There is an answer to the question what is LBA. You will know more about LBA, a helper aiming to specify the location of blocks of data saved on your computer storage devices.
About LBA
What is LBA? Short for Logical Block Addressing, it is a common scheme used for specifying the location of blocks of data stored on computer storage devices. In other words, it is a new form of hard disk addressing.
LBA was first developed around SCSI hard drives. Nowadays, it is the dominant form of hard disk addressing, since its addressing mode is simpler than that of CHS (Cylinder Head Sector).
Difference between LBA and CHS
As we know, our data is saved on hard disk in sectors. When we want to find the specified data, sector addressing mode helps us to specify the locations of the data stored on computers. The following content will show something about the hard disk addressing.
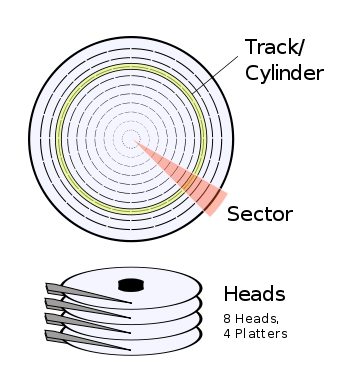
CHS is an earlier form of hard disk addressing. It stands for:
- C: cylinder, the valid range is between 0 and 1023 cylinders.
- H: Head, the valid range is between 0 and 254 heads (formerly 0-15).
- S: Sector, the valid range is between 1 and 63 sectors.
Addressing Mode
From the full name of CHS, we can predicate how it specifies the location of blocks of data saved in the hard disk. For example, if hard drives are accessed through CHS, they are addressed by specifying its cylinder, head and sector address.
With LBA, each sector is assigned a unique number rather than referring to a cylinder, head, and sector to access the hard drive. Using it, the hard disk is simply addressed as a single, large device, which simply counts the existing blocks starting at 0.
In other words, LBA is a way by which a drive is accessed by linearly addressing sector addresses. Therefore, it seems that this addressing mode is simpler than that of CHS.
- LBA doesn’t allow to address more sectors than CHS style addressing does.
- In order to apply LBA, you should make sure it must be supported by both the BIOS and OS.
- The hard drive itself must support LBA as well. Luckily,all newer hard drives do in fact support LBA.
Even though CHS now no longer maintains a physical relationship with the disk’s actual characteristics, CHS is still used by many utilities.
Addressing Space
For CHS, the maximum number of cylinders supported is 1024, of heads is 16, and of sectors is 63, and the number of bytes per sector is 512. Therefore, the maximum capacity of the supported hard disk is 512 x 63 x 16 x 1024=528 MB.
However, with the fast development of science and technology, the capacity of hard disks has been greatly increased. It is far beyond addressing range featuring 8 GB.
Therefore, how to address a space beyond 8 GB? The bit of CHS has expanded from 24 to 28 to get addressing space reaching 128 GB, and it seems that there’s nothing we can do about 2 TB disk capacity.
In this situation, generating a new form of hard disk addressing is a helpful solution, and the new one is LBA.
By contrast, logical block addressing (LBA) features a completely new method of addressing sectors. It can manage a hard drive space up to 8.4 GB. What’s more, the addressing space can reach up to 144,000,000 GB by using 48-bit LBA addressing mode.

User Comments :