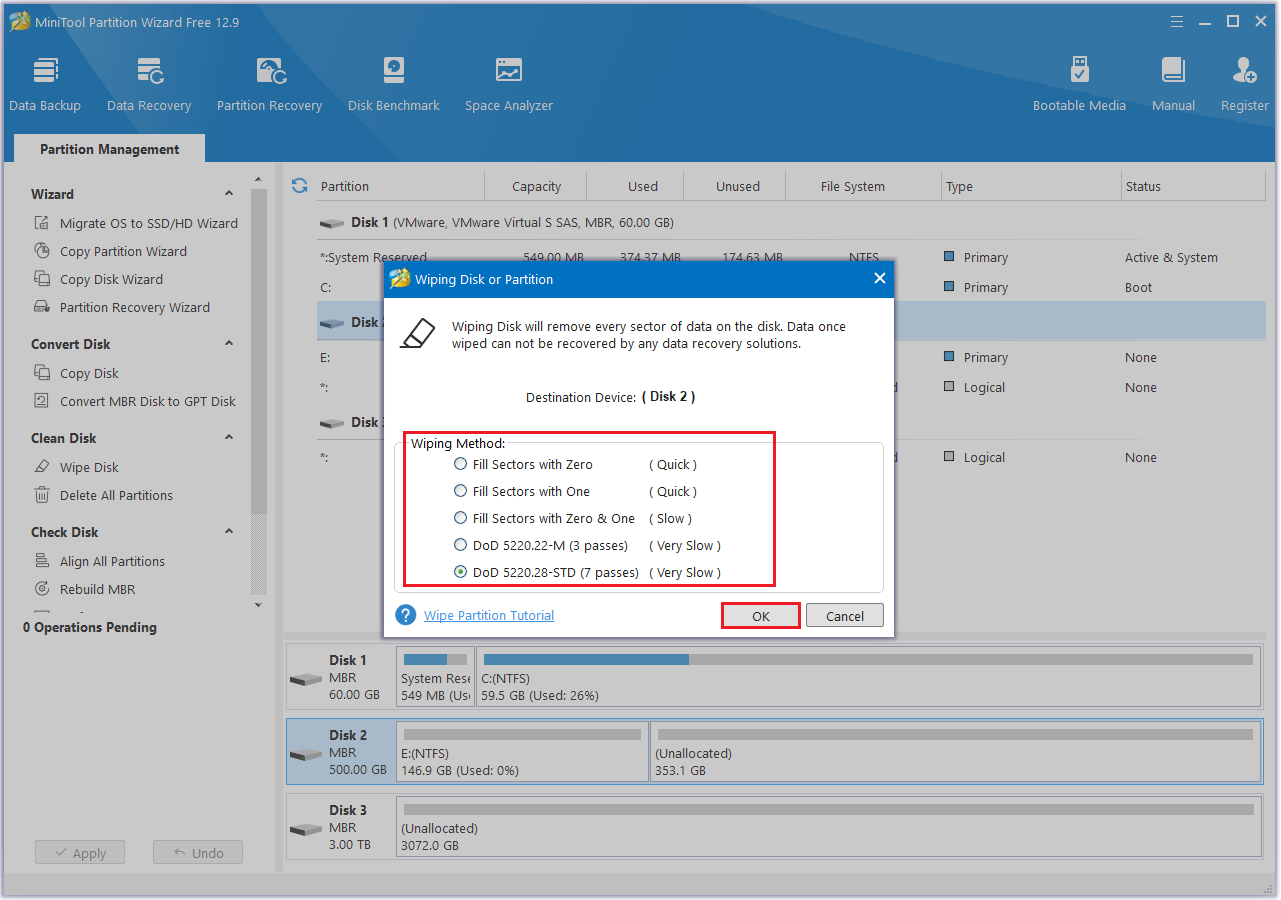
If you plan to sell an old disk, you can use the Wipe Disk feature to completely erase all data, making it unrecoverable and preventing any potential data leakage.
Here are the steps:
Step 1: Right-click the disk you want to wipe and select Wipe Disk, or choose the target disk and click Wipe Disk in the left action panel.
Step 2: A window will pop up as illustrated below. Choose a method to wipe and click OK to advance to the next step.
Step 3: After the process is complete, you will be returned to the main interface. The target disk is labeled as “Unallocated”. To apply the changes, you must click the Apply button.
#4. Format Partition
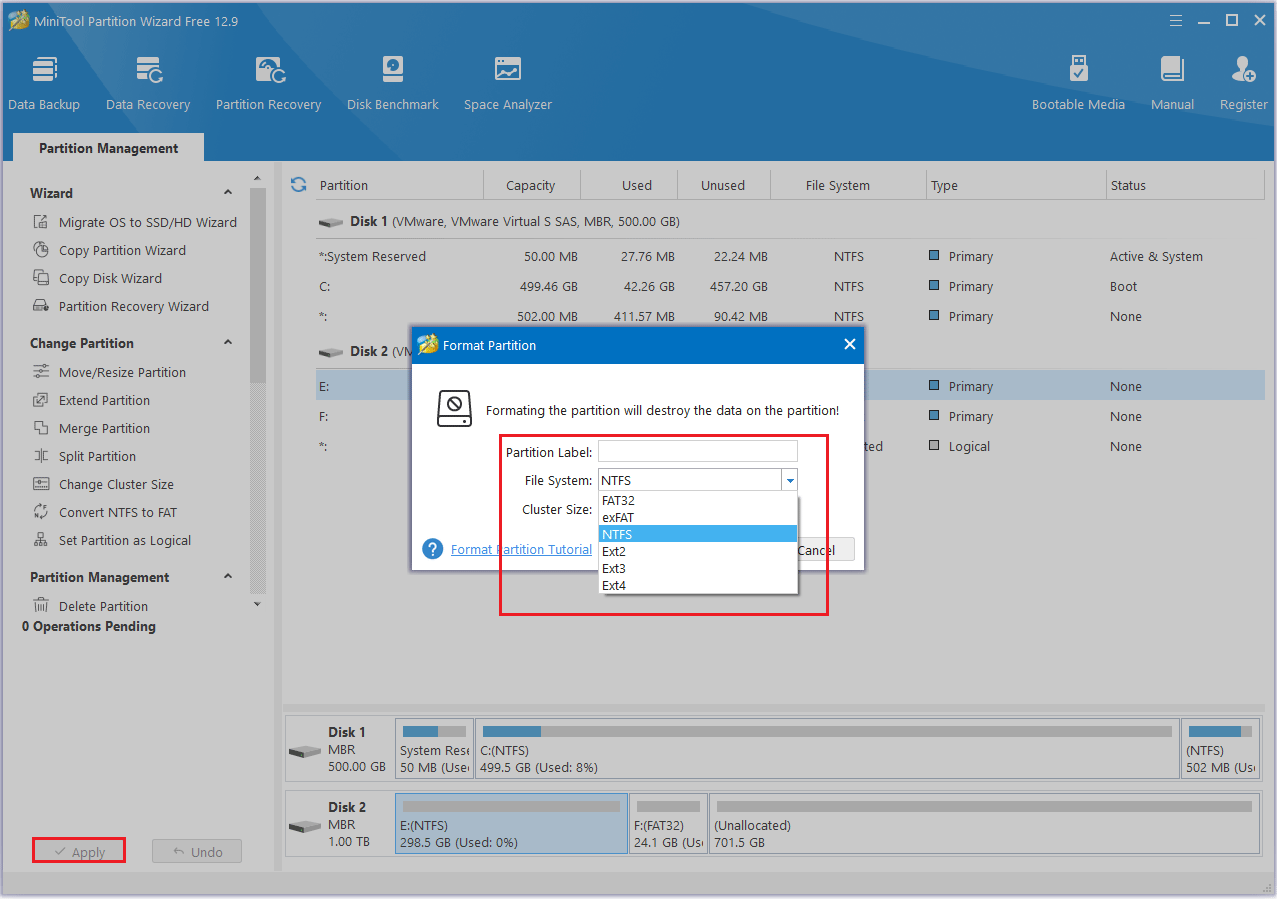
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard first. Right-click the partition to select Format.
Step 2: Choose the File System that you need and click OK.
Step 3: Click the Apply > Yes to perform all changes.
Bottom Line
This article ends here. It provides a detailed overview of how much hard drive I need, including information on SSD capacities, form factors, and more.
It also explains how to upgrade your data from the old SSD to a new one and how to manage your old SSD after replacement.
If you have any questions or suggestions while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can contact us via [email protected] to get a quick reply.
How Much SSD Do I Need FAQ
TBW (Terabytes Written) refers to the total amount of data that can be written to an SSD over its lifespan. For example, a 500 TBW SSD can handle up to 500 terabytes of written data before it's likely to wear out.
DWPD (Drive Writes Per Day) indicates how many times the entire capacity of an SSD can be written to each day over its warranty period. For example, if the DWPD is 1 and the warranty lasts 5 years, it means you can write the full capacity of the drive once per day for 5 years before reaching its endurance limit.
If the disk space you see is much lower than 930GB (for example, only 800GB), it may be:
1. There are hidden partitions (system partition, recovery partition)
2. Dual operating systems or BitLocker encryption installed
3. Space is taken away by other software
To ensure data security, we recommend that you back up your data regularly to prevent data loss.
1. 256GB: $15 to $25
2. 512GB: $25 to $40
3. 1TB: $50 to $75
4. 2TB: $90 to $150
5. 4TB: $150 to $300

User Comments :